* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the brain - WordPress.com
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
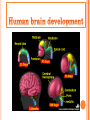
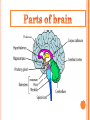
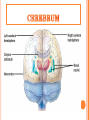
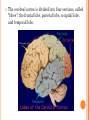
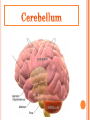
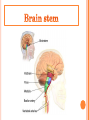
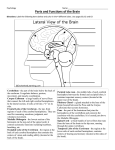
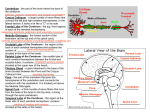
Introduction Structure of brain Human brain development Parts of brain functions The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body. It is made up of more than 100 billion nerves that communicate in trillions of connections called synapses. Interconnecting these brain cells are circuits complex than those most powerful supercomputers. The adult human brain weighs on average about 1.3–1.4 kg , or about 2% of total body weight. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. The human brain is composed of neurons, glial cells, and blood vessels. The living brain is very soft, having a consistency similar to soft gelatin or soft tofu. During the first three weeks of gestation, the human embryo's ectoderm forms a thickened strip called the neural plate. The neural plate then folds and closes to form the neural tube. This tube flexes as it grows, forming the crescentshaped cerebral hemispheres at the head, and the cerebellum and pons towards the tail. Our brain is our most powerful organ. It has a texture similar to firm jelly. It has three main parts: i. CEREBRUM ii. CEREBELLUM iii. BRAIN STEM cerebrum, the largest and uppermost portion of the brain. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral hemispheres and accounts for two-thirds of the total weight of the brain. One hemisphere, usually the left, is functionally dominant, controlling language and speech. The other hemisphere interprets visual and spatial information. The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of myelinated nerve fibres, the white matter, and an outer cortex of gray matter. The cerebral cortex is responsible for integrating sensory impulses, directing motor activity, and controlling higher intellectual functions. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech. cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Limbic System: The limbic system, often referred to as the "emotional brain", is found buried within the cerebrum. Like the cerebellum, evolutionarily the structure is rather old. This system contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus. The The cerebellum receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates motor movements. The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements such as posture. -balance. -coordination. -speech. It is also important for learning motor behaviors. The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior part of the brain. In humans it is usually described as including the medulla oblongata , pons and midbrain. The brainstem also plays an important role in the regulation of cardiac and respiratory function. all information relayed from the body to the cerebrum and cerebellum and vice versa must traverse the brainstem. It plays an important role in conduction. medulla The lower half of the brainstem that contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor centers and deals with autonomic, involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. pons Contains nuclei that relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with nuclei that deal primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture. THANK YOU