* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
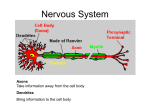
Chapter 15/16 - The Nervous System: Organization Divisions of the Vertebrate Nervous System • The central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the nerves and ganglia. (Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS.) CONT’D Somatic Nervous System • The somatic nervous system provides conscious, voluntary control. • It includes all of the nerves that serve the skeletal muscles and the exterior sense organs. Reflex Arc http://www.brainviews.com/abFiles/AniPatellar.htm Autonomic Nervous System CLASSES OF NEURONS • Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct sensory information toward the CNS. Sensory neurons have a long dendrite and a short axon. • The brain and spinal cord contain interneurons. These receive information and if they are sufficiently stimulated, they stimulate other neurons. • Motor neurons (efferent neurons) send information from interneurons to muscle or gland cells (effectors). Neurons STRUCTURE • Cell Body- contains nucleus and organelles • Dendrites- receive input • Axon -conducts impulses away from the cell body • Axon Terminals - Neurotransmitters are manufactured in the cell body but released from axon terminals. The neurotransmitters stimulate other neurons. CONT’D Nerves and Ganglia • Axons and dendrites are bundled with axons or dendrites from other neurons to form nerves. • Clusters of neuron cell bodies are called ganglia. SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP NEURON MEMBRANE ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic cell responds with an action potential. http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/neurotrans.htm l Synaptic integration Temporal and Spatial Summation • The effect of more than one synaptic potential arriving at a neuron is additive if the time span between the stimuli is short. This is called temporal summation. • The effect of more than one synaptic potential arriving at a given region of a neuron can also be additive. This is called spatial summation. Synaptic Transmission Central Nervous System • The central nervous system is the brain and spinal cord. • It is wrapped in 3 layers of membranes called meninges. Meningitis is an infection of these coverings. • The brain contains fluid-filled ventricles that are continuous with the central canal of the cord. The Spinal Cord The Brain …Hopefully not yours http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/brainanatomy.swf Regions of Disease and Disorders Lobes of the cerebral cortex Summary Lobe Function Frontal motor functions; permits conscious control of skeletal muscles; contains the primary motor cortex conscious thought Parietal sensory areas from the skin; contains the primary sensory cortex Occipital The primary visual cortex is located within the occipital lobe. Temporal hearing and smell Parts of the Brain Summary of Brain Structure Brain Structure Function Medulla oblongata Vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure Reflexes such as vomiting, coughing, sneezing, hiccupping, swallowing, and digestion Neurons cross Pons Breathing, connects spinal cord, cerebellum and higher brain centers Cerebellum Motor coordination Midbrain Receives visual, auditory, and tactile information In mammals, this information is sent to the thalamus and higher brain centers. In lower vertebrates, the information is further processed in the midbrain. Thalamus Relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex. Contains part of the reticular formation (controls arousal). Hypothalamus Maintains homeostasis, regulates the endocrine system Contains part of the Limbic system (controls emotion) Cerebrum Processes sensory information and produces signals that move the skeletal muscles. Cerebral Cortex This is the outer layer of the cerebrum. Thinking, intelligence, and cognitive functions are located here. Processing of sensory information and motor responses