* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the limbic system
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
reductionism
Animal survival and reproduction
depends on rapid & flexible responses
to changes in the environment.
A diversity of nervous systems
has evolved in various animal phyla.
As in many other organ systems,
animal nervous systems
are remarkably similar at the
cellular level - how neurons work - but
differ at higher levels of organization,
such as the structure and function
of their brains.
holism
Ch. 48:
Nervous Systems:
(from molecules to mind?)
http://www-gpi.physik.uni-karlsruhe.de/pub/robert/Diplom/node5.html
In 1911 Ramón y Cajál came up with the idea of
the neuron as the basic component of the brain.
… a human brain contains some 100 billion ( 1011) neurons with
about 1,000 to 10,000 connections each (resulting in 1014 -1015 interconnections).
Although one neuron is about 106 times slower than a transistor of a computer
the massively parallel processing capability of the brain
gives it a much higher efficiency.
… it takes about 100-200 msec for the brain to recognize a familiar face …
this simple task causes great problems to the computer - if it can do it at all.
{efforts at developing AI have been disappointing}
Functional organization of fundamental (neural) units
Effector?
A Neural Network is
an assembly of simple processing elements,
whose functionality is loosely based on the neuron.
The processing ability of the network
is stored in the inter-unit connection strengths,
obtained by a process of adaptation to,
or learning from, a set of training patterns.
{function ‘emerges’ from interactions,
that evolve by selection on performance}
A simple functional network:
the Postural (knee-jerk) reflex;
recall: herpes emerge from
dorsal root ganglia
to become shingles
+
-
Muscle length and velocity are monitored by
muscle-spindle stretch receptors.
Activation of these receptors initiates
the stretch reflex: motor neurons of
antagonists are inhibited (-) & those of
synergists are activated (+).
{voluntary contraction}
Tension on the stretch receptors
is maintained by gamma efferent activation
of the spindle muscle fibers.
{alpha efferent to power effector muscle,
gamma efferent (not shown) to spindle
keeps sensor stretched
as effector shortens}
Alpha and gamma motor neurons are often
coactivated {in voluntary movement}.
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
All cells have a resting potential (ionic gradients) across plasma membrane,
but neurons have voltage-sensitive permeability (voltage-gated ion channels)
Ions cannot dissolve in the
phospholipid plasma membrane;
they must either be
pumped by membrane proteins or
diffuse through ion channels,
which are aqueous pores made
of specific transmembrane
protein molecules.
These molecular channels
are selective for specific ions.
Membrane potentials are generated by the diffusion of ions and are determined by
(a) the ionic concentration differences across the membrane, and
(b) the membrane's relative permeabilities to different ions.
Plasma membrane Na,K-ATPase pumps maintain
intracellular sodium concentration low and potassium high.
In almost all resting cells, the plasma membrane
is much more permeable to potassium than to sodium; {see gates Fig 48.9}
the membrane potential is close to the potassium equilibrium potential,
that is, the inside is negative relative to the outside. {about -70mV}
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
Within neurons, graded potentials integrate inputs (like AM, adding analog signals)
and action potentials transmit decisions (like FM, w/o degradation)
At an inhibitory synapse: an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
{hyperpolarization} results when channels to potassium are opened.
At an excitatory synapse: an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
{depolarization} results when channels to sodium are opened.
The postsynaptic cell's membrane potential is the result of
temporal and spatial summation of the EPSPs and IPSPs
at the many excitatory and inhibitory synapses on the cell.
{this integrates information; a ‘decision’ at axon hillock}
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
MS results from
autoimmune destruction
of myelin
An action potential (AP) is a rapid change in the membrane potential
during which the potential rapidly depolarizes and repolarizes.
{the axon hillock ‘decides’ to fire off an all-or-none AP
when local graded potentials integrate to above the threshold, -50mV}
APs provide long-distance transmission of information
through the nervous system. {along the axon, w/o degradation}
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
APs occur in excitable membranes because
these membranes contain voltage-gated sodium channels,
which open as the membrane depolarizes, {Fig 48.9}
causing a positive feedback toward the sodium equilibrium potential.
{Na+ channels open & as Na+ enters, opposing electrical gradient develops}
In myelinated nerve fibers, APs manifest saltatory {skippy} conduction.
