* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Synapses
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
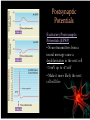
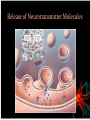
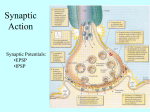
Chapter 3 Synapses Synapses Presynaptic Neuron • Sends the signal Postsynaptic Neuron • Receives the signal Postsynaptic Potentials Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials (EPSP) • Neurotransmitters from a neural message cause a deplolarization in the next cell -70 mV up to -67 mV • Make it more likely the next cell will fire Postsynaptic Potentials Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials (IPSP) • Neurotransmitters cause a hyperpolarization in the next cell -70 mV up to -72 mV • Less likely the next cell will fire Postsynaptic Potentials Factors: Determining EPSP and IPSP • Type of neurotransmitter • Type of receptor Post Synaptic Potentials Graded Responses • EPSP and IPSP can vary in strength Video: Lecture 4 Neural Communication_Excititory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials “The postsynaptic potentials created at a single synapse typically have little effect on the firing of the postsynaptic neuron (Bruno & Sakmann, 2006). The receptive areas of most neurons are covered with thousands of synapses, and whether or not a neuron fires is determined by the net effect of their activity.” –Pinel, p. 81 Postsynaptic Potentials Integration • EPSP and IPSP travel to the base of the axon hillock where they are summed Postsynaptic Potential Temporal Summation • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs Spatial Summation • Synaptic inputs from separate locations combine their effects on a neuron Postsynaptic Potentials “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with more than a few representative synaptic contacts, most neurons receive thousands of such contacts.” -Pinel, p. 82 Post Synaptic Potentials Reflexes Sensory neuron, goes to spine (afferent signal) Stimulates a motor neuron, which contracts the muscle (efferent signal) Temporal Summation One light tap does not produce reflex Two light taps in a row will Spatial Summation Two taps in slightly different locations will also stimulate a reflex Synapses Structure of Synapses • Synapses can occur between axon and * Dendrite (most common) * Soma * Axons Neurotransmitter Molecules Neurotransmitters • Over 100 neurotransmitters molecules • Different categories based on different chemical compounds • Most neurons make and release 1 or 2 types of neurotransmitters Neurotransmitter Molecules Notable Notable • GABA • Endorphines • Glutamate • Endocanabanoids • Acetylcholine • Serotonin • Adenosine • Dopamine • Norepinephrine • Epinephrine • Neuropeptide Y Release of Neurotransmitters Molecules Exocytosis • Release of neurotransmitter molecules • Action potential causes positive calcium ions to enter the terminal *This depolarizes the terminal Exocytosis • Vesicles to fuse to membrane • Contents emptied into synaptic cleft Release of Neurotransmitter Molecules Activation of Receptors Receptor • Protein that contains binding sites for neurotransmitters “Most neurotransmitters bind to several different types of receptors.” –p. 89 Reuptake and Degradation Reuptake • Almost immediately, neurotransmitters that have been released are drawn back into the presynaptic neuron • Recycling Enzyme Degradation • Enzymes break apart neurotransmitters Hormones Hormones • Chemicals secreted in most cases by glands (or neurons), carried by blood to other organs, where they exert their effects