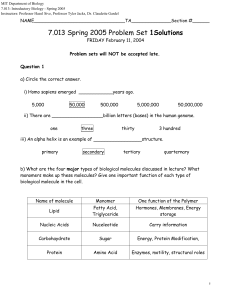
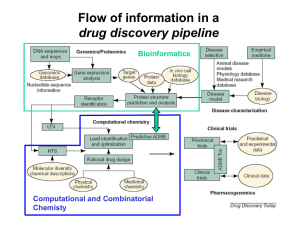
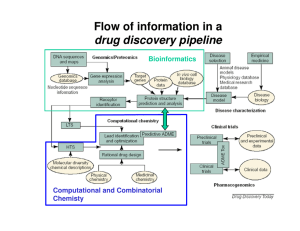
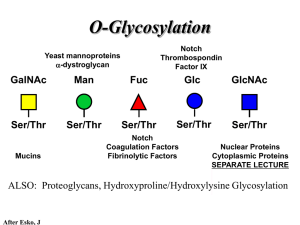
Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 1
... peptide bonds after tyrosine or phenylalanine. a) Enzyme E is the product of gene G that encodes a protein with the molecular weight of 50 kilodaltons (50 kD). When purify enzyme E, only the expected polypeptide is present. However, active enzyme E has a molecular weight of 250 kilodaltons (250 kD), ...
... peptide bonds after tyrosine or phenylalanine. a) Enzyme E is the product of gene G that encodes a protein with the molecular weight of 50 kilodaltons (50 kD). When purify enzyme E, only the expected polypeptide is present. However, active enzyme E has a molecular weight of 250 kilodaltons (250 kD), ...
7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 1Solutions
... transmembrane region of the receptor? Circle these amino acids and briefly explain your reasoning below. The circled amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that reside within the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. When a “LIGAND” binds to the extracellular domain of the receptor, a conformation ...
... transmembrane region of the receptor? Circle these amino acids and briefly explain your reasoning below. The circled amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that reside within the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. When a “LIGAND” binds to the extracellular domain of the receptor, a conformation ...
Identification and Cloning of a Cryptococcal Deacetylase That
... Therefore, thè Identification of cryptococcal antigens capable of producing T-cell-mediated responses, sudi as delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reactions, may be useful in thè development of immune-based strategies to contro! cryptococcosis. In order to characterize DTH-producing antigens, cultur ...
... Therefore, thè Identification of cryptococcal antigens capable of producing T-cell-mediated responses, sudi as delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reactions, may be useful in thè development of immune-based strategies to contro! cryptococcosis. In order to characterize DTH-producing antigens, cultur ...
procite - UWI St. Augustine
... with the cell surface membrane [4]. Proteins known to contain a Gla domain are listed below: - A number of plasma proteins involved in blood coagulation. These proteins are prothrombin, coagulation factors VII, IX and X, proteins C, S, and ...
... with the cell surface membrane [4]. Proteins known to contain a Gla domain are listed below: - A number of plasma proteins involved in blood coagulation. These proteins are prothrombin, coagulation factors VII, IX and X, proteins C, S, and ...
ATP– and ADP–DnaA protein, a molecular switch in gene regulation
... little effect on the regulation of dnaA (Smith et al., 1997). In order to define whether this lack of repression was due to the ADP–DnaA/ATP–DnaA switch, we analyzed a DNA fragment containing ATP–DnaA boxes a, b, c and DnaA boxes 1 and 2 in the BIAcore. Binding of ATP– and ADP–DnaA protein to a wild ...
... little effect on the regulation of dnaA (Smith et al., 1997). In order to define whether this lack of repression was due to the ADP–DnaA/ATP–DnaA switch, we analyzed a DNA fragment containing ATP–DnaA boxes a, b, c and DnaA boxes 1 and 2 in the BIAcore. Binding of ATP– and ADP–DnaA protein to a wild ...
