* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Long-term depression
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
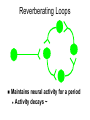
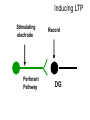
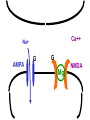
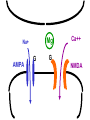
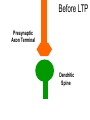
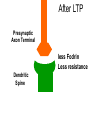
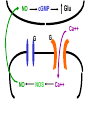
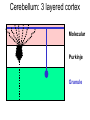
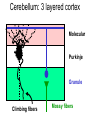
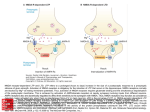
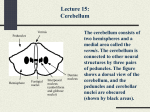
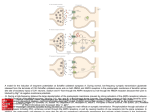
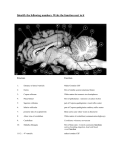
Neural Plasticity Lecture 7 Neural Plasticity Nervous System is malleable learning occurs Structural changes increased dendritic branching new synapses Changes in synaptic efficiency Long-term potentiation Long-term depression ~ Neural Mechanism of Memory Donald Hebb Short-term Memory Change in neural activity not structural temporary Reverberatory Circuits cortical loops of activity ~ Reverberating Loops Maintains neural activity for a period Activity decays ~ Hebb’s Postulate Long-Term Memory required structural change in brain relatively permanent Hebb Synapse use strengthens synaptic efficiency concurrent activity required • pre- & postsynaptic neurons ~ Long-term Potentiation According to Hebb rule use strengthens synaptic connection Synaptic facilitation Structural changes Simultaneous activity Experimentally produced hippocampal slices associative learning also ~ Inducing LTP Stimulating electrode Perforant Pathway Record DG Postsynaptic Potential Single elec. stimulation + -70mv - 100 stim. burst Single stim. Pattern Of Stimulation Strong, high frequency stimulation Minimum stimulation 1 + burst of 4 4-7 Hz • Theta HC: Arousal & REM ~ LTP Duration Experimentally-induced LTP Intact animals seconds - months HC slice 40 hrs ~ LTP: Molecular Mechanisms Presynaptic & Postsynaptic changes HC ---> Glutamate excitatory 2 postsynaptic receptor subtypes AMPA ---> Na+ NMDA ---> Ca++ Glu ligand for both ~ NMDA Receptor N-methyl-D-aspartate Glu binding opens channel? required, but not sufficient Membrane must be depolarized before Glu binds ~ Single Action Potential Glu ---> AMPA depolarization Glu ---> NMDA does not open Mg++ blocks channel no Ca++ into postsynaptic cell Followed by more APs ~ Ca++ Na+ AMPA G G Mg NMDA Mg Na+ AMPA G Ca++ G NMDA Activation of NMDA-R Ca++ channel chemically-gated voltage-gated Mg++ blocks channel Ca++ influx --->post-synaptic changes strengthens synapse ~ LTP: Postsynaptic Changes Receptor synthesis More synapses Shape of dendritic spines Nitric Oxide synthesis ~ Before LTP Presynaptic Axon Terminal Dendritic Spine After LTP Presynaptic Axon Terminal less Fodrin Less resistance Dendritic Spine Nitric Oxide - NO Retrograde messenger Hi conc. ---> poisonous gas Hi lipid solubility storage? Synthesis on demand Ca++ ---> NO synthase ---> NO Increases NT synthesis in presynaptic neuron more released during AP ~ NO cGMP Glu Ca++ G NO NOS G Ca++ The Cerebellum & Long-term Depression Cerebellum Motor functions Coordination of movements Regulation of posture Indirect control Adjust outputs of descending tracts Also nonmotor functions memory/language ~ Cerebellum: Anatomy Folia & lobules analogous to sulci & gyri Vermis - along midline output ---> ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output ---> lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei fastigial, interposed, & dentate Major output structures ~ Cerebellum Programs ballistic movements feed-forward control no feedback during execution direction, force, & timing long term modification of circuits Motor learning shift from conscious ---> unconscious ~ Cerebellum Acts as comparator for movements compares intended to actual performance Correction of ongoing movements internal & external feedback deviations from intended movement ~ Cerebellum: 3 layered cortex Molecular layer parallel fibers axons of granule cells runs parallel to long axis of folium Purkinge cell layer large somas axons to underlying white matter perpendicular to main axis of folium ~ Cerebellum: 3 layered cortex Purkinge cell layer large somas axons to underlying white matter perpendicular to main axis of folium ~ Cerebellum: 3 layered cortex Granular layer innermost layer small, densely packed granule cells > # neurons in cerebral cortex ~ Cerebellum: 3 layered cortex Molecular Purkinje Granule Cerebellum: & Motor Learning Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers from spinal cord & brainstem nuclei climbing fibers cerebral cortex & spinal cord via inferior olivary nucleus ~ Cerebellum: & Motor Learning 1 Purkinje cell synapses.. 1 each with 200,000 parallel fibers Many with 1 climbing fiber strong synaptic connections Climbing fibers effects of mossy fibers transient ~ Cerebellum: 3 layered cortex Molecular Purkinje Granule Climbing fibers Mossy fibers Cerebellum: & Motor Learning Long-term depression (LTD) requires concurrent activity climbing & parallel fibers active together in activity of specific Purkinje cells Climbing fibers may carry error signals corrections ---> parallel fiber influence input specificity only affects active synapses of a parallel fiber ~ LTD Mechanisms Similar to LTP * changes are postsynaptic Glutamate receptors LTD Mechanisms *Requires concurrent activity Climbing fiber 1. Ca++ *influx - voltage-gated Parallel fibers activate 2. AMPA - Na+ influx 3. mGLUR1 AMPA desensitized Na+ influx ~ LTD Mechanisms mGluR1 metabotropic cGMP-mediated intracellular Ca++ stores activation of phosphatases Knockout mice lack mGluR1 loss of motor coordination ~