* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcranial direct-current stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neurostimulation wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
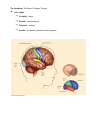
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior Communication in the Nervous System • • Glia – structural support and insulation Neurons – communication – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – receive – Axon – transmit away – Myelin sheath – speeds up transmission – Terminal Button – end of axon; secretes neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters – chemical messengers The Neuron at Rest • Hodgkin & Huxley (1952) - giant squid – Fluids inside and outside neuron – Electrically charged particles (ions) – Neuron at rest – negative charge on inside compared to outside – -70 millivolts – resting potential The Action Potential • • • • • Stimulation causes cell membrane to open briefly Positively charged sodium ions flow in Shift in electrical charge travels along neuron The Action Potential All – or – none law The Synapse • • • Synaptic cleft Presynaptic neuron – Synaptic vesicles – Neurotransmitters Postsynaptic neuron – Receptor sites When a Neurotransmitter Binds: The Postsynaptic Potential • • • Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) – Not all-or-none – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP Integrating Signals • • • One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially Synaptic connections – Elimination and creation – Synaptic pruning Neurotransmitters and Behavior • • • • • Specific neurotransmitters work at specific synapses – Lock and key mechanism Agonist – mimics neurotransmitter action Antagonist – opposes action of a neurotransmitter More than 40 neurotransmitters known at present Interactions between neurotransmitter circuits Organization of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) • Peripheral nervous system – Afferent = toward the CNS – Efferent = away from the CNS – Somatic nervous system – Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic Studying the Brain: Research Methods • • • • Damage studies/lesioning Electrical stimulation (ESB) Brain imaging – – computerized tomography – positron emission tomography magnetic resonance imaging Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) Brain Regions and Functions • • • Hindbrain – vital functions – medulla, pons, and cerebellum Midbrain – sensory functions – dopaminergic projections, reticular activating system Forebrain – emotion, complex thought – thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, cerebral cortex Right Brain/Left Brain: Cerebral Specialization • Cerebral Hemispheres – two specialized halves connected by the corpus collosum – Left hemisphere – verbal processing: language, speech, reading, writing – Right hemisphere – nonverbal processing: spatial, musical, visual recognition The Cerebrum: The Seat of Complex Thought • Four Lobes: – Occipital – vision – Parietal - somatosensory – Temporal - auditory – Frontal – movement, executive control systems The Endocrine System: Another Way to Communicate • • Hormones – chemical messengers in the bloodstream Endocrine glands – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas – sugar metabolism – Gonads – sex hormones Basic Principles of Genetics • Chromosomes – strands of DNA carrying genetic information • Polygenic traits – Human cells contain 46 chromosomes in pairs (sex-cells – 23 single) – Each chromosome – thousands of genes, also in pairs Research Methods in Behavioral Genetics • • • Family studies – does it run in the family? Twin studies – compare resemblance of identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins on a trait Adoption studies – examine resemblance between adopted children and their biological and adoptive parents The Evolutionary Bases of Behavior • Based on Darwin’s ideas of natural selection • Adaptations – behavioral as well as physical – Reproductive success key – Fight-or-flight response – Taste preferences – Parental investment and mating