Carnitine metabolism and biosynthesis in yeast Saccharomyces
... Carnitine plays an essential role in eukaryotic metabolism by mediating the shuttling of activated acyl residues between intracellular compartments. This function of carnitine, referred to as the carnitine shuttle, is supported by the activities of carnitine acyltransferases and carnitine/acylcarnit ...
... Carnitine plays an essential role in eukaryotic metabolism by mediating the shuttling of activated acyl residues between intracellular compartments. This function of carnitine, referred to as the carnitine shuttle, is supported by the activities of carnitine acyltransferases and carnitine/acylcarnit ...
Reducing Ryanodine Receptor Open Probability as a Means to
... of the cells studied. Isoproterenol also produced diastolic Ca2⫹ release, and this occurred in 11 of 49 of cells studied in 1 mmol/L [Ca2⫹]o and 28 of 38 cells studied in 2 mmol/L [Ca2⫹]o. When a steady state had been achieved (2 to 3 minutes), tetracaine was applied to reduce the RyR Po. Two concen ...
... of the cells studied. Isoproterenol also produced diastolic Ca2⫹ release, and this occurred in 11 of 49 of cells studied in 1 mmol/L [Ca2⫹]o and 28 of 38 cells studied in 2 mmol/L [Ca2⫹]o. When a steady state had been achieved (2 to 3 minutes), tetracaine was applied to reduce the RyR Po. Two concen ...
Towards functional effects of polyphenols : modulation of energy
... roots and symbiotic root nodules are formed that can convert nitrogen from the soil into ammonia used for amino acid production for plant growth [6]. The small molecule signal that initiates the interaction is a polyphenol [7]. The biochemical mechanism by which polyphenols initiate the interaction ...
... roots and symbiotic root nodules are formed that can convert nitrogen from the soil into ammonia used for amino acid production for plant growth [6]. The small molecule signal that initiates the interaction is a polyphenol [7]. The biochemical mechanism by which polyphenols initiate the interaction ...
The interaction between bacteria and bile
... cycling. These include lipovitamins (particularly the biologically active forms of vitamin D2), water-soluble vitamins (particularly vitamin B12, folic acid and pyrodoxine), all estrogenic steroids, progesterone, testosterone, corticosteroids and essential trace metals [2]. Many exogenous substances ...
... cycling. These include lipovitamins (particularly the biologically active forms of vitamin D2), water-soluble vitamins (particularly vitamin B12, folic acid and pyrodoxine), all estrogenic steroids, progesterone, testosterone, corticosteroids and essential trace metals [2]. Many exogenous substances ...
Regulation of the phosphotransferase system (PTS)
... It blocks the first step of glycolysis and directs the glucose-derived carbon flux towards the NADPHproducing pentose phosphate pathway. However, despite that C. glutamicum Δpgi grows well with sucrose as a sole carbon source, addition of glucose arrests growth by causing repression of ptsS, encodin ...
... It blocks the first step of glycolysis and directs the glucose-derived carbon flux towards the NADPHproducing pentose phosphate pathway. However, despite that C. glutamicum Δpgi grows well with sucrose as a sole carbon source, addition of glucose arrests growth by causing repression of ptsS, encodin ...
Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 1
... Alanine, cysteine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, tyrosine, valine. ...
... Alanine, cysteine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, tyrosine, valine. ...
procite - UWI St. Augustine
...) [3,4]. Calcium ions induce conformational changes in
the Gla
domain and are necessary for the Gla domain to fold properly. A
common
structural feature of functional Gla domains is the clustering of Nterminal
hydrophobic residues into a hydrophobic patch that mediates interaction
with
the ...
...
A tale of two stories: astrocyte regulation of
... strength or the efficacy of synaptic transmission therein in a way that depends on the timing and frequency of prior activity at that same synaptic terminal [5]. One widely studied mechanism responsible for the dependence of synaptic transmission on past activity has been dubbed presynaptic short-te ...
... strength or the efficacy of synaptic transmission therein in a way that depends on the timing and frequency of prior activity at that same synaptic terminal [5]. One widely studied mechanism responsible for the dependence of synaptic transmission on past activity has been dubbed presynaptic short-te ...
THE SUBFORNICAL ORGAN AND AREA POSTREMA MEDIATE
... individual expends, the excess energy will be stored as adipose tissue with a prolonged imbalance leading to an individual becoming overweight and, eventually, obese. Adipose tissue, once thought of as solely a storage depot for excess triglycerides, also serves as an endocrine organ which plays a c ...
... individual expends, the excess energy will be stored as adipose tissue with a prolonged imbalance leading to an individual becoming overweight and, eventually, obese. Adipose tissue, once thought of as solely a storage depot for excess triglycerides, also serves as an endocrine organ which plays a c ...