A STUDY OF THE ROLES OF SELECTED ARGININE AND
... Thrombin-activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFI) is a 60 kDa plasma protein that can be activated to the enzyme, TAFIa, by thrombin, plasmin or trypsin. TAFIa is a carboxypeptidase B-like enzyme that attenuates fibrinolysis. Thrombomodulin (TM) is a cofactor which increases the overall efficiency ...
... Thrombin-activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFI) is a 60 kDa plasma protein that can be activated to the enzyme, TAFIa, by thrombin, plasmin or trypsin. TAFIa is a carboxypeptidase B-like enzyme that attenuates fibrinolysis. Thrombomodulin (TM) is a cofactor which increases the overall efficiency ...
Identification and first characterization of pairing
... risk (Ross et al., 2012). Besides the resulting and underestimated socio economic importance (King, 2010), schistosomes are also of basic economic relevance as they can infect animals as well (Quack et al., 2006; DeBont & Vercruysse, 1998). Pathology is not induced by adult worms, but by eggs. One f ...
... risk (Ross et al., 2012). Besides the resulting and underestimated socio economic importance (King, 2010), schistosomes are also of basic economic relevance as they can infect animals as well (Quack et al., 2006; DeBont & Vercruysse, 1998). Pathology is not induced by adult worms, but by eggs. One f ...
two types of titin interactions lead to an asymmetrical sorting of actinin
... 2A isoform are given above each construct. (C) The interaction of α-actinin and titin was mapped on titin by successive deletions of the Zq–Z4 bait. Interaction of the deletion constructs with the smallest α-actinin-fragment R2–R3 shown to interact above was tested in the two-hybrid system. The dele ...
... 2A isoform are given above each construct. (C) The interaction of α-actinin and titin was mapped on titin by successive deletions of the Zq–Z4 bait. Interaction of the deletion constructs with the smallest α-actinin-fragment R2–R3 shown to interact above was tested in the two-hybrid system. The dele ...
Cytochrome P450 and Polymorphism - uni
... (CAR) is found in the cytoplasm and dimerizes with PXR in the nucleus. Analog to PXR, the CYP2B gene is regulated. Likewise high sequence homology has been found for the vitamine D receptor (VDR) that regulates CYP27, and for the arylhydrocarbon receptor (AHR) (dioxin receptor). ...
... (CAR) is found in the cytoplasm and dimerizes with PXR in the nucleus. Analog to PXR, the CYP2B gene is regulated. Likewise high sequence homology has been found for the vitamine D receptor (VDR) that regulates CYP27, and for the arylhydrocarbon receptor (AHR) (dioxin receptor). ...
CYP 2D6 Polymorphism
... CYP 2C19 individuals with inactive enzyme (3-6 % of the caucasian and 15-20 % of the asian population) CYP 2D6 poor metabolizers in 5-8 % of the european, 10 % of the caucasian, and <1% of the japanese population. Over expression (gene duplication) among parts of the african and oriental population. ...
... CYP 2C19 individuals with inactive enzyme (3-6 % of the caucasian and 15-20 % of the asian population) CYP 2D6 poor metabolizers in 5-8 % of the european, 10 % of the caucasian, and <1% of the japanese population. Over expression (gene duplication) among parts of the african and oriental population. ...
Matching catalytic activity to developmental function: Tolloid
... al., 2003). Each family member has a highly similar structure containing an astacin-like protease domain followed by CUB protein-protein interaction domains that are interspersed with EGF-like motifs (Bond and Beynon, 1995). These proteases are synthesized as pro-enzymes that are activated upon remo ...
... al., 2003). Each family member has a highly similar structure containing an astacin-like protease domain followed by CUB protein-protein interaction domains that are interspersed with EGF-like motifs (Bond and Beynon, 1995). These proteases are synthesized as pro-enzymes that are activated upon remo ...
