* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
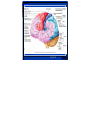
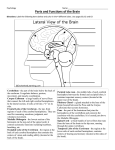
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another Review the meninges of the spinal cord and brain, and integrate the formation and flow of CSF with this information. If people only knew how hard I work to gain my mastery, it wouldn't seem so wonderful at all. Michaelangelo Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ventricles of the Brain p 381 CSF filled chambers Communicating with central canal of spinal cord Lined by ependymal cells Central Canal of Spinal Cord Fig 13.9 Four Major Brain Subdivisions 1. Brain Stem a. Medulla oblongata b. Pons c. Midbrain 2. Cerebellum 3. Diencephalon a. Hypothalamus b. Thalamus c. Epithalamus 4. Cerebral Hemispheres AKA Cerebrum Fig 13.11 1) Brain stem a. Medulla oblongata b. Pons c. Midbrain • • • Location of autonomic nuclei involved in respiratory and cardiovascular control Relay stations for sensory and motor neurons Decussation 1a) Medulla oblongata Pyramids – Motor output to spinal cord – Decussation Reticular formation – Lower functions – Respiration, sleep, etc. Cranial nerves – VIII, IX, X, XI, XII 1b) Pons Pons = bridge Connects to cerebellum – Via cerebellar peduncles Cranial Nerves – V, VI, VII 1c) Midbrain Cerebral aqueduct – Old term: Aqueduct of Sylvius Several nuclei (ganglia) – Substantia nigra Sensory reflexes – Aural, visual 2) Cerebellum Dorsal to the Pons Two hemispheres Maintains posture and equilibrium – Connected by the vermis – Smooths motor activities – Some cognitive function Cortex - gray surface – Purkinje cells (p 354), axons of which become arbor vitae (white matter) in center » Large cell bodies visible in gray matter of cerebellum » Use GABA as NT » Motor output from cerebellum White matter: Arbor Vitae 3) Diencephalon p 390 3a. Hypothalamus 3b. Thalamus 3c. Epithalamus Thalamus = 80% of diencephalon. Gateway (relay station) to the cerebral cortex not just for sensory input but for all info. Processing and editing also takes place. About 12 nuclei Hypothalamus also about 12 nuclei. Main visceral control center of the body 3a. Hypothalamus Just superior to optic chiasma Infundibulum - connects to pituitary gland Some functions: – Control of autonomic nervous system – Coordination of nervous and endocrine systems – Manufacture of hormones - ADH and oxytocin (Ch 17) 3b. Thalamus (80% of diencephalon) Next to 3rd ventricle Communication with hemispheres 3c. Epithalamus – Pineal gland - produces melatonin, – sets diurnal cycles – Choroid Plexus – produces CSF 4) Cerebrum (Telencephalon) 83% of total brain mass The right and left halves (cerebral hemispheres) – are separated by the Longitudinal Fissure – and connected by the Corpus Callosum and Anterior Commissure – are separated from the cerebellum by the transverse fissure Sulcus and Gyrus Gray Matter vs. White Matter The cortex (gray matter) of the cerebrum is the site of conscious thought – Central Sulcus In 90-95% of people left side has more control over language, math and logic. Right side is more involved withy visual-spatial skills, intuition, emotion, artistic and musical skill. 4) Cerebral Hemispheres, cont’d . . have functional regions – Sensory and motor areas » e.g. Broca’s area (speech) – Prefrontal Cortex (Cognitive functions) . . . have some functional differences (in spite of anatomical resemblance) → Lateralization of cortical functioning – Right brain: artistic skill – Left Brain: math, logic . . . receive sensory information and generate commands for opposite side of body – Decussation of sensory input is in the spinal cord – Decussation of motor output is in the pyramids In 90-95% of people left side has more control over language, math and logic. Right side is more involved withy visual-spatial skills, intuition, emotion, artistic and musical skill. Fig 13.18 fMRI An fMRI of the brain. Green areas were active while subjects remembered information presented visually. Red areas were active while they remembered information presented aurally. Yellow areas were active for both types. 4) Cerebrum, cont’d Regions of the Cortex Lobes named after the bones of the calvarium Sensory vs. Motor Areas – Homunculus Gyrus and Sulcus – Central Sulcus 4) Cerebral Cortex and Central White Matter Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts internally Projection tracts (fibers) – connect more or less vertically Association tracts (fibers) – connect one gyrus to another in the same hemisphere Basal Ganglia p 402 More proper term: basal nuclei A collection of several nuclei Gray matter deep to the cerebral cortex, below floor of lateral ventricles. Function: modulate motor output from the cerebral cortex. Subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone and coordination of learned movement patterns. Parkinson's disease is caused by the loss of at least 80% of the dopaminergic neurons in basal nuclei and substantia nigra of the midbrain (resting tremor) Substantia nigra is in mesencephalon Gray & White Matter Organization In brain stem similar to spinal cord (nuclei around ventricles, tracts on outside) In cerebrum and cerebellum: white matter covered with layer of neural cortex (grey) sagittal image showing brain and normal pituitary with bright spot in posterior, neurohypophysis, which is secretory granules which are made in base of brain and transported down infundibulum or pituitary stalk. Contrast enhanced MRI contrast enhances pituitary because of no blood brain barrier, the adenoma has less blood supply and is therefore less enhanced. The Pit. is an endocrine organ so it is highly vascular to release various endocrine hormones into the circulation quickly.