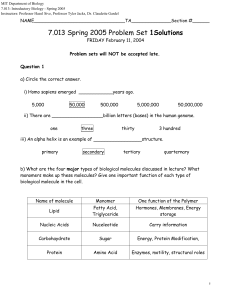
7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 1Solutions
... When the protein folds into its final form, amino acid residues that are far apart in the primary structure can be closely aligned to one another. ...
... When the protein folds into its final form, amino acid residues that are far apart in the primary structure can be closely aligned to one another. ...
A Novel Functionally Distinct Subtype of Striatal Neuropeptide Y
... NPY–PLTS interneurons. IPSP/Cs could only rarely be elicited in spiny projection neurons (SPNs) in paired recordings with NPY–PLTS interneurons. In contrast, the probability of SPN innervation by NPY–neurogliaform interneurons was extremely high, the synapse very reliable (no failures were observed) ...
... NPY–PLTS interneurons. IPSP/Cs could only rarely be elicited in spiny projection neurons (SPNs) in paired recordings with NPY–PLTS interneurons. In contrast, the probability of SPN innervation by NPY–neurogliaform interneurons was extremely high, the synapse very reliable (no failures were observed) ...
elsevier second proof - Michigan State University
... subunits that are expressed in few other tissues; when stimulated, the G-protein activates type III adenylyl cyclase (Nakamura, 2000; Ronnett and Moon, 2002). The details of olfactory transduction are well understood for only a small number of vertebrate species, and involve myriad mechanisms (Fires ...
... subunits that are expressed in few other tissues; when stimulated, the G-protein activates type III adenylyl cyclase (Nakamura, 2000; Ronnett and Moon, 2002). The details of olfactory transduction are well understood for only a small number of vertebrate species, and involve myriad mechanisms (Fires ...
What the young brain tells the spinal cord: top down modulation of
... descending facilitation at P40. Thus, there is a switch from ongoing descending facilitation to inhibition between P21 and P40. Experiments in chapter 4 demonstrate anatomical maturation of descending serotonergic pathways from the RVM to the spinal cord during postnatal development. In chapter 5, t ...
... descending facilitation at P40. Thus, there is a switch from ongoing descending facilitation to inhibition between P21 and P40. Experiments in chapter 4 demonstrate anatomical maturation of descending serotonergic pathways from the RVM to the spinal cord during postnatal development. In chapter 5, t ...
Structure and dynamics of the corticothalamic driver pathway in the
... beginning of trying to understand how it works. The standard building elements giving rise to brain function are neurons, whose defining characteristics are active electric signal propagation by action potentials and integration of synaptic inputs (Kandel et al. 2013). Their sheer number (humans: >8 ...
... beginning of trying to understand how it works. The standard building elements giving rise to brain function are neurons, whose defining characteristics are active electric signal propagation by action potentials and integration of synaptic inputs (Kandel et al. 2013). Their sheer number (humans: >8 ...
THE SUBFORNICAL ORGAN AND AREA POSTREMA MEDIATE
... tissue, once thought of as solely a storage depot for excess triglycerides, also serves as an endocrine organ which plays a critical role in energy homeostasis, secreting adipokines that control feeding and energy metabolism. Although a certain degree of fat storage is normal, the expansion of adipo ...
... tissue, once thought of as solely a storage depot for excess triglycerides, also serves as an endocrine organ which plays a critical role in energy homeostasis, secreting adipokines that control feeding and energy metabolism. Although a certain degree of fat storage is normal, the expansion of adipo ...
Calcium Transients in the Garter Snake Vomeronasal Organ
... Functional studies have demonstrated that ESS and ES20 evoke depolarizing currents in VN neurons and increase unit activity in the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB) mitral cells, the targets of the axons of receptor neurons of the VN epithelium (Jiang et al. 1990; Luo et al. 1994; Taniguchi et al. 1998 ...
... Functional studies have demonstrated that ESS and ES20 evoke depolarizing currents in VN neurons and increase unit activity in the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB) mitral cells, the targets of the axons of receptor neurons of the VN epithelium (Jiang et al. 1990; Luo et al. 1994; Taniguchi et al. 1998 ...
neuronal reward and decision signals: from theories to data
... 853–951, 2015. Published June 24, 2015; doi:10.1152/physrev.00023.2014.—Rewards are crucial objects that induce learning, approach behavior, choices, and emotions. Whereas emotions are difficult to investigate in animals, the learning function is mediated by neuronal reward prediction error signals ...
... 853–951, 2015. Published June 24, 2015; doi:10.1152/physrev.00023.2014.—Rewards are crucial objects that induce learning, approach behavior, choices, and emotions. Whereas emotions are difficult to investigate in animals, the learning function is mediated by neuronal reward prediction error signals ...