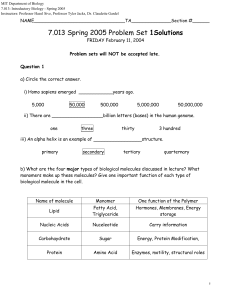
7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 1Solutions
... receptors in the cell membrane. Upon dimerization, the intracellular domains of the receptors become activated. See schematic below. ...
... receptors in the cell membrane. Upon dimerization, the intracellular domains of the receptors become activated. See schematic below. ...
Redefining the role of ectoderm in somitogenesis
... et al., 1998), suggesting that ectodermal signals, most likely Wnts (Borycki et al., 2000; Schmidt et al., 2004), are essential for morphological somite formation. Interactions between PSM cells and the extracellular matrix molecule fibronectin have been implicated in somitogenesis (Duband et al., 1 ...
... et al., 1998), suggesting that ectodermal signals, most likely Wnts (Borycki et al., 2000; Schmidt et al., 2004), are essential for morphological somite formation. Interactions between PSM cells and the extracellular matrix molecule fibronectin have been implicated in somitogenesis (Duband et al., 1 ...
A STUDY OF THE ROLES OF SELECTED ARGININE AND
... plasmin modified fibrin (FN’), which has exposed C-terminal lysine residues that result in an up-regulation of plasminogen activation by t-PA. This results in an overall increase in the catalytic efficiency of plasminogen activation by a factor of 3000 compared to that of t-PA alone [14]. TAFIa poss ...
... plasmin modified fibrin (FN’), which has exposed C-terminal lysine residues that result in an up-regulation of plasminogen activation by t-PA. This results in an overall increase in the catalytic efficiency of plasminogen activation by a factor of 3000 compared to that of t-PA alone [14]. TAFIa poss ...
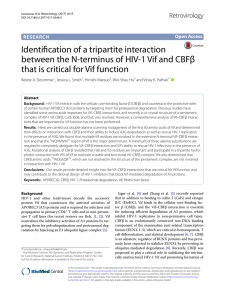
PDF - Retrovirology
... Background: HIV-1 Vif interacts with the cellular core-binding factor β (CBFβ) and counteracts the protective roles of certain human APOBEC3 (A3) proteins by targeting them for proteasomal degradation. Previous studies have identified some amino acids important for Vif–CBFβ interactions, and recent ...
... Background: HIV-1 Vif interacts with the cellular core-binding factor β (CBFβ) and counteracts the protective roles of certain human APOBEC3 (A3) proteins by targeting them for proteasomal degradation. Previous studies have identified some amino acids important for Vif–CBFβ interactions, and recent ...
Document
... strengths of synaptic connections are altered. For example, long-term changes in synaptic connection may result in more postsynaptic receptors being embedded in the postsynaptic membrane, resulting in the strengthening of the synapse. Synaptic plasticity is also found to be the neural mechanism that ...
... strengths of synaptic connections are altered. For example, long-term changes in synaptic connection may result in more postsynaptic receptors being embedded in the postsynaptic membrane, resulting in the strengthening of the synapse. Synaptic plasticity is also found to be the neural mechanism that ...
Inactivation of mouse Twisted gastrulation reveals its
... The Drosophila Tsg product is necessary for peak Dpp/Bmp activity in the early Drosophila embryo, which is required to form the amnioserosa (Mason et al., 1994). Tsg contains two conserved cysteine-rich domains and was shown to bind both Bmp and Chd (Oelgeschläger et al., 2000). The Tsg N-terminal d ...
... The Drosophila Tsg product is necessary for peak Dpp/Bmp activity in the early Drosophila embryo, which is required to form the amnioserosa (Mason et al., 1994). Tsg contains two conserved cysteine-rich domains and was shown to bind both Bmp and Chd (Oelgeschläger et al., 2000). The Tsg N-terminal d ...
Bettendorff L, Wins P. Biological functions of thiamine
... phosphate esters, or whether it is specific. The group of Yulia Parkhomenko in Kiev extensively studied thiamine-binding proteins from brain. By affinity chromatography (thiamine covalently bound to a Sepharose 4B matrix), they isolated a thiamine-binding protein from a synaptosomal acetone powder26 ...
... phosphate esters, or whether it is specific. The group of Yulia Parkhomenko in Kiev extensively studied thiamine-binding proteins from brain. By affinity chromatography (thiamine covalently bound to a Sepharose 4B matrix), they isolated a thiamine-binding protein from a synaptosomal acetone powder26 ...
Leaf Senescence
... identified. For example, HSR203J is upregulated during HR but not during leaf senescence (54). Similarly, the Arabidopsis SAG12 gene expression is associated with leaf senescence but is not detected in the HR PCD in tobacco. Thus, these two genes may be a specific part of signaling steps for HR PCD an ...
... identified. For example, HSR203J is upregulated during HR but not during leaf senescence (54). Similarly, the Arabidopsis SAG12 gene expression is associated with leaf senescence but is not detected in the HR PCD in tobacco. Thus, these two genes may be a specific part of signaling steps for HR PCD an ...
