* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-5_Chem_postsyn_KolozsvariB
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
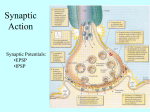
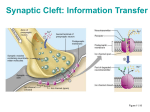
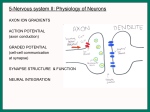
Postsynaptic elements and event by chemical synapses Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons signal can be exchanged to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body. After the opening of the vesicles, their neurotransmitter contents are dumped into the synaptic cleft, the narrow space between the membranes of the pre- and postsynaptic cells. The neurotransmitter diffuses within the cleft. Some of it escapes, but some of it binds to chemical receptor molecules located on the membrane of the postsynaptic cell, the opposite side of the synaptic gap. Receptors can respond in either of two general ways, and this response is the key step by which the synaptic process affects the behavior of the postsynaptic cell. First, the receptors may directly open ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic cell membrane, causing ions to enter or exit the cell and changing the local transmembrane potential. The resulting change in voltage is called a postsynaptic potential. In general, the result is excitatory in the case of depolarizing currents, and inhibitory in the case of hyperpolarizing currents. Whether a synapse is excitatory or inhibitory depends on what type(s) of ion channel conduct the postsynaptic current(s), which in turn is a function of the type of receptors and neurotransmitter employed at the synapse. The second way a receptor can affect membrane potential is by modulating the production of chemical messengers inside the postsynaptic neuron. These second messengers can then amplify the inhibitory or excitatory response to neurotransmitters. After a neurotransmitter molecule binds to a receptor molecule, it must be removed to allow for the postsynaptic membrane to continue to relay subsequent EPSPs and/or IPSPs (excitatory and/or inhibitory postsynaptic potencial). This removal can happen through one or more processes: The neurotransmitter may diffuse away due to thermally-induced oscillations/vibrations of both it and the receptor, making it available to be broken down metabolically outside the neuron or to be reabsorbed. Enzymes within the subsynaptic membrane may inactivate/metabolize(break down) the neurotransmitter. Reuptake pumps may actively pump the neurotransmitter back into the presynaptic axon terminal for reprocessing and repackaging for future release.