* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 3 S. 1
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
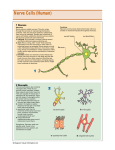
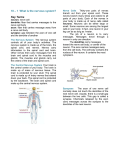
Ch. 3 S. 1 1 Ch. 3 S. 1 The Nervous System Obj: Explain how __________________ are transmitted by neurons, and describe the functions of the ______________________________ and the _________________ nervous system. The Nervous System The _________________ system regulates our internal functions. It is also involved in how we react to the external world. Even learning and __________________ are made possible by the nervous system. When we learn a new behavior or acquire new information, the nervous system registers that experience and changes to accommodate its _________________. Two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • ___________________ nervous system – consists of the brain and the spinal cord. • ____________________________ nervous system – made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and all the parts of the ____________. Neurons Nerve cells, called __________________, run through our entire bodies and __________________ with each other. Neurons send and receive messages from other structures in the body, such as muscles and glands. These messages can affect events ranging from the sensation of a pinprick to the first steps of a child, from the writing of a poem to the memory of a past event. Each of us has more than 100 ___________________ neurons, most of which are found in the brain. Components of a Neuron Neurons are somewhat like _______________ in structure. Parts of neurons resemble the _______________________, trunk, and _______________ of a tree. And, as in forests, many nerve cells lie alongside one another like a thicket of trees. Unlike tress, however, neurons can also lie end to end. Their “roots” are intertwined with the “branches” of neurons that lie below. Every neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The ______________________ produces energy that fuels the activity of the cell. Branching out from the cell body are think fibers called _____________________. The dendrites receive information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body. While the dendrites carry information to the cell body, the _______________ carries messages away. A neuron has many dendrites but usually only one axon. Axons vary greatly in _______________. Some are just a tiny fraction of an inch, while others stretch to several feet. Because of the length of their axons, some neurons in your legs are several feet long. Many axons are covered with __________________, a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. This myelin sheath, or casing, also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. At the end of the axon, smaller fibers branch out. These fibers are called __________________________________. The Communication Process _______________________ are sent from the axon terminals of one neuron to the dendrites of other neurons. In order for a message to be sent from one neuron to another neuron, it must cross the _______________. The synapse is a junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. Messages travel in only one direction. Thus, messages are received by the dendrites and _______________ through the cell body and the axon to the axon terminals. From there, they cross synapses to the dendrites of other neurons. New synapses can develop between neurons that were not previously connected, as when we learn something new. The information that is sent and the place to which it goes depend on a number of factors. These Ch. 3 S. 1 2 factors include the ____________________ of the neuron in the body and the _______________ that produced the message. Sensory neurons are nerve cells that carry information received by the senses to the central nervous system. ________________ neurons, on the other hand, are nerve cells that carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles and the glands and influence their functioning. Occasionally, something happens to _______________ the message-sending process. For example, a hard ______________ to the head from a car accident or a sports injury can cause a ________________________-an injury in which the soft tissue of the brain hits against the skull. Sometimes, the person is affected for only a few seconds. Other times, the person may experience effects for a much longer time. Neurotransmitters: Chemical Messengers Neurons send messages across synapses through the release of ______________________. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are stored in ____________ in the axon terminals. A neuron ______________, or sends its message, by releasing neurotransmitters-much like droplets of water shooting out of a spray bottle. Neurons can fire hundreds of times every second. There are several types of neurotransmitters. Each has its own structure and fits into a receptor site on the next neuron, similar to the way in which a key fits into a lock. The message is converted into an _____________________ impulse that travels the length of the neuron. The message is then transmitted to the next neuron by neurotransmitters. The process continues until the message arrives at its _____________________. This whole process takes only a _______________ of a second. Neurotransmitters are involved in _____________________ people do. Whenever a person waves a hand, yawns, or thinks about a friend, neurotransmitters are involved. Some diseases and psychological disorders may also be caused by the presence of too much or too little of various neurotransmitters. Researchers have identified _________________ of neurotransmitters and their functions. Examples: noradrenaline-prepares the body for action; seratonin-emotional arousal and sleep; dopaminemotor behavior, but a deficiency plays a role in Parkinson’s and an excess may contribute to _____________________________. The Central Nervous System Consists of the neurons of the spinal cord and the brain. The _____________________ extends from the brain down the back. It is a column of nerves about as thick as a ______________, and it is protected by the bones of the spine. It transmits messages between the brain and the muscles and the ________________ throughout the body. The spinal cord is also involved in spinal _____________________. A spinal reflex is a simple, _______________________ response to something. For example, if a person touches a hot stove, a message goes immediately from his or her hand to the spinal cord. A message to remove the hand is then sent back to motor neurons in the hand. The ________________ of the hand is a spinal reflex. (The person may also register pain in his or her brain. But the pain is not what causes the reflex. In fact, the pain may not even be felt until after the hand has been removed.) The Peripheral Nervous System The ________________________ nervous system lies outside the central nervous system and is responsible for transmitting ________________________ between the central nervous system and all parts of the body. The two main _______________________ of the peripheral nervous system are the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The Somatic Nervous System The ____________________ nervous system transmits sensory messages to the central nervous Ch. 3 S. 1 3 system. It is activated by touch, pain, changes in temperature, and changes in body position. The somatic nervous system enables us to experience the sensations of hot and cold and to feel pain and pressure. For example, we can feel the softness a cat’s fur. The somatic system also __________________ us that parts of the body have moved or changed positions. It sends messages to the muscles and the glands and helps us maintain ___________________ and balance. The Autonomic Nervous System The word autonomic means “occurring involuntarily,” or automatically. The __________________ nervous system regulates the body’s _______________ functions, such as heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and blood pressure. We generally do not have to think about these activities-they occur _________________________ and are essential for keeping us alive. Psychologists are interested in the autonomic system because of its involvement in the experience of _________________. The response of the autonomic nervous system is particularly important when a person experiences something ____________________ in the environment. This system has two ____________________: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system. These systems generally have opposing functions. The ______________________ system is activated when a person is going into action. This is the “fight or flight” response. It does this by ____________________ digestion, increasing the heart and respiration rates, and _____________________ the blood pressure. The __________________________ system restores the body’s reserves of energy after an action has occurred. Heart rate and blood pressure are normalized, breathing is slowed, and digestion returns to normal.