{which allows small diameter axons to be fast; invertebrates have ‘giant axons’}
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
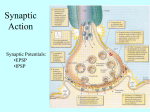
Most graded signals originate at synapses on the dendritic tree
The signal from a pre- to a postsynaptic neuron
is a neurotransmitter stored in synaptic vesicles
in the presynaptic axon terminal.
Depolarization of the axon terminal,
which raises the calcium concentration within the terminal,
causes the release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft.
The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft
and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic cell;
the activated receptor usually opens {chemically-gated} ion channels.
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
http://www.csuchico.edu/psy/BioPsych/neurotransmission.html
• Endorphins/Enkephalins are endogenous opiates
found in a variety of places (limbic system, midbrain).
They are also released as hormones by the pituitary.
They are involved in pain reduction and
pleasure (they enhance the effects of dopamine).
• Recall NO & Adenosine!
•Human mood disorders (depressions) are effectively treated with drugs that
block the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic axon terminal,
for example fluoxetine (Prozac).
• Cocaine, opiates, and alcohol produce rewarding effects by
promoting the release or inhibiting the presynaptic re-uptake of dopamine.
{addiction is associated with reduced density of dopamine receptors:}
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is accompanied by a selective destruction of dopamine neurons
in the substantia nigra of the midbrain. PD is treated with L-dopa, a precursor of dopamine in the brain.
Schizophrenia is treated with drugs which block the binding of dopamine to its postsynaptic receptor sites.
Nature 419, 872-874
(2002)
•Each time you move a muscle it is because acetylcholine
has been released from a neuron to activate muscle
Alzheimer's Disease is associated with a 90% loss in the brain's
production of acetylcholine in the basal forebrain and hippocampus
•Some of the drugs which are used to treat depressive disorders (tricyclic antidepressants)
block the reuptake of monoamines like serotonin at the synapse {and extend it’s effect}.
• GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
• GLU (glutamate) is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Its actions are mediated at two types of receptor (NMDA and AMPA) involved in memory formation
A good source of info: http://www.pharmcentral.com/
Chronic systemic pesticide exposure
reproduces features of Parkinson's disease.
Betarbet et al. 2000 Nature Neuroscience 3:1301-1306.
The New York Times November 5, 2000
HEADLINE: Pesticide Found to Produce Parkinson's Symptoms in Rats.
BYLINE: By SANDRA BLAKESLEE
… in … Nature Neuroscience. …
An organic pesticide widely used on home-grown fruits and vegetables
and for killing unwanted fish in the nation's lakes and rivers
produces all the classic symptoms of Parkinson's disease in rats
Rotenone is extracted from … various tropical plants …
Like many plants that produce what are in effect their own pesticides,
these plants apparently evolved to produce the compound
as a way of warding off insects and other pests. {secondary compounds}
Rotenone is found in 680 compounds … organic garden pesticides and flea powders …
Parkinson's disease … is caused by the steady loss of cells,
in a tiny region of the brain called the substantia nigra,
that produce a chemical, dopamine, which is crucial for movement and cognition. …
The role of environmental agents in Parkinson's disease
Di Monte DA CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH 1 (6): 419-426 DEC 2001
Association of coffee and caffeine intake with the risk of Parkinson disease.
Ross GW et al.
Journal Of The American Medical Association 283: (20) 2674-2679 MAY 24 2000
Data were analyzed from 30 years of follow-up of 8004 Japanese American men
(aged 45-68 years) enrolled in the … Honolulu Heart Program
Age-adjusted incidence of PD
declined consistently with increased amounts of coffee intake,
from 10.4 per 10000 person-years in men who drank no coffee
to 1.9 per 10000 person-years in men who drank at least 28 oz/d.
Our findings indicate that higher coffee and caffeine intake
is associated with a significantly lower incidence of PD.
The data suggest that the mechanism is related to caffeine intake.
{Consider correlation vs cause?}
http://ci.mond.org/9522/952214.html
From venoms to toxins to drugs:
Toxins have been used scientifically
to elucidate physiological mechanisms,
as shown by Claude Bernard's classical experiments
in the 1850s with curare, the South American arrow poison…
the pure alkaloid, tubocurarine, isolated from curare,
has been used as a muscle relaxant
to accompany general anaesthetic since 1942.
