A Novel Functionally Distinct Subtype of Striatal Neuropeptide Y
... protein)-NPY reporter mice. In vitro whole-cell recordings and biocytin staining demonstrated the existence of a novel class of neostriatal NPY-expressing GABAergic interneurons that exhibit electrophysiological, neurochemical, and morphological properties strikingly different from those of previous ...
... protein)-NPY reporter mice. In vitro whole-cell recordings and biocytin staining demonstrated the existence of a novel class of neostriatal NPY-expressing GABAergic interneurons that exhibit electrophysiological, neurochemical, and morphological properties strikingly different from those of previous ...
A tale of two stories: astrocyte regulation of
... astrocytes – the main type of glial cells in the hippocampus and the cortex [16-18] – together with the discovery of two-way astrocyte-neuron communication [19, 20], suggest an active role of these cells in modulation of synaptic transmission and information processing in the brain ...
... astrocytes – the main type of glial cells in the hippocampus and the cortex [16-18] – together with the discovery of two-way astrocyte-neuron communication [19, 20], suggest an active role of these cells in modulation of synaptic transmission and information processing in the brain ...
Orexin/Hypocretin: A Neuropeptide at the Interface of Sleep, Energy
... cells (Tang et al., 2008). Moreover, food deprivation exerted a differential effect on coupling between orexin receptors and G proteins (Karteris et al., 2005). C. Orexin-Producing Neurons Orexin-producing neurons (orexin neurons) are exclusively localized to the perifornical area and the lateral an ...
... cells (Tang et al., 2008). Moreover, food deprivation exerted a differential effect on coupling between orexin receptors and G proteins (Karteris et al., 2005). C. Orexin-Producing Neurons Orexin-producing neurons (orexin neurons) are exclusively localized to the perifornical area and the lateral an ...
Calcium Transients in the Garter Snake Vomeronasal Organ
... neurons via two pathways: Ca2⫹ release from IP3-sensitive intracellular stores and, to a lesser extent, Ca2⫹ influx through the plasma membrane. Both components seem to be dependent on IP3 production. Chemoattractants evoke a short-latency Ca2⫹ elevation even in the absence of extracellular Ca2⫹, su ...
... neurons via two pathways: Ca2⫹ release from IP3-sensitive intracellular stores and, to a lesser extent, Ca2⫹ influx through the plasma membrane. Both components seem to be dependent on IP3 production. Chemoattractants evoke a short-latency Ca2⫹ elevation even in the absence of extracellular Ca2⫹, su ...
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Reelin Signaling in the Adult
... demonstrate a specific context in which Reelin signaling may be initiated in the intact brain and further emphasize that extracellular proteolysis of Reelin by tPA and other yet-to-be identified proteases is important to consider when trying to understand how altered Reelin processing and/or express ...
... demonstrate a specific context in which Reelin signaling may be initiated in the intact brain and further emphasize that extracellular proteolysis of Reelin by tPA and other yet-to-be identified proteases is important to consider when trying to understand how altered Reelin processing and/or express ...
elsevier second proof - Michigan State University
... Figure 3 Diagram illustrating the basic elements of the olfactory system in nonmammalian vertebrates. a, Schematic dorsal view of the forebrain and nasal sensory epithelia of a generalized nonmammalian vertebrate. The olfactory epithelium (oe) and vomeronasal organ (vno) lie rostral to the brain, an ...
... Figure 3 Diagram illustrating the basic elements of the olfactory system in nonmammalian vertebrates. a, Schematic dorsal view of the forebrain and nasal sensory epithelia of a generalized nonmammalian vertebrate. The olfactory epithelium (oe) and vomeronasal organ (vno) lie rostral to the brain, an ...
Structure and dynamics of the corticothalamic driver pathway in the
... The posterior group nucleus of the thalamus (PO) is in a key position of the whisker sensory system. In addition to being part of the ascending paralemniscal pathway it is mainly driven by somatosensory barrel cortex (BC) and projects to many cortical and subcortical areas. Due to its poor excitabil ...
... The posterior group nucleus of the thalamus (PO) is in a key position of the whisker sensory system. In addition to being part of the ascending paralemniscal pathway it is mainly driven by somatosensory barrel cortex (BC) and projects to many cortical and subcortical areas. Due to its poor excitabil ...
Mitochondrial support of persistent presynaptic vesicle mobilization
... perfusion-fixed (Figure 2E). It is unlikely that these spines simply retracted, leaving intact presynaptic boutons, because the frequency of nonsynaptic boutons did not increase (Figure 2E). The frequency of single synaptic boutons in the LTP condition was comparable to the perfusion-fixed and great ...
