* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neural Pathways
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
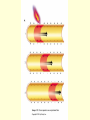
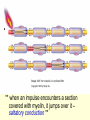
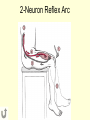
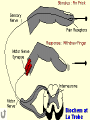
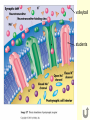
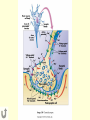
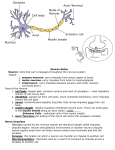
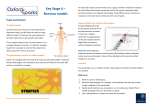
Neural Pathways • information is carried via chains of neurons • neurons secrete chemicals that cause changes in adjacent neurons • chemicals travel between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another Nerve Impulses (Action Potentials) • routes traveled by nerve impulses are called neural pathways • one type of neural pathway is a reflex arc • the simplest and quickest • consists only of 2 neurons • bypasses the brain impulse generated by stimulus -pres., temp., chem. changes dendrites of sensory neuron axon of sensory neuron synapse (space b/w 2 neurons) -chemical signals sent across gap dendrites of motor neuron axon of motor neuron synapse effector organ -muscle that puts nerve signals into effect reflex (quick, jerky response) How Do Impulses Travel? -like a spark along a fuse, or like a volleyball :) 1. membrane of the neurons has a positive charge on the outside (excess Na+) and a negative charge on the inside 2. when stimulated, Na+ channels open temporarily becomes + and and Na+ rushes in -inside outside 3. channels then automatically close very quickly, but this causes the neighboring channels to open 4. it proceeds like a wave along the membrane to the tip of the axon 5. then it arrives at the synapse ** when an impulse encounters a section covered with myelin, it jumps over it – saltatory conduction ** What Happens When an Impulse Arrives at a Synapse? Synapse • where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another (empty space) 1. when an impulse reaches the synaptic -of the knob, neurotransmitters are released presynaptic into the synaptic cleft neuron -from vesicles 2. neurotransmitters initiate an impulse in the postsynaptic neuron and will then cause the Na+ channels to open in that neuron (excite) -by binding to the proteins 3. the impulse will continue thru the axon ** some neurotransmitters may inhibit the impulse (stop conduction) and NOT open up the Na+ channels** Examples of Neurotransmitters 1. Endorphins • inhibit conduction of pain impulses -release of these increases during exercise 2. Serotonin, Norepinephrine, Dopamine • conduct pleasurable impulses • if there is a serotonin deficiency, may lead to depression • serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s) -blocks the uptake of serotonin back into presynaptic knob 2-Neuron Reflex Arc volleyball students