* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
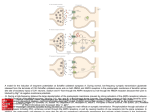
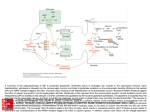
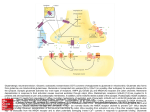
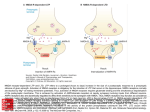
Long term potentiation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vso9jgfpI_c 1. Hippocampus regions: CA1/ CA3 2. Memory processing begins in these areas 3. Pyramidal neurons, get passed out to the cortex 4. Long term potentiation: Cellular, molecular underpinngs of memory 5. Most commonly studied at CA1/CA3 6. Post syn: Receptors (AMPA and NMDA): Localized together at many post syn sites and are activated with Glutamate 7. NMDA receptor: Permeability to Calcium and Sodium but blocked by Magnesium, prevents ions passing thru 8. Action potential: Release glutamate and binds to receptors 9. Small release of glutamate: AMPA receptors open—slight depolarization (NMDA not enough for response)—studying just a little bit, not activating high action potential 10. More study, more glutamate, higher frequency axn potential 11. AMPA: higher depolarization, repels Mg (electrostatic repulsion) allows both Na and Ca to come through, pre and post syn event for channel to open 12. LTP: Strengthen the connection btwn 2 neurons. Secondary cascades 13. Inc CA: 2 phases 1) CA binds to proteins to activate more receptors, only insert when large influx of CA—these last only a few hours; 2) prolonged CA, gene expression and new proteins— AMPA receptors and synthesis of growth factorsadd more synapses between CA1/CA3 neurons. These can last 24 hours to a lifetime 14. LTP is not a mechanism, but an outcome of the inc activity between two neurons; result in more receptors and more connections to create greater depolarization. 15. Hippocampus is not only place for memory formation, cortex 16. Fire same pathways, inc pre syn activity and post syn activation