* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System Functions
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
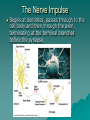
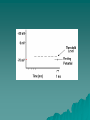
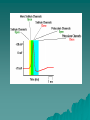
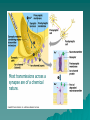
Body Systems Nervous System Nervous System Functions Sensory input – sense organs, receptors, – afferent neurons Integration – Central Nervous System(CNS) – interneurons Motor output – glands, muscles – efferent neurons The Neuron Consists of –Cell body –Dendrite –Axon Label your diagram The Nerve Impulse Begins at dendrites, passes through to the cell body and then through the axon, terminating at the terminal branches before the synapse. The Nerve Impulse Occurs as a result of both electrical and chemical changes across the membrane of the neuron. Electrochemical nature of membrane Due to the presence of ions, a positive electrical charge is present outside the membrane. (excess of sodium ions) A negative charge is present inside the membrane. (mostly potassium ions) Since both sodium (outside) and potassium (inside) are both positive ions, how can one side of the membrane be + and the other -? Although diffusion of ions will occur, the membrane actively pumps Na+/K+. What do you call the membrane structures through which the ions will be pumped through? Resting potential- unstimulated (-70 millivolts) Action potential – channels open, Na+ ions rush in, depolarization occurs. What is the threshold potential? Like a domino effect, once stimulated the nerve impulse is an all or nothing response. Repolarization – In response to the inflow of Na+, K+ rushes out of the cell, followed by closing of the Na+ channel gