* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
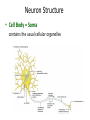
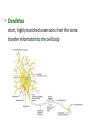
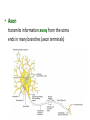
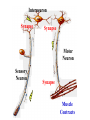
Intro to the Nervous System Chapter 12 The Nervous System • The most complex system • Coordinates activities of all body systems • Two divisions: The Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain & spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = all neural tissue not included in CNS Histology of Nervous Tissue 2 cell types: • Neurons transmit nerve impulses • Neuroglia: support neurons Neurons • Very long lived • Amitotic mature neurons lose the ability to divide • High metabolic rate need a large supply of O2 and C6H12O6 Neuron Structure • Cell Body = Soma contains the usual cellular organelles • Dendrites short, highly branched extensions from the soma transfer information to the cell body • Axon transmits information away from the soma ends in many branches (axon terminals) • Action potentials (nerve impulses) start at the axon hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron • Myelin sheath = lipid-rich covering on axons, myelinated fibers conduct impulses 10-150x faster than unmyelinated fiber Nodes of Ranvier = gaps between myelin; impulses jump from node to node Functions of the Nervous System • Sensory Input Sensory neurons deliver info (stimulus) from sensory receptors to the CNS • Integration Interneurons in the CNS process & interpret sensory stimulus • Motor Output Motor neurons cause response by carrying info from the CNS to various effector organs Interneuron Synapse Synapse Motor Neuron Sensory Neuron Synapse Muscle Contracts NERVES Nerves = bundles of neurons • Can contain all motor neurons, all sensory neurons, or be mixed