* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve Impulse Transmission
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
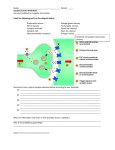
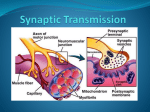
Synaptic Transmission Impulses Along a Neuron • Dendrites receive the nerve impulse and carry it toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. • The axon carries the impulse from the cell body toward the synaptic knobs where it will be transferred to other neurons. Transmission at the Synapse • There is a tiny gap between the synaptic knobs of one neuron and the dendrites of the next one. • This gap is called the synapse or synaptic cleft. • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. The Synapse Neurotransmitters 1. Are released from the presynaptic knobs by exocytosis (active) 2. Diffuse across the synapse (passive) 3. React with special receptors in the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron 4. This causes sodium gates to open, an action potential starts and the nerve impulse continues 5. Once the neurotransmitters have passed along the impulse, the “extra” neurotransmitters still remaining in the synapse are either: a) broken down by enzymes or b) transported back into vesicles in the synaptic knob by endocytosis. Synapse animation Structure of the Synapse Diagram 1. 2. 3. 4. axon mitochondria synaptic knob vesicles containing neurotransmitters 5. synapse 6. neurotransmitter 7. receptors Diagram of Synapse 1.________________ 2.________________ 3.________________ 4.________________ 5.________________ 6.________________ 7.________________ Neurotransmitters, cont’d • • There are excitatory neurotransmitters which start impulses in neighboring neurons Ex: acetylcholine (Ach) – opens sodium ion channels on postsynaptic neurons, broken down by cholinesterase Neurotransmitters, cont’d • Inhibitory neurotransmitters which prevent impulses (ex. serotonin, dopamine). They make the postsynaptic membrane more permeable to K+ so that the membrane becomes even more negative in its resting state (called hyperpolarized) Neuron Impulse and Synaptic Transmission Neurotoxins Neurotoxins • Many animals (snakes, spiders, pufferfish, scorpion) use neurotoxins as a form of defence. • Most act to block or open Na+ or K+ channels or block the release of acetylcholine.