* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download steps in nerve impulse transmission
Theta model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
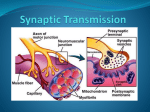
NERVE IMPULSE TRANSMISSION I. Transmission Along a Neuron 1. RESTING POTENTIAL Na K pump moves 3 Na out for every 2 K in ( -70mV) 2. THE ACTION POTENTIAL Triggered by a stimulus strong enough to produce a depolarization through a special phenomenon ALL OR NOTHING PHENOMENON Increasing the intensity of the stimuli above threshold will not produce an increased response. Neurons either fire maximally or not at all. STAGES OF THE ACTION POTENTIAL A. DEPOLARIZATION PHASE Na channels open to let Na rush in K channels stay closed (+30mV) B. REPOLARIZATION PHASE K channels open and let K rush out Na stays in since gate is closed (down to -80mV) (extra dip is refractory period) 3. UNDERSHOOT (AKA REFRACTORY PERIOD) Na and K channels close but NaK pump restores order (-70mV) after hyperpolarization II. Transmission Between Neurons Communication between neurons is accomplished by moving across a small gap called the synapse. Synapse: space between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector. Presynaptic neuron: carries impulse toward synapse. Postsynaptic neuron: carries impulse away from synapse. 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarization or hyperpolarization EXAMPLES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (Ach) GABA Serotonin Dopamine Neurotransmitters can be destroyed in different ways if they are no longer needed Example-enzymatic degradation Acetylcholinesterase breaks Ach into choline Summation: Effect produced by the accumulation of NTs from two or more neurons. a. Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Depolarization makes it MORE likely that an action potential will fire b. Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Hyperpolarization makes it LESS likely that an action potential will fire.

















![b6-5 synapse worksheet[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/024482271_1-9636d95ba53cc122ea04ace9fe914658-150x150.png)