* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 35.2
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
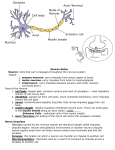
Ch. 35.2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Nearly all multicellular organisms have communication systems Specialized cells carry messages from one cell to another. NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTROLS AND COORDINATES FUNCTIONS THROUGHOUT THE BODY AND RESPONDS TO INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL STIMULI Neurons Electrical signals are called impulses NEURONS cells that transmit the electrical impulses SENSORY: impulses from sense organs to spinal cord and brain INTERNEURONS: connect sensory ad motor neurons Neuron Structure Largest part is the CELL BODY contains the nucleus and cytoplasm Metabolic activity takes place in the cell body Short, branched extensions DENDRITES carry impulses from the environment or other neurons TOWARD the cell body Long fibers AXON carry impulses AWAY from the cell body Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together Some neurons are surrounded by an insulated layer MYELIN SHEATH The Nerve Impulse Nerve impulse is like electricity through a wire Sodium/potassium pump ions diffuse across the cell membrane Builds up charges and creates a RESTING POTENTIAL Moving Impulse Nerve impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by its environment The protein channels help ions pass in and out of the cell When positive ions flow in, gains a positive charge an then switches to a negative charge ACTION POTENTIAL One impulse causes another impulse at the next point on the membrane Threshold Strength of impulse is always the same Minimum level of a stimulus that is required to activate a neuron is THRESHOLD The Synapse Neurons make contact with other cells at the axon terminal Neuron transfer impulses to another cell is a SYNAPSE NEUROTRASMITTERS chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell