Fine Tuning of Sympathetic Transmitter Release via Ionotropic and
... indeed a presynaptic one, or could it also be a postsynaptic one? Taken together, it appears somewhat difficult to define by just morphological means what may be a real presynaptic receptor. Therefore, various procedures have been used to identify by functional means whether a receptor is a presynap ...
... indeed a presynaptic one, or could it also be a postsynaptic one? Taken together, it appears somewhat difficult to define by just morphological means what may be a real presynaptic receptor. Therefore, various procedures have been used to identify by functional means whether a receptor is a presynap ...
13C MRS: An outstanding tool for metabolic studies
... C in specific positions have made it possible to follow in vivo and in vitro the activity of a large variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cyc ...
... C in specific positions have made it possible to follow in vivo and in vitro the activity of a large variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cyc ...
Analgetika kuat, Schunack
... It controls a wide range of biological functions ranging from nociception to food intake, from memory processes to cardiovascular and renal functions, from spontaneous locomotor activity to gastrointestinal motility, from anxiety to the control of neurotransmitter release at peripheral and central s ...
... It controls a wide range of biological functions ranging from nociception to food intake, from memory processes to cardiovascular and renal functions, from spontaneous locomotor activity to gastrointestinal motility, from anxiety to the control of neurotransmitter release at peripheral and central s ...
A tale of two stories: astrocyte regulation of
... ultimately depends on specific values of synaptic parameters and the rate and the pattern of synaptic activation [55]. The biophysical correlates of different synaptic parameters (e.g., time of recovery from synaptic depression and per-spike usage of synaptic resource) have been extensively document ...
... ultimately depends on specific values of synaptic parameters and the rate and the pattern of synaptic activation [55]. The biophysical correlates of different synaptic parameters (e.g., time of recovery from synaptic depression and per-spike usage of synaptic resource) have been extensively document ...
Extracellular Glutamate, Glutamine, and GABA in the Hippocampus
... lesion (46.9 ± 9.0 µM) sites compared to non-epileptic cortex (2.6 ± 0.3 µM). In the hippocampus, glutamate was significantly higher in the epileptogenic (10.3 ± 1.9 µM) and propagated sites (33.0 ± 13.8 µM) than non-epileptic sites (2.8 ± 0.5 µM). Glutamine was not significantly different between s ...
... lesion (46.9 ± 9.0 µM) sites compared to non-epileptic cortex (2.6 ± 0.3 µM). In the hippocampus, glutamate was significantly higher in the epileptogenic (10.3 ± 1.9 µM) and propagated sites (33.0 ± 13.8 µM) than non-epileptic sites (2.8 ± 0.5 µM). Glutamine was not significantly different between s ...
Central Role of Glutamate Metabolism in the Maintenance of
... excess of those of other amino acids. In glutamate-containing vesicles in the brain, the concentration of glutamate may even exceed 100 mM. Yet because glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter, the concentration of this amino acid in the cerebral extracellular fluid must be kept low—typicall ...
... excess of those of other amino acids. In glutamate-containing vesicles in the brain, the concentration of glutamate may even exceed 100 mM. Yet because glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter, the concentration of this amino acid in the cerebral extracellular fluid must be kept low—typicall ...
Central Role of Glutamate Metabolism in the Maintenance of
... excess of those of other amino acids. In glutamate-containing vesicles in the brain, the concentration of glutamate may even exceed 100 mM. Yet because glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter, the concentration of this amino acid in the cerebral extracellular fluid must be kept low—typicall ...
... excess of those of other amino acids. In glutamate-containing vesicles in the brain, the concentration of glutamate may even exceed 100 mM. Yet because glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter, the concentration of this amino acid in the cerebral extracellular fluid must be kept low—typicall ...
purification and properties of glutamate dehydrogenase from the
... purified 500-fold to a final specific activity of 37.5/~mol NADH utilized/min mg- 1 protein. The enzyme is a hexamer of tool. wt 350,000 _+ 30,000 and subunit size 57,000 _+ 5000. Both nicotinamide coenzymes were utilized with activity ratios, NADH/NADPH, of 3.5 at pH 6.75 and 11 at pH 7.5; NAD/NADP ...
... purified 500-fold to a final specific activity of 37.5/~mol NADH utilized/min mg- 1 protein. The enzyme is a hexamer of tool. wt 350,000 _+ 30,000 and subunit size 57,000 _+ 5000. Both nicotinamide coenzymes were utilized with activity ratios, NADH/NADPH, of 3.5 at pH 6.75 and 11 at pH 7.5; NAD/NADP ...
Invulnerability of retinal ganglion cells to NMDA excitotoxicity
... receptors. These receptors are encoded by at least six gene families: a single family for AMPA receptors (GluR1, 2, 3, 4), two for kainate (GluR5, 6, 7 and KA1, 2), and three for NMDA (NR1, NR2A, B, C, D, and NR3A, B) (Dingledine et al., 1999). These subunits combine into multimeric complexes to for ...
... receptors. These receptors are encoded by at least six gene families: a single family for AMPA receptors (GluR1, 2, 3, 4), two for kainate (GluR5, 6, 7 and KA1, 2), and three for NMDA (NR1, NR2A, B, C, D, and NR3A, B) (Dingledine et al., 1999). These subunits combine into multimeric complexes to for ...
Indexing Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Flux in Intact Hearts by Carbon
... magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy with 13Cenriched substrates. Together they can be exploited to repetitively and nondestructively quantify the time course of the appearance of labeled carbon nuclei within intracellular metabolite pools in intact organs, animals, or humans. Such an approach has ...
... magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy with 13Cenriched substrates. Together they can be exploited to repetitively and nondestructively quantify the time course of the appearance of labeled carbon nuclei within intracellular metabolite pools in intact organs, animals, or humans. Such an approach has ...
[Ca2+]c dynamics in spontaneously firing dopamine neurons of the
... was affected by the spontaneous firing rate. In the presence of the Na+ channel antagonist, TTX (0.5 µM), glutamate increased [Ca2+]c by activating different glutamate receptors depending on the glutamate concentration used. Addition of glutamate at low concentrations (<3 µM) raised [Ca2+]c mainly b ...
... was affected by the spontaneous firing rate. In the presence of the Na+ channel antagonist, TTX (0.5 µM), glutamate increased [Ca2+]c by activating different glutamate receptors depending on the glutamate concentration used. Addition of glutamate at low concentrations (<3 µM) raised [Ca2+]c mainly b ...
Metabolism of [14C]glutamate and [14C]glutamine by
... deamination of the amino acids. In preliminary experiments the mycelium was fed with both the 14Csource and the inhibitor (MSX or AZA), thus blocking the uptake system(s) for amino acids competitively. Under these conditions, the level of radioactivity recovered in the amino acid fraction of the myc ...
... deamination of the amino acids. In preliminary experiments the mycelium was fed with both the 14Csource and the inhibitor (MSX or AZA), thus blocking the uptake system(s) for amino acids competitively. Under these conditions, the level of radioactivity recovered in the amino acid fraction of the myc ...
Ionized Intracellular Calcium Concentration Predicts Excitotoxic
... calcium (Choi, 1987; Rothman et al., 1987). Studies with radioactive 45Ca 21 isotope demonstrated substantial calcium entry during toxic NMDA receptor activation but much lower 45C a 21 influx during nonlethal AMPA treatment (Marcoux et al., 1988; Hartley et al., 1993; Eimerl and Schramm, 1994; Lu e ...
... calcium (Choi, 1987; Rothman et al., 1987). Studies with radioactive 45Ca 21 isotope demonstrated substantial calcium entry during toxic NMDA receptor activation but much lower 45C a 21 influx during nonlethal AMPA treatment (Marcoux et al., 1988; Hartley et al., 1993; Eimerl and Schramm, 1994; Lu e ...
NMDA Receptor Function and Physiological Modulation
... continuous presence of agonist, a process referred to as desensitization. Three different types of desensitization have been reported for NMDA receptors, a glycine-sensitive, a glycine-insensitive, and a calciumdependent type. The glycine-sensitive desensitization refers to the transition of the NMD ...
... continuous presence of agonist, a process referred to as desensitization. Three different types of desensitization have been reported for NMDA receptors, a glycine-sensitive, a glycine-insensitive, and a calciumdependent type. The glycine-sensitive desensitization refers to the transition of the NMD ...
Glutamate Controls the Induction of GABA
... spontaneous GDPs with GABA (20 mM) or AMPA (5 mM) and to evoke GDPs by focal stimulation. The effect of AMPA was usually associated to a 5- to 12-mV membrane depolarization. Both GDPs as well as membrane depolarization disappeared when AMPA was applied in the presence of bicuculline (10 mM, data not ...
... spontaneous GDPs with GABA (20 mM) or AMPA (5 mM) and to evoke GDPs by focal stimulation. The effect of AMPA was usually associated to a 5- to 12-mV membrane depolarization. Both GDPs as well as membrane depolarization disappeared when AMPA was applied in the presence of bicuculline (10 mM, data not ...
Glutamate Decreases Mitochondrial Size and Movement in Primary
... potential may impede the movement of mitochondria. Exposure of neurons to 30 M glutamate with 1 M glycine produced a somewhat different response. Although the mitochondria clearly stopped moving within 2– 4 min of glutamate application, we also noted a profound alteration in mitochondrial morpholo ...
... potential may impede the movement of mitochondria. Exposure of neurons to 30 M glutamate with 1 M glycine produced a somewhat different response. Although the mitochondria clearly stopped moving within 2– 4 min of glutamate application, we also noted a profound alteration in mitochondrial morpholo ...
Receptor Activation and Homer Differentially Control the Lateral
... receptor (between the Ser-22 and Ser-23 codons of mGluR5a, amino acid 1 being the initiating methionine) or just before the stop codon for the C -terminal epitope-tagged receptor, using a PCR overlap extension method. Sense and antisense oligonucleotides coding the c-myc epitope (TREQK LISEEDL AR) w ...
... receptor (between the Ser-22 and Ser-23 codons of mGluR5a, amino acid 1 being the initiating methionine) or just before the stop codon for the C -terminal epitope-tagged receptor, using a PCR overlap extension method. Sense and antisense oligonucleotides coding the c-myc epitope (TREQK LISEEDL AR) w ...
glial versus neuronal uptake of glutamate
... inputs to the hippocampus were shown in autoradiographic studies to be localized in the known target areas of these projections (Storm-Mathisen, 1977). Aspartate is taken up by a high-affinity transport system which appears to be the same as that for glutamate and therefore cannot be distinguished i ...
... inputs to the hippocampus were shown in autoradiographic studies to be localized in the known target areas of these projections (Storm-Mathisen, 1977). Aspartate is taken up by a high-affinity transport system which appears to be the same as that for glutamate and therefore cannot be distinguished i ...
Diabetes & The Endocannabinoid System: Prospects For
... and insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells”. Cell Calcium 39: 155-162. Kalia, K., et al. 2004. “Non-enzymatic glycosylation of immunoglobulins in diabetic nephropathy”. Clinica Chimica Acta 347: 169-176. Li, X., et al. 2001. “Examination of the immunosuppressive effect of delta-9-THC in streptozoto ...
... and insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells”. Cell Calcium 39: 155-162. Kalia, K., et al. 2004. “Non-enzymatic glycosylation of immunoglobulins in diabetic nephropathy”. Clinica Chimica Acta 347: 169-176. Li, X., et al. 2001. “Examination of the immunosuppressive effect of delta-9-THC in streptozoto ...
Glutamate Dehydrogenases: Enzymology, Physiological
... noteworthy that because of its overall high Km for ammonium, this reaction can only be used for the synthesis of glutamate when the ammonium concentration is high (>1 mM). When the ammonium concentration is lower, ammonia is incorporated to glutamate mainly via the GS-GOGAT pathway. Generally, GDH a ...
... noteworthy that because of its overall high Km for ammonium, this reaction can only be used for the synthesis of glutamate when the ammonium concentration is high (>1 mM). When the ammonium concentration is lower, ammonia is incorporated to glutamate mainly via the GS-GOGAT pathway. Generally, GDH a ...
Glutamine and glutamate—their central role in cell metabolism and
... Glucose is widely accepted as the primary nutrient for maintenance and promotion of cell function. However, we propose that the 5-carbon amino acids, glutamine and glutamate, should be considered to be equally important for maintenance and promotion of cell function. The functions of glutamine are m ...
... Glucose is widely accepted as the primary nutrient for maintenance and promotion of cell function. However, we propose that the 5-carbon amino acids, glutamine and glutamate, should be considered to be equally important for maintenance and promotion of cell function. The functions of glutamine are m ...
Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Steroid Receptors
... the 5’ flanking region of the collagenase gene. However, DNA footprinting studies show that AP-1 still DOES bind the AP-1 site during GR-induced inhibition of AP-1 stimulated transcription. GR may inhibit transcriptional activation by AP-1 once bound to the site. ...
... the 5’ flanking region of the collagenase gene. However, DNA footprinting studies show that AP-1 still DOES bind the AP-1 site during GR-induced inhibition of AP-1 stimulated transcription. GR may inhibit transcriptional activation by AP-1 once bound to the site. ...
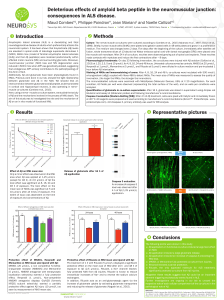
Deleterious effects of amyloid beta peptide in the neuromuscular
... Pre-treatment of 1 h with Riluzole (5 µmol/L) displayed a significant protective effect on the mean size of NMJ after 24 h and 48 h of exposure to Aβ (2,5 µmol/L). Riluzole, a Na+ channel blocker, fully protected NMJ from Aβ injuries. Riluzole is known to reduce intracellular increases of Na+ and to ...
... Pre-treatment of 1 h with Riluzole (5 µmol/L) displayed a significant protective effect on the mean size of NMJ after 24 h and 48 h of exposure to Aβ (2,5 µmol/L). Riluzole, a Na+ channel blocker, fully protected NMJ from Aβ injuries. Riluzole is known to reduce intracellular increases of Na+ and to ...
Glutamate receptor

Glutamate receptors are synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system and especially prominent in the human brain where it is the body's most prominent neurotransmitter, the brain's main excitatory neurotransmitter, and also the precursor for GABA, the brain's main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Glutamate receptors are responsible for the glutamate-mediated postsynaptic excitation of neural cells, and are important for neural communication, memory formation, learning, and regulation.Glutamate receptors are implicated in a number of neurological conditions. Their central role in excitotoxicity and prevalence in the central nervous system has been linked or speculated to be linked to many neurodegenerative diseases, and several other conditions have been further linked to glutamate receptor gene mutations or receptor autoantigen/antibody activity.







![[Ca2+]c dynamics in spontaneously firing dopamine neurons of the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003492398_1-2708bc56966b4cab721b0073b5bc49ec-300x300.png)
![Metabolism of [14C]glutamate and [14C]glutamine by](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002383503_1-555972945f32c24447774c3be1b0f14a-300x300.png)