{blocks acetylcholine at neuromuscular junction}
Another toxin used for its muscle relaxant properties
is botulinum toxin, from bacteria Clostridium botulinum
The toxin gets into motor nerve terminals and
prevents the release of
the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
… botulinum toxin is often regarded as
one of the most toxic substances known …
However, its specificity and irreversibility
have been useful …
When Botox is injected into a muscle,
it blocks the nerve impulse from reaching that area,
and as a result, the muscle weakens.
As the muscle weakens, the skin overlying the muscle relaxes
and the wrinkles in the skin gradually soften and often disappear.
Actin-based plasticity in dendritic spines
Matus A
SCIENCE 290: (5492) 754-758 OCT 27 2000
Abstract:
The central nervous system functions primarily
to convert patterns of activity in sensory receptors
into …. appropriate behavior.
At the anatomical level this requires
two complementary processes:
a set of genetically encoded rules
for building the basic network of connections, and
a mechanism for subsequently fine tuning these
connections on the basis of experience. …
Evidence has accumulated implicating …
excitatory synapses made onto dendritic spines,
as the sites where connective plasticity occurs. …
Learning & memory:
dynamic
complex interactions!
Signal-processing machines at the postsynaptic density
Kennedy MB
SCIENCE 290: (5492) 750-754 OCT 27 2000
Abstract:
Dendrites of individual neurons
in the vertebrate central nervous system
are contacted by thousands of synaptic terminals
relaying information about the environment.
The postsynaptic membrane at each synaptic terminal
is the first place where information is processed
as it converges on the dendrite.
At the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses,
neurotransmitter receptors
are attached to large protein "signaling machines" that
delicately regulate the strength of synaptic transmission.
These machines are visible in the electron microscope and
are called the postsynaptic density.
By changing synaptic strength
in response to neural activity,
the postsynaptic density contributes to information
processing and the formation of memories.
Postsynaptic Signaling and Plasticity Mechanisms
Morgan Sheng & Myung Jong Kim
Science Oct 25 2002: 776-780.
Excitatory synapses of the brain primarily use glutamate
as their neurotransmitter.
Different classes of postsynaptic glutamate receptors
transduce the glutamate signal into
electrical & biochemical events in the postsynaptic neuron.
The -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
(AMPA)-type glutamate receptor opens {unconditionally}
in response to glutamate binding and mediates most
of the rapid excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC).
The N-methyl-D-aspartate
(NMDA)-type glutamate receptor … opens {conditionally}
in response to glutamate only when the postsynaptic
membrane is concomitantly depolarized.
Different patterns of activation of NMDA receptors
(NMDARs) can lead to either long-term potentiation (LTP)
or long-term depression (LTD) of synaptic strength.
These long-lasting forms of synaptic plasticity
are intensively studied because they may represent
ways of encoding "memories" in the brain.
Not everything that we learn is useful, {except in this class, of course!}
so the brain needs a mechanism to prevent itself being burdened by unhelpful
details.
The molecular
details ofand
this
mechanism
are now
being uncovered.
Studies
of the molecular
cellular
foundations
of cognitive
processes
have come of age with the development of techniques
that allow genes to be over-expressed, deleted or modified in mice.
These altered animals have been studied from a variety of aspects simultaneously
by molecular biologists, neurophysiologists and psychologists.
The result is the birth of a field that is unravelling the basis of learning, remembering,
and now — as a paper in this issue shows — forgetting.
On page 970, Genoux and colleagues report that an enzyme known as protein
phosphatase 1
(PP1) actively suppresses
in mice,
during and after
a learning
One ofmemories
PP1's targets
is aboth
gene-transcription
factor
called
exercise. …
CREB,
which becomes inactive when dephosphorylated by PP1.
CREB is required for the synthesis of proteins
7. in ageing
These
data in
…insuggest
forgetting
involved
memorythat
formation
may not … result from an irreversible rundown
of molecular components
but rather from the active intervention of PP1
Excite:
Relax:
Rest & Digest Fight or Flight
The autonomic nervous system innervates
cardiac and smooth muscle, glands …
Each autonomic pathway consists of
a preganglionic neuron with its cell body in the CNS and
a postganglionic neuron with its cell body in a ganglion outside the CNS.
