* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of the Brain - Bellarmine University
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
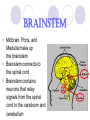
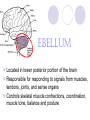
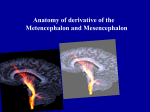
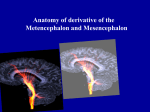
Parts of the Brain By: Derrick Yeagle Subdivided into six main regions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Midbrain Pons Brainstem Medulla Diencephalon Cerebrum Cerebellum Brainstem Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla make up the brainstem Brainstem connects to the spinal cord Brainstem contains neurons that relay signals from the spinal cord to the cerebrum and cerebellum Midbrain Within the midbrain, there are cell bodies containing red nucleus which is for controlling muscle coordination and maintains posture Pons Contains neurons that relay signals for: Chewing sensations to the head and face Certain respiratory functions Eye movement Taste Salivation Facial expressions equilibrium Medulla Contains tracts that travel in both directions between the brain and spinal cord Various nuclei of the medulla transmits nerve impulses that control: Heart rate Constriction Dilation of blood vessels Blood pressure Swallowing sneezing Diencephalon Composed of two major compartments: Thalamus Complex of nuclei that facilitate hearing, taste, vision, sensation, wakefulness, voluntary motor control Hypothalamus Collection of nuclei that controls the autonomic nervous system, secretion from various glands, heart rate, movement of food in the intestines, rage, aggression, body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep CEREBRUM Cerebrum • Two Hemispheres Accounts for approximately 80% of total mass of the brain Uppermost 2-to 4-mm layer of the cerebrum is crammed with cell bodies and neuroglia, called the cerebral cortex Cerebral Cortex Functions: Human consciousness Motor skills Awareness of subtle variations in the external environment Language Reasoning Imaginations Composed of regions with specific neuronal responsibilities Beneath the cerebral cortex Number of different nuclei Basal ganglia contain a number of different nuclei and subdivisions within some of these nuclei: Caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Subthalamic nucleus Nuclei interconnect with neurons of the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus and control involuntary skeletal muscle movements Other neuronal structures Limbic system Lies deep within the cerebrum near the diencephalon and midbrain Hipocampus Component of the limbic system Contributes to emotional states, such as fear, anger, rage, pleasure, and sorrow. Also with learning and memory capabilities Cerebellum Located in lower posterior portion of the brain Responsible for responding to signals from muscles, tendons, joints, and sense organs Controls skeletal muscle contractions, coordination, muscle tone, balance and posture References Pasternak,Jack. An Introduction to Human Genetics. pg. 400-401.