REGULATION OF CYTOCHROME P450 BY
... Cytochrome P450s are a family of enzymes represented in all kingdoms with expression in many species. Over 3,000 enzymes have been identified in nature. Humans express 57 putatively functional enzymes with a variety of critical physiological roles. They are involved in the metabolic oxidation, perox ...
... Cytochrome P450s are a family of enzymes represented in all kingdoms with expression in many species. Over 3,000 enzymes have been identified in nature. Humans express 57 putatively functional enzymes with a variety of critical physiological roles. They are involved in the metabolic oxidation, perox ...
Plasma Gelsolin
... Abstract: Gelsolin is a highly conserved, multifunctional actin-binding protein initially described in the cytosol of macrophages and subsequently identified in many vertebrate cells. A unique property of gelsolin is that in addition to its widely recognized function as a cytoplasmic regulator of ac ...
... Abstract: Gelsolin is a highly conserved, multifunctional actin-binding protein initially described in the cytosol of macrophages and subsequently identified in many vertebrate cells. A unique property of gelsolin is that in addition to its widely recognized function as a cytoplasmic regulator of ac ...
University of Groningen Polymerization of the bacterial cell division
... the β- and γ-phosphates (only the α-tubulin structure contains GTP, both FtsZ and β-tubulin structures contain GDP) and contains conserved Asn and Asp residues (in E. coli FtsZ, N43 and D45, respectively). The Asp residue may be involved in the co-ordination of the Mg2+ ion at the nucleotide-binding ...
... the β- and γ-phosphates (only the α-tubulin structure contains GTP, both FtsZ and β-tubulin structures contain GDP) and contains conserved Asn and Asp residues (in E. coli FtsZ, N43 and D45, respectively). The Asp residue may be involved in the co-ordination of the Mg2+ ion at the nucleotide-binding ...
Collagen Diversity, Synthesis and Assembly
... characterized by the repeating amino acid motif (Gly-X-Y), where X and Y can be any amino acid. This motif allows the chains to form a right-handed triple-helical structure (Fig. 2.1), with all glycine residues buried within the core of the protein, and residues X and Y exposed on the surface. Depen ...
... characterized by the repeating amino acid motif (Gly-X-Y), where X and Y can be any amino acid. This motif allows the chains to form a right-handed triple-helical structure (Fig. 2.1), with all glycine residues buried within the core of the protein, and residues X and Y exposed on the surface. Depen ...
Calreticulin, a multi-process calcium
... The C-domain of calreticulin is of special interest because it contains a large number of negatively charged residues that are responsible for the Ca2+ -buffering function of the protein. It binds over 50 % of ER luminal Ca2+ [21] with high capacity (25 mol of Ca2+ per mol of protein) and low affini ...
... The C-domain of calreticulin is of special interest because it contains a large number of negatively charged residues that are responsible for the Ca2+ -buffering function of the protein. It binds over 50 % of ER luminal Ca2+ [21] with high capacity (25 mol of Ca2+ per mol of protein) and low affini ...
Functional Interactions Between the Subunits of the Lactose
... observed during lactose accumulation driven by the proton motive force (∆p), but not for the lactose exchange mode of transport. Within a LacS subunit, two domains can be discerned. The N-terminal membrane-embedded carrier domain catalyzes the translocation event. The C-terminal hydrophilic LacS-IIA ...
... observed during lactose accumulation driven by the proton motive force (∆p), but not for the lactose exchange mode of transport. Within a LacS subunit, two domains can be discerned. The N-terminal membrane-embedded carrier domain catalyzes the translocation event. The C-terminal hydrophilic LacS-IIA ...
Receptor-like activity evoked by extracellular ADP in Arabidopsis
... (αßATP) and ADP. All these were inhibited by Gd3+ and the purinoceptor antagonist, suramin (Demidchik et al., 2009). AMP (as an ADP breakdown product) up to 1 mM has been shown to be ineffective (Demidchik et al., 2009). A test concentration of 0.1 mM ADP was used in the present study as it is a fea ...
