* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
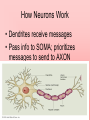
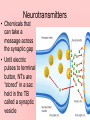
Understanding the Neuron 2 Internal Messaging Systems 1. Nervous System- fast acting- messages travel through neurons (nerve cells) 2. Endocrine System- slower acting- messages travel through hormones 3 Types of Neurons 1. Sensory- afferent- receives messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons How Neurons Work • Dendrites receive messages • Pass info to SOMA; prioritizes messages to send to AXON How a neural message is “Fired” • Resting potential: resting axon has a – charge • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the process starts, it cannot stop: All-ornone principle. • After neuron has “fired” there is a period of time where it cannot “fire” again. This is called the refractory period. Synaptic Transmission • The end of the axon = terminal button • When electric pulse reaches TB, it converts to a chemical message which can cross the synapse = (space between neurons) – This is called a synaptic transmission Neurotransmitters • Chemicals that can take a message across the synaptic gap • Until electric pulses to terminal button, NTs are “stored” in a sac held in the TB called a synaptic vesicle • Like a lock and key, specific neurotransmitters are designed to “fit” specific receptors. • NTs are broken down and recycled to be reused • Through reuptake, recycled NTs are sucked back into synaptic vesicles, resulting in a more muted message ***Memorize table 3.1 on page 76*** Plasticity • Refers to neural ability to change, create new and strengthen existing connections –Means recovery is possible when brain is damaged • Especially effective in children Glial Cells • Support neurons by holding them together and providing structural support • Form myelin sheath (fatty insulation) around axonsimportant b/c it protects the neurons while electrically charged!