Neurophysiology - American Physiological Society
... Cellular Neurophysiology, Blood Brain Barrier, Cerebrovascular Physiology A. Physiology of the Neuron NEU 1. Define, and identify on a diagram of a motor neuron, the following regions: dendrites, axon, axon hillock, soma, and an axodendritic synapse. NEU 2. Define, and identify on a diagram of a pri ...
... Cellular Neurophysiology, Blood Brain Barrier, Cerebrovascular Physiology A. Physiology of the Neuron NEU 1. Define, and identify on a diagram of a motor neuron, the following regions: dendrites, axon, axon hillock, soma, and an axodendritic synapse. NEU 2. Define, and identify on a diagram of a pri ...
ORAL UPF/ TESI DOCT Nicotine addiction phenotypes in a BAC transgenic mouse
... nicotine addiction. Specifically, we focus on the cluster CHRNA5/A3/B4 of human chromosome 15, which human genetic studies have identified as a strong candidate for nicotine dependence and smoking-related behaviours. This cluster codifies for the alpha5, alpha3 and beta4 subunits of the nicotinic ac ...
... nicotine addiction. Specifically, we focus on the cluster CHRNA5/A3/B4 of human chromosome 15, which human genetic studies have identified as a strong candidate for nicotine dependence and smoking-related behaviours. This cluster codifies for the alpha5, alpha3 and beta4 subunits of the nicotinic ac ...
Neuronal uptake and propagation of a rare phosphorylated high-molecular-weight tau
... protein tau1, as intracellular inclusions known as neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), is a pathological hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD)2,3. Cognitive deficits in AD are most closely linked with progression of NFTs in a hierarchical pattern, starting in the entorh ...
... protein tau1, as intracellular inclusions known as neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), is a pathological hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD)2,3. Cognitive deficits in AD are most closely linked with progression of NFTs in a hierarchical pattern, starting in the entorh ...
Understanding the process of multisensory integration
... context. Cross-modal cues that are near-simultaneous are likely to be derived from the same event, and the neural inputs they generate are integrated more strongly than those from cues that are temporally displaced from one another. However, the present results from studies of cat SC neurons show th ...
... context. Cross-modal cues that are near-simultaneous are likely to be derived from the same event, and the neural inputs they generate are integrated more strongly than those from cues that are temporally displaced from one another. However, the present results from studies of cat SC neurons show th ...
Bettendorff L, Wins P. Biological functions of thiamine
... most important being mitochondrial pyruvate and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes as well as the cytosolic transketolase. Therefore, it is generally believed that thiamine deficiency leads to decreased oxidative metabolism, which eventually causes cell death. In animals, the brain heavily relies ...
... most important being mitochondrial pyruvate and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes as well as the cytosolic transketolase. Therefore, it is generally believed that thiamine deficiency leads to decreased oxidative metabolism, which eventually causes cell death. In animals, the brain heavily relies ...
Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington`s disease
... Production of BDNF is stimulated by wild-type huntingtin: physiology and mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.1. Huntingtin and BDNF co-localise in cortical neurons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2. Wild-type huntingtin i ...
... Production of BDNF is stimulated by wild-type huntingtin: physiology and mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.1. Huntingtin and BDNF co-localise in cortical neurons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2. Wild-type huntingtin i ...
Propagation of tau pathology in Alzheimer`s disease
... from HEK cells inducibly expressing human tau, rather than transiently overexpressing tau, revealed soluble extracellular tau but no detectable tau in the exosome fraction [33]. Exosomes isolated from SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, infected with a lentivirus to express human GFPtagged tau, also did no ...
... from HEK cells inducibly expressing human tau, rather than transiently overexpressing tau, revealed soluble extracellular tau but no detectable tau in the exosome fraction [33]. Exosomes isolated from SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, infected with a lentivirus to express human GFPtagged tau, also did no ...
Characterization of Agouti-Related Protein
... thought to play an important role in the hypothalamic control of feeding behavior. The exact mechanism of AGRP and Agouti protein action has been difficult to examine, in part because of difficulties in producing homogeneous forms of these molecules that can be used for direct binding assays. In thi ...
... thought to play an important role in the hypothalamic control of feeding behavior. The exact mechanism of AGRP and Agouti protein action has been difficult to examine, in part because of difficulties in producing homogeneous forms of these molecules that can be used for direct binding assays. In thi ...
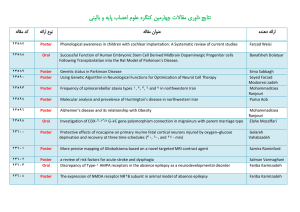
ﻧﺘﺎﯾﺞ داوری ﻣﻘﺎﻻت ﭼﻬﺎرﻣﯿﻦ ﮐﻨﮕﺮه ﻋﻠﻮم اﻋﺼﺎب ﭘﺎﯾﻪ و ﺑﺎ
... The exercise effect on excitability and paired-pulse inhibition response at dentate gyrus of hippocampus in chronic stress rats The Role of protein phosphatase ١ in the spatial learning and memory improvement induced by salicylate in rats Orexin-٢ receptors in hippocampal CA١ area are involved in ex ...
