* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
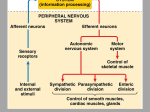
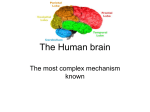
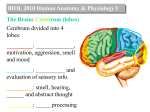
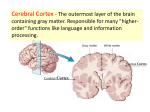
The Brain By: Natikwa Goodwin How it works.. • It controls the body temperature, blood pressure, and breathing. • • • It collects informations around you, using the 5 senses. It handles physical movement. It allows you to think, dream, reason and experience emotion. Neuron Structure • • The brain is made of 100 billion nerve cells, called neurons. • Axon- carries the electrochemical message along the lengths of the cell. • Dendrites- these parts of the cells make connections with other cells and allow neurons to to talk to tother cells or perceieve the environment. Dendrites are located on both ends of the cell. Cell Body- contrians the main parts and necessary ocomponents of the cell. The Brain The brain has 5 main parts that work together.. • • • • • cerebrum cerebellum brain stem pituitary gland hypothalamus Brain Stem • The brain stem consists of the medulla, pons, and midbrain. • The brain stem controls the reflexes and automatic functions. • -the heart rate, blood pressure, limb movements and visceral functions (digestion, urination). The Cerebrum The biggest portion of the brain.. • The cerebrum is responsible for 85% of the weight of the brain. • The cerebrum is the thinking portion of your brain, it controls the voluntary muscles. The Cerebellum • Integrates informations from the vestibular system. • It indicates positions, movements, and uses data to coordinate limb movements. The Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland • Along with the hypothalamus the pituitary gland is responsible for visceral functions. • It’s responsible for body temperature, and behavioral responses. Such as.. • • • • -feeding -drinking -sexual response -aggression Lower Brain • Medulla- Contains nuclei for regulation blood. • Pons- Relay movement and position information to the cerebellum. • Midbrain- Contains nuclei that links parts of the brain involved in motor functions. • Thalamus- Relays incoming sensory pathways to the appropriate parts of the cortex. • Parietal Lobe- Receives and processes all somatosensory input from the body such as pain and touch. • • • • • Frontal Lobe- Uses motor skills such as speech and cognitive functions. • • • Hippocampus- Important for short term memory. Occipital Lobe- Receives and processes information from the eyes. Temporal Lobe- Processes auditory information from the ears. Basal Ganglia- Helps to coordinate fine motions, such as fingertip movements. Limbic System- Important for emotional behavior and controlling movements of visceral muscles. Amygdala- Controls social and sexual behavior. Insula- Influences automatic functions of the brain.