... (αßATP) and ADP. All these were inhibited by Gd3+ and the purinoceptor antagonist, suramin (Demidchik et al., 2009). AMP (as an ADP breakdown product) up to 1 mM has been shown to be ineffective (Demidchik et al., 2009). A test concentration of 0.1 mM ADP was used in the present study as it is a fea ...
Ca2+-Dependent Regulations and Signaling in Skeletal Muscle
... handling, and like CASQ, also serves as a Ca2+ buffering molecule in the SR [17]. However, SAR has been shown to be phosphorylated and to modulate the activity of the junctional ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) channel complex and thereby also Ca2+ release characteristics [18]. SAR supports proper Ca2+ r ...
... handling, and like CASQ, also serves as a Ca2+ buffering molecule in the SR [17]. However, SAR has been shown to be phosphorylated and to modulate the activity of the junctional ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) channel complex and thereby also Ca2+ release characteristics [18]. SAR supports proper Ca2+ r ...
npr review - Olivamine
... indirect molecular targets. These targets modulated by curcumin can be upregulated or downregulated depending upon the target. Included among these molecular targets are transcription factors, enzymes, inflammatory mediators, protein kinases, drug resistance proteins, cell-cycle regulatory proteins, ...
... indirect molecular targets. These targets modulated by curcumin can be upregulated or downregulated depending upon the target. Included among these molecular targets are transcription factors, enzymes, inflammatory mediators, protein kinases, drug resistance proteins, cell-cycle regulatory proteins, ...
Understanding the Regulation of Metabolic Enzyme Acetylation in E
... Global protein acetylation is a newly discovered phenomenon in bacteria. Of the more than 250 acetylations reported in E. coli, many are of metabolic enzymes [1-3]. Thus, acetylation could represent a novel posttranslational mechanism of metabolic control. Yet, almost nothing is known about the regu ...
... Global protein acetylation is a newly discovered phenomenon in bacteria. Of the more than 250 acetylations reported in E. coli, many are of metabolic enzymes [1-3]. Thus, acetylation could represent a novel posttranslational mechanism of metabolic control. Yet, almost nothing is known about the regu ...
Structure-Function Analysis of SH3 Domains: SH3
... family protein tyrosine kinases (13, 14). This domain mediates protein-protein interactions that are important for coupling of intracellular signaling pathways, regulation of catalytic activity of proteins, recruitment of substrates to enzymes, and localization of proteins to a specific subcellular ...
... family protein tyrosine kinases (13, 14). This domain mediates protein-protein interactions that are important for coupling of intracellular signaling pathways, regulation of catalytic activity of proteins, recruitment of substrates to enzymes, and localization of proteins to a specific subcellular ...
Advances in Chemical Protein Modification
... examples of the next generation of Lys modifications are depicted in Scheme 2. A highly selective Lys modification protocol, based on the rapid 6π-aza-electrocyclization reaction, has been successfully developed by Tanaka and Fukase (Scheme 2a).27 The efficiency of this procedure depends on the accessib ...
... examples of the next generation of Lys modifications are depicted in Scheme 2. A highly selective Lys modification protocol, based on the rapid 6π-aza-electrocyclization reaction, has been successfully developed by Tanaka and Fukase (Scheme 2a).27 The efficiency of this procedure depends on the accessib ...
Ser/Thr
... • Major extracellular vertebrate O-glycan • Begins in cis-Golgi by attachment of GalNAc in alinkage to specific Ser/Thr residues • Assembly is simpler than Nlinked chains - no lipid intermediate is used • Always involves nucleotide sugars • Always occurs by addition to non-reducing terminus or by br ...
... • Major extracellular vertebrate O-glycan • Begins in cis-Golgi by attachment of GalNAc in alinkage to specific Ser/Thr residues • Assembly is simpler than Nlinked chains - no lipid intermediate is used • Always involves nucleotide sugars • Always occurs by addition to non-reducing terminus or by br ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).