* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synaptic Transmission
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Theta model wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
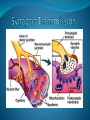
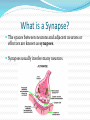
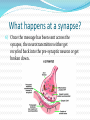
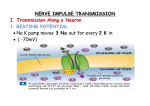
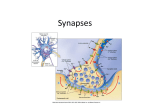
What is a Synapse? The spaces between neurons and adjacent neurons or effectors are known as synapses. Synapses usually involve many neurons. What happens at a Synapse? 1) The nerve impulse (action potential) moves along the presynaptic neuron towards the synapse. 2) This causes calcium ions to enter the neuron. What happens at a Synapse? 3) Calcium ions cause chemicals called neurotransmitters that are stored in vesicles at the end of the presynaptic axon to be released into the synapse (synaptic cleft). What happens at a Synapse? 4) They diffuse across the synaptic cleft and attach to membrane receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. 5) This opens up sodium channels and allows sodium into the postsynaptic neuron which causes the depolarization to continue on. What happens at a Synapse? Sometimes neurotransmitters can work against sending a message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! This is called hyperpolarization. What happens at a synapse? 6) Once the message has been sent across the synapse, the neurotransmitters either get recycled back into the pre-synaptic neuron or get broken down. Time lag… The diffusion of neurotransmitters is a slow process, so a neural response that involves many synapses takes a relatively longer time than a simple reflex arc. And in summation… Summation is when two or more neurons are needed to create an action potential in a further neuron. The sum of their firing causes an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.