... The exercise effect on excitability and paired-pulse inhibition response at dentate gyrus of hippocampus in chronic stress rats The Role of protein phosphatase ١ in the spatial learning and memory improvement induced by salicylate in rats Orexin-٢ receptors in hippocampal CA١ area are involved in ex ...
Leptin Signaling in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarii
... Abstract—The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus was initially regarded as the principal site of leptin action, but there is increasing evidence for functional leptin receptors in extrahypothalamic sites, including the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS). We demonstrated previously that arcuate injection of le ...
... Abstract—The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus was initially regarded as the principal site of leptin action, but there is increasing evidence for functional leptin receptors in extrahypothalamic sites, including the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS). We demonstrated previously that arcuate injection of le ...
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Reelin Signaling in the Adult
... pave the path for new disciplines. Finally, the most recent and formative phase of my metamorphosis, has been under the tutelage of Dr. Edwin Weeber, who has provided unbridled support for my countless curiosities and epitomized the loving mentor that every graduate student longs for. One of the mos ...
... pave the path for new disciplines. Finally, the most recent and formative phase of my metamorphosis, has been under the tutelage of Dr. Edwin Weeber, who has provided unbridled support for my countless curiosities and epitomized the loving mentor that every graduate student longs for. One of the mos ...
REM Sleep - Test Page
... neurons, rather than axons of passage. If damage to a particular region causes the loss of a sleep state, one cannot conclude that this is where a "center" for th state resides. Lesion effects are usually maximal immediate] after the lesion is created. Swelling and circulatory disruption make the fu ...
... neurons, rather than axons of passage. If damage to a particular region causes the loss of a sleep state, one cannot conclude that this is where a "center" for th state resides. Lesion effects are usually maximal immediate] after the lesion is created. Swelling and circulatory disruption make the fu ...
The Role of Kv7 in Peripheral Neurons
... in the regulation of cellular excitability and axonal conduction. Previous studies have shown that peripheral sensory neurons express Kv7.2, Kv7.3, and Kv7.5 subunits, and that suppression of Kv7 activity with pharmacological blockers can lead to increased nociception. However, the specific localiza ...
... in the regulation of cellular excitability and axonal conduction. Previous studies have shown that peripheral sensory neurons express Kv7.2, Kv7.3, and Kv7.5 subunits, and that suppression of Kv7 activity with pharmacological blockers can lead to increased nociception. However, the specific localiza ...
Spinal sympathetic interneurons: Their identification and roles after
... brainstem are lost. Sympathetic activity after spinal cord injury is enigmatic because it ranges from abnormally low, leading to bouts of hypotension, to abnormally high, leading to hypertensive crises (Mathias and Frankel, 1992). One characteristic upon which there appears to be little disagreement ...
... brainstem are lost. Sympathetic activity after spinal cord injury is enigmatic because it ranges from abnormally low, leading to bouts of hypotension, to abnormally high, leading to hypertensive crises (Mathias and Frankel, 1992). One characteristic upon which there appears to be little disagreement ...
Selective stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson`s
... positive effects on the motor symptoms and become a major burden for both the patient and relatives. The challenge is to obtain good therapeutic effects and to prevent the occurrence of undesired psychiatric side effects. The undesired psychiatric side effects are thought to be caused by stimulation ...
... positive effects on the motor symptoms and become a major burden for both the patient and relatives. The challenge is to obtain good therapeutic effects and to prevent the occurrence of undesired psychiatric side effects. The undesired psychiatric side effects are thought to be caused by stimulation ...
Mass spectrometry of oligosaccharides
... secreted proteins are glycosylated—a fact that impacts on efforts to understand the biological relevance of specific protein expression and modification patterns. Unlike the core proteins, glycans are expressed as a set of variations on a core structure and are polydisperse in nature. Therefore, gly ...
... secreted proteins are glycosylated—a fact that impacts on efforts to understand the biological relevance of specific protein expression and modification patterns. Unlike the core proteins, glycans are expressed as a set of variations on a core structure and are polydisperse in nature. Therefore, gly ...
Behavioural Brain Research Ventral pallidum roles in reward and
... well as early lateral hypothalamic lesions, in published histological figures indicates the aphagia-inducing lesions damaged ventral pallidum as well as their intended target structure. These data, ...
... well as early lateral hypothalamic lesions, in published histological figures indicates the aphagia-inducing lesions damaged ventral pallidum as well as their intended target structure. These data, ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.