... perfusion-fixed (Figure 2E). It is unlikely that these spines simply retracted, leaving intact presynaptic boutons, because the frequency of nonsynaptic boutons did not increase (Figure 2E). The frequency of single synaptic boutons in the LTP condition was comparable to the perfusion-fixed and great ...
Antagonistic roles of Wnt5 and the Drl receptor in patterning the
... The perception of odors requires that stimulus information be systematically organized in a ‘map’ in the olfactory bulb. Indeed, axons of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a given odorant receptor sort out from other axons and terminate specifically in one of a field of discrete synaptic ...
... The perception of odors requires that stimulus information be systematically organized in a ‘map’ in the olfactory bulb. Indeed, axons of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) expressing a given odorant receptor sort out from other axons and terminate specifically in one of a field of discrete synaptic ...
Spinal sympathetic interneurons: Their identification and roles after
... were significantly larger than those of correlated neurons, and they were often larger than the excitatory fields for renal sympathetic nerve activity. Excitatory fields are defined as the area of body surface from which stimulation of sensory receptors evoked excitation of the neuron. Once identified n ...
... were significantly larger than those of correlated neurons, and they were often larger than the excitatory fields for renal sympathetic nerve activity. Excitatory fields are defined as the area of body surface from which stimulation of sensory receptors evoked excitation of the neuron. Once identified n ...
Clarinet (CLA-‐1), a novel active zone protein required for
... homologs of Piccolo, Bassoon, Fife, or of the coiled-‐coil domain of BRP have been identified for C. ...
... homologs of Piccolo, Bassoon, Fife, or of the coiled-‐coil domain of BRP have been identified for C. ...
Clarinet (CLA-‐1), a novel active zone protein required for synaptic
... homologs of Piccolo, Bassoon, Fife, or of the coiled-‐coil domain of BRP have been identified for C. ...
... homologs of Piccolo, Bassoon, Fife, or of the coiled-‐coil domain of BRP have been identified for C. ...
Dopaminergic control of the globus pallidus and its impact
... The work of my thesis is a part of integrative neurobiology and focuses on studying the control exerted by dopamine on basal ganglia (BG), especially the "external part of globus pallidus or GPe". GPe being a nucleus, which plays a key role in the control of movement by exerting an inhibitory influe ...
... The work of my thesis is a part of integrative neurobiology and focuses on studying the control exerted by dopamine on basal ganglia (BG), especially the "external part of globus pallidus or GPe". GPe being a nucleus, which plays a key role in the control of movement by exerting an inhibitory influe ...
Examination of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
... inactive rT3 or T2 [14]. The liver and kidney, where D1 participates in the clearance of TH derivatives, contains a relatively large concentration of this enzyme, but D1 is also present in the anterior pituitary, intestine, placenta and thyroid gland [16, 20]. In rats, D1 is also present in the cere ...
... inactive rT3 or T2 [14]. The liver and kidney, where D1 participates in the clearance of TH derivatives, contains a relatively large concentration of this enzyme, but D1 is also present in the anterior pituitary, intestine, placenta and thyroid gland [16, 20]. In rats, D1 is also present in the cere ...
Same Spinal Interneurons Mediate Reflex Actions of Group Ib and
... neurons on spinal motoneurons by contralaterally located commissural interneurons. To this end reticulospinal tract fibers were stimulated in the contralateral medial longitudinal fascicle (MLF) in chloralose-anesthetized cats in which the ipsilateral half of the spinal cord was transected rostral t ...
... neurons on spinal motoneurons by contralaterally located commissural interneurons. To this end reticulospinal tract fibers were stimulated in the contralateral medial longitudinal fascicle (MLF) in chloralose-anesthetized cats in which the ipsilateral half of the spinal cord was transected rostral t ...
The physiological role of orexin/hypocretin neurons in the regulation
... Orexin neurons are strongly inhibited by both a GABAA agonist, muscimol (Yamanaka et al., 2003b), and a GABAB receptor agonist, baclofen (Xie et al., 2006). Orexin neurons are also innervated by cells in the VLPO that also contain GABA (Sakurai et al., 2005; Yoshida et al., 2006). These observations ...
... Orexin neurons are strongly inhibited by both a GABAA agonist, muscimol (Yamanaka et al., 2003b), and a GABAB receptor agonist, baclofen (Xie et al., 2006). Orexin neurons are also innervated by cells in the VLPO that also contain GABA (Sakurai et al., 2005; Yoshida et al., 2006). These observations ...
- Wiley Online Library
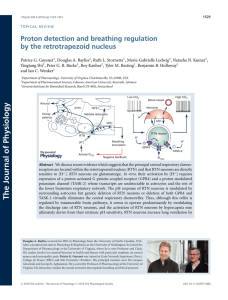
... Abstract figure legend Left: location and core function of the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN). RTN neurons reside at the ventral surface of the rostral medulla oblongata. Their axonal projections, depicted on a parasagittal section of the rodent lower brainstem, target principally the respiratory patt ...
