* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
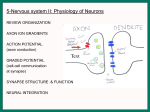
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms Key Terms Neurons Brain Ganglia Information Processing o Sensory input o Integration o Motor output Sensory neurons Interneurons Motor neurons Central Nervous System (CNS) Stimuli Resting Potential Concentration Gradient Sodium-Potassium Pumps Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cell Body Dendrites Axon Axon Hilock Synapse Synaptic Terminal Neurotransmitters Presynaptic Cell Postsynaptic Cell Glial Cells Membrane Potential Hydrolysis Ion Channels Selective Permeability Equilibrium Potential Nernst Equation Gated Ion Channel Polarity Hyperpolarization Depolarization Graded Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channel Action Potential Threshold Positive Feedback Cycle Rising Phase Falling Phase Undershoot Refractory Period Zone of depolarization Zone of repolarization Myelin sheath Oligodendrocytes Schwann Cells Nodes of Ranvier Saltatory Conduction Electrical Synapses Gap Junction Chemical Synapses Synaptic Vesicles Synaptic Cleft Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Postsynaptic Potential Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials Temporal Summation Spatial Summation Draw and label a neuron Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when someone calls your name. What properties of the nervous system could account for the rapid action of some venom? How would severing an axon affect the flow of information in a neuron? Explain the role of each of the following in creating a membrane potential in the Nervous System: Sodium-potassium pump: Potassium Channel: Sodium Channel: Under what circumstances could ions flow through ion channels from regions of low ion concentration to regions of high ion concentration? Suppose a cell’s membrane potential shifts from -70mV to -50mV. What changes in the cell’s permeability could cause such a shift? Suppose you treated a neuron with a drug that specifically disables the sodiumpotassium pump. What change in the resting potential would you expect? Describe the steps in the process of voltage-gated channels shaping action potentials How does an action potential differ from a graded potential? In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? Suppose that a mutation caused gated sodium channels to remain inactivated for a longer time following an action potential. How would such a mutation affect the maximum frequency at which action potentials could be generated? When are the steps that occur after a chemical synapse is triggered? Complete the following chart with information about the major groups of neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitter Structure Functional Class Secretion Sites How is it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to produce opposite effects in different tissues? Organophosphate pesticides work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Explain how these toxins would affect EPSPs produced by acetylcholine. If a drug mimicked the activity of GABA in the CNS, what general effect on behavior might you expect and why?