The preganglionic neurons in both divisions release acetylcholine;
the postganglionic parasympathetic neurons release mainly acetylcholine, and
the postganglionic
sympathetic neurons release mainly norepinephrine.
Effector organs innervated by the autonomic nervous system
generally receive dual innervation.
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/vander/student/olc/index.htm
The Brain evolved (phylogeny) & develops (ontogeny)
as an elaboration of the dorsal hollow neural tube
sensory & motor mapping
& ‘cognition’
homeostasis & emotions
routing & switching
homeostasis & movement
visceral homeostasis
“As anyone who has sat through a lecture on a warm spring day knows,
attentiveness and mental alertness vary from moment to moment. “ !!!
The Reticular Activating System is a functional group of neurons
that plays a role in sleep, arousal and attention.
Seems to ‘decide’ what needs to be brought to conscious attention,
ex: ‘the cocktail party phenomenon’ - hearing your name in a noisy room …
Motor and sensory body surfaces
are topographically mapped
onto the cerebral cortex
w/ ‘association areas’ nearby.
(note cross mapping right-to-left
& lateralization of ‘jobs’)
These mappings are
variable across people,
and ‘plastic’ within people
(ex after injury)
During an infant’s or child’s brain development, …
The right hemisphere is stronger at
The left hemisphere is most adept at
pattern recognition, face recognition,
spatial relations, nonverbal ideation,
emotional processing in general, music;
perception of the relationship between
images and the whole context
in which they occur.
{the ‘holostic hemisphere’}
language, math, logic operations,
serial sequences of information,
detailed, speed-optimized activities,
fine visual and auditory details.
focused perception.
{the ‘reductionist hemisphere’}
While working with their hands, most right-handed people
use the left hand (right hemisphere) for context or holding and
use the right hand (left hemisphere) for fine detailed movement.
http://www.bio.psy.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/asymhumans.htm
We use different methods to investigate functional cerebral asymmetries …
One of them is the visual half-field technique
in which stimuli (faces, words, figures, illusory figures) are presented for 180 ms
in the left or the right visual field of a person which fixates a cross
in the middle of a computer screen. {180ms is too brief to shift eyes}
Due to the pattern of projections within the human visual system,
stimuli shown on the right are represented in the left hemisphere and vice versa.
If words are shown on the right side (left hemisphere),
reaction times are faster and percent correct measures are higher
due to the language-dominance of the left hemisphere.
The opposite is true for faces and abstract figures (Hausmann and Güntürkün, 1999).
The ability to observe which structures
participate in specific functions
is due to a new technique called
functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI:
provides high resolution, noninvasive reports
of neural activity detected by
a blood oxygen level dependent signal …
This new ability to directly observe brain function {blood flow}
opens an array of new opportunities
to advance our understanding of brain organization …
to mental operations … maps of human brain function.
http://www.alumni.berkeley.edu/Alumni/Cal_Monthly/September_2001/Making_up_your_mind.asp
Functional MRI of a volunteer
committing a list of words to memory.
The colored spots represent
increased blood flow and brain activity.
The circled region is a part of the frontal cortex
where activity was higher
for words that were later remembered
than for words that were later forgotten.
The hippocampus, amygdala,
some inner portions of the cortex’s lobes and
sections of the thalamus and hypothalamus,
form a ring around the brainstem called
the limbic system:
- interacts with neocortex & generates emotions.
Amygdala activity related to enhanced memory
for pleasant and aversive stimuli
Hamann et al. 1999 Nature Neurosci 2, 289-293.
Pleasant or aversive events
are better remembered than neutral events.
Using positron emission tomography, {not fMRI}
Maps of pixels in which individual subject rCBF
we show that
was significantly correlated with
bilateral amygdala activity during memory encoding individual-subject episodic-memory enhancement
is correlated with enhanced episodic recognition memory …
The human amygdala
seems to modulate the strength of conscious memory for events
according to emotional importance …
{Serotonin is a neurotransmitter arising from emotional stimuli of the limbic system.
Prozac is a serotonin uptake blocker.}
This is still
controversial
We know where the brain is, but where is the mind?