... Abstract figure legend Left: location and core function of the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN). RTN neurons reside at the ventral surface of the rostral medulla oblongata. Their axonal projections, depicted on a parasagittal section of the rodent lower brainstem, target principally the respiratory patt ...
Modulation of premotor circuits controlling locomotor activity by
... supraspinal brain structures and circuits in the spinal cord. Understanding how the central nervous system generates a large repertoire of motor sequences, coordinate limbs and body orientation in an ever-changing environment while adapting to a myriad of sensory cues remains a central question in t ...
... supraspinal brain structures and circuits in the spinal cord. Understanding how the central nervous system generates a large repertoire of motor sequences, coordinate limbs and body orientation in an ever-changing environment while adapting to a myriad of sensory cues remains a central question in t ...
The Pedunculopontine Nucleus (PPN) in Parkinson`s Disease
... In rats, cholinergic neurons contribute to the PPN projections to medullary and pontine reticular formation (Rye et al., 1988, JCN 269: 315). Some of these neurons send axon collaterals to the thalamus (Semba et al., 1990, Neuroscience, 38:643). In rats, PPN projections to cervical spinal cord o ...
... In rats, cholinergic neurons contribute to the PPN projections to medullary and pontine reticular formation (Rye et al., 1988, JCN 269: 315). Some of these neurons send axon collaterals to the thalamus (Semba et al., 1990, Neuroscience, 38:643). In rats, PPN projections to cervical spinal cord o ...
Rapid Translocation of Zn 2+ from Nerve Terminals
... presynaptic terminals into postsynaptic hippocampal neurons after physiological stimulation. J Neurophysiol 86: 2597–2604, 2001. Zn2⫹ is found in glutamatergic nerve terminals throughout the mammalian forebrain and has diverse extracellular and intracellular actions. The anatomical location and poss ...
... presynaptic terminals into postsynaptic hippocampal neurons after physiological stimulation. J Neurophysiol 86: 2597–2604, 2001. Zn2⫹ is found in glutamatergic nerve terminals throughout the mammalian forebrain and has diverse extracellular and intracellular actions. The anatomical location and poss ...
Limbic systems for emotion and for memory, but no
... grand lobe limbique’ was mainly an olfactory structure common to all mammalian brains, although he argued that its functions were not limited to olfaction. Limbic structures are frequently taken to include cortical structures such as the hippocampus and cingulate cortex, and structures to which they ...
... grand lobe limbique’ was mainly an olfactory structure common to all mammalian brains, although he argued that its functions were not limited to olfaction. Limbic structures are frequently taken to include cortical structures such as the hippocampus and cingulate cortex, and structures to which they ...
Implication of novel neurotransmitter systems in the regulation of
... a maximum diameter of 10 to 20 µm. The fine structural properties of these neurons do not differ from the general neuronal attributes, except that some of the GnRH nerve cells are ciliated (8, 15). Most of the GnRH neurons show either uni- or bipolar shapes. The dendritic processes of GnRH cells ori ...
... a maximum diameter of 10 to 20 µm. The fine structural properties of these neurons do not differ from the general neuronal attributes, except that some of the GnRH nerve cells are ciliated (8, 15). Most of the GnRH neurons show either uni- or bipolar shapes. The dendritic processes of GnRH cells ori ...
Discrete coding of stimulus value, reward expectation, and reward
... the activity of many neurons was linearly correlated with the reward probability indicated by the CSs. ...
... the activity of many neurons was linearly correlated with the reward probability indicated by the CSs. ...
Neocortical Very Fast Oscillations (Ripples, 80–200 Hz) During
... in Fig. 11) had this pattern, which was revealed in filtered traces. Sometimes, recordings with macroelectrodes did not show this pattern, while local field potential recorded with a micropipette or cellular recordings did (see for example Fig. 11, DC field and glial cell recordings vs. EEG). Ripple ...
... in Fig. 11) had this pattern, which was revealed in filtered traces. Sometimes, recordings with macroelectrodes did not show this pattern, while local field potential recorded with a micropipette or cellular recordings did (see for example Fig. 11, DC field and glial cell recordings vs. EEG). Ripple ...
Limbic structures, emotion, and memory
... Tier 2 is that any learning in Tier 2 of the value of an object or face seen in one location on the retina, size, and view will generalize to other views etc. In rodents, there is no such clear separation of “what” from “value” representations. For example, in the taste system, satiety influences tas ...
... Tier 2 is that any learning in Tier 2 of the value of an object or face seen in one location on the retina, size, and view will generalize to other views etc. In rodents, there is no such clear separation of “what” from “value” representations. For example, in the taste system, satiety influences tas ...