* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons - edl.io
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
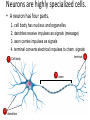
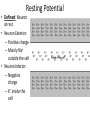
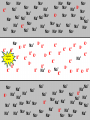
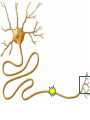
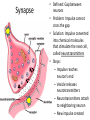
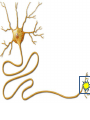
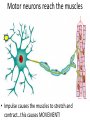
Neurons Neurons are highly specialized cells. • A neuron has four parts. 1. cell body has nucleus and organelles 2. dendrites receive impulses as signals (message) 3. axon carries impulses as signals 4. terminal converts electrical impulses to chem. signals terminal 4 1 Cell body 3 axon 2 dendrites Resting Potential • Defined: Neuron at rest • Neuron Exterior: – Positive charge – Mainly Na+ outside the cell • Neuron Interior: – Negative charge – K+ inside the cell Action Potentional • Defined: a moving electrical impulse. – generated by a stimulus. – Na+ enters, and cell becomes + charged. – K+ leaves, and area of + charge moves. imp ulse Na+ Na+ + + + Na Na Na + + + + + + K+ Na Na Na Na + Na Na Na + K + Na Na + + + + + Na+ K Na Na + + Na Na Na Na Na+Na+ Na+ + + + + + Na Na + + + Na Na Na + K Na Na + + Na + Na Na Na Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ Na K+ K+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ + + K K K+ negative + impulse + Na + K+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ K++ Na K+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+Na+ Na+ + Na+ Na+ Na + Na + + Na+ Na Na+ Na+ Na Na+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ K+ +Na Na K+ + Na+ Na+ Na + Na Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ + Na+ Na+ Synapse • Defined: Gap between neurons • Problem: Impulse cannot cross the gap • Solution: Impulse converted into chemical molecules that stimulate the next cell, called neurotransmitters • Steps: – Impulse reaches neuron’s end – Vesicle releases neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters attach to neighboring neuron – New impulse created Impulse stimulates a vesicle, which contains neurotransmitters Vesicle exits the cell and dissolves impul se End of one cell Start of another cell Neurotransmitters stimulate a new impulse Neurotransmitters cross the synapse and attach to receptors of a neighboring neuron imp ulse End of one cell imp ulse Start of another cell Brain Feet Motor neurons reach the muscles • Impulse causes the muscles to stretch and contract…this causes MOVEMENT!