* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
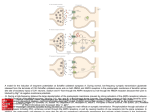
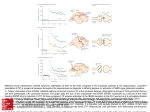
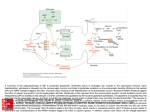
NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD. LTP refers to a prolonged (hours to days) increase in the size of a postsynaptic response to a presynaptic stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. This is achieved by activation of AMPA/kainate receptors at nearby synapses involving inputs from different neurons. AMPA receptors also are dynamically regulated to affect their sensitivity to the synergism with NMDA. Thus, NMDA receptors may function as coincidence detectors, being activated only when there is simultaneous firing of 2 or more neurons. LTD is the converse of LTP. A. NMDA receptor-dependent LTP Source: Neurotransmission and the Central Nervous System, Goodman and Gilman's Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2e requires post synaptic NMDA receptor activation leading to a rise in Ca2+ and activation of CaM kinase II (CaMKII). AMPA receptor insertion into the Hilal-Dandan R, mechanism Brunton LL. Goodman Gilman's Manual Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2016 Available at:entry through postsynaptic Citation: membrane is a major underlyingand LTP expression. B. ofNMDA receptor-dependent LTD is2e; triggered by Ca2+ http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: April 29, 2017 postsynaptic NMDA receptor channels, leading to increases in the activity of the protein phosphatases calcineurin and PP1. LTD occurs when © 2017 are McGraw-Hill Education. All with rights reserved from Nestler EJ, Hyman SE, Malenka RC, eds. Molecular Neuropharmacology. postsynaptic Copyright AMPA receptors internalized. (Redrawn permission New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009, p 132. © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)