Arabidopsis Formin3 Directs the Formation of Actin
... referred to as group I and group II. Group I formins are characterized by the presence of a signal peptide and a transmembrane domain at its N terminus, which are presumably involved in their targeting to the plasma membrane (PM). No conserved domains were identified beside FH1 and FH2 in group II f ...
... referred to as group I and group II. Group I formins are characterized by the presence of a signal peptide and a transmembrane domain at its N terminus, which are presumably involved in their targeting to the plasma membrane (PM). No conserved domains were identified beside FH1 and FH2 in group II f ...
Structure and Function of Thymosin β4
... To further confirm that thymosin 4 forms a complex with G-actin, the heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectra was recorded at 25C with thymosin 4 containing [U- 15N] thymosin 4 with an unlabeled actin. A large spreading of amide protons was observed, which is expected of fully struc ...
... To further confirm that thymosin 4 forms a complex with G-actin, the heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectra was recorded at 25C with thymosin 4 containing [U- 15N] thymosin 4 with an unlabeled actin. A large spreading of amide protons was observed, which is expected of fully struc ...
INVESTIGATION OF THE REPLACEMENT OF CYSTEINE
... Dr. T.V.V. Ramakrishna (Ramki), Maria Gomes, Dr. Delshanee Kotandeniya, Sundari Rallapalli and Shorouk Dannoon, for their friendship through my graduate career. I would also like to acknowledge several other friends, who have been wonderful company and have been helpfu ...
... Dr. T.V.V. Ramakrishna (Ramki), Maria Gomes, Dr. Delshanee Kotandeniya, Sundari Rallapalli and Shorouk Dannoon, for their friendship through my graduate career. I would also like to acknowledge several other friends, who have been wonderful company and have been helpfu ...
Aqua-BioSci. Monogr. (ABSM), Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 1–57 (2008)
... fish cells seem to require more lipid than mammalian cells. Eel hepatocytes were cultured in a serum-free medium, as shown in Table 1B, for 2 to 3 weeks (Hayashi and Ooshiro 1986). Insulin, glucagon, prolactin, growth hormone, epidermal growth factor (EGF), and H2SeO3 were used for culture instead o ...
... fish cells seem to require more lipid than mammalian cells. Eel hepatocytes were cultured in a serum-free medium, as shown in Table 1B, for 2 to 3 weeks (Hayashi and Ooshiro 1986). Insulin, glucagon, prolactin, growth hormone, epidermal growth factor (EGF), and H2SeO3 were used for culture instead o ...
E7.5 endoderm induction by adjacent germ layers
... 1997; St-Onge et al., 1997; Sussel et al., 1998). How these transcription factors interact to generate specific cell types is as yet unclear, although some target genes of Pdx1, including insulin and somatostatin (Goudet et al., 1999), have been identified. In the studies mentioned above, particular ...
... 1997; St-Onge et al., 1997; Sussel et al., 1998). How these transcription factors interact to generate specific cell types is as yet unclear, although some target genes of Pdx1, including insulin and somatostatin (Goudet et al., 1999), have been identified. In the studies mentioned above, particular ...
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Reelin Signaling in the Adult
... The study of Reelin signaling and its role in cortical development is responsible for the large preponderance of known signaling mechanism. For that reason, section one will consist of an overview of cortical development followed by a more specific discussion of major and aspiring players in the Re ...
... The study of Reelin signaling and its role in cortical development is responsible for the large preponderance of known signaling mechanism. For that reason, section one will consist of an overview of cortical development followed by a more specific discussion of major and aspiring players in the Re ...
Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington`s disease
... 3.2. Wild-type huntingtin increases BDNF production by stimulating gene transcription from BDNF exon II promoter 3.3. Wild-type huntingtin influences the activity of the RE1/NRSE silencer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.3.1. RE1/NRSE neuronal genes and REST/NRSF trans ...
... 3.2. Wild-type huntingtin increases BDNF production by stimulating gene transcription from BDNF exon II promoter 3.3. Wild-type huntingtin influences the activity of the RE1/NRSE silencer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.3.1. RE1/NRSE neuronal genes and REST/NRSF trans ...
Control of Extracellular Dopamine at Dendrite and Axon Terminals
... 2004), thereby decreasing dopamine release in terminal areas. The release of dopamine from axons and dendrites occurs via vesicular exocytosis; however, the mechanisms that regulate exocytosis may differ between the two sites (Rice et al., 1997; Jaffe et al., 1998; Li et al., 2005; Fortin et al., 20 ...
... 2004), thereby decreasing dopamine release in terminal areas. The release of dopamine from axons and dendrites occurs via vesicular exocytosis; however, the mechanisms that regulate exocytosis may differ between the two sites (Rice et al., 1997; Jaffe et al., 1998; Li et al., 2005; Fortin et al., 20 ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.