* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Broca's area wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
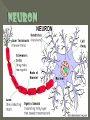
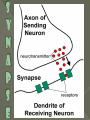
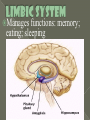
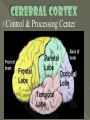
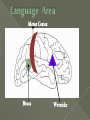
All or none = the least amount of energy needed to start the motion Action Potential = the movement of neural activity Refractory Period = the time where no motion can occur (no energy) Rest Potential = the time where the neuron is waiting to move Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain throughout the body A typical neuron has about 1,000 to 10,000 synapses There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RWS32l3dTsM Part – Function Dendrite - treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active role in the transmission of the neural signal; instead, keeps the neuron alive. Part – Function Axon - the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information Myelin Sheath - fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator. These myelinated axons transmit information much faster than other neurons Axon terminal – at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons (through synapses) Synapse – small gap at the end of a neuron that allows information to pass from one neuron to the next Neurotransmitter – is a chemical messenger that sends and moderates signals between neurons and other cells in the body (Acetylcholine, GABA, Serotonin, Dopamine, etc.) Receptor – an area on the dendrite where neurotransmitters bind Reuptake – is the process of unused neurotransmitters being taken back into the axon terminal There are different types of neurons, which all carry electro-chemical nerve signals throughout the Central Nervous System (CNS) Sensory neurons or Afferent neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. Motorneurons or Efferent neurons carry signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands. Interneurons are the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons. Interneurons * * * * * Brain Stem Frontal Lobe Reticular Formation Parietal Lobe Medulla Temporal Lobe Pons Occipital Lobe Thalamus Corpus Cerebellum Hypothalamus Hippocampus Amygdala Pituitary Gland Callosum Longitudinal fissure Motor Cortex Wernicke’s Area Broca Area Right =Random; Intuitive; Holistic; Synthesizing; Subjective; Looks at whole Left =Logical; Sequential; Rational; Analytical; Objective; Looks at parts Corpus Callosum = tissue that connects the two sides of the brain and allows communication Life Sustaining Center Corpus Callosum Thalamus Brainstem Thalamus = “The Relay Station” in the brain: sensory signals, auditory, visual, somatosensory (touch) Medulla = helps control the body's autonomic functions like respiration, digestion and heart rate Cerebellum = deals with movement through regulation and coordination of bodily movements, posture and balance Pons = monitors the level of stimulation or consciousness and sleep (while asleep) Reticular Formation = monitors the state of the body and functions in such processes as arousal and sleep and attention and muscle tone (FS/WU) Manages functions: memory; eating; sleeping Hippocampus = primary role is in memory formation, classifying information, long-term memory Amygdala (AH-mig-doll-la) = stores & classifies emotionally charged memories, as well as plays a role in producing our emotions, especially fear and anger. Triggers responses to strong emotions; causes sweaty palms, increased heart-beat & stress hormone release Hypothalamus = linked with the pituitary gland (hormones). Monitors & controls your circadian rhythms (your daily sleep/wake cycle), homeostasis (making sure your body is running smoothly), appetite, thirst Pituitary Gland = “master gland” for the endocrine system – send hormones – mainly for growth and development Control & Processing Center Frontal Lobe = responsible for functions such as reasoning, problem solving, judgment, impulse control (develops later than most parts and area most susceptible to drugs & alcohol) Parietal Lobe involved in processing pain & touch sensation. Where the somatosensory (from your skin and internal organs) Cortex resides. Associated with cognition (including calculating location & speed of objects), movement, orientation, recognition & speech Occipital Lobe = controls visual sensation and processing Temporal Lobe = involved in auditory (sound) sensation Motor Cortex Broca Wernicke Broca = speech production; facial and mouth control; and language Processing (language output) Wernicke = language Comprehension; semantic Processing; language Recognition; and language Interpretation (language structure) Motor Cortex = movement of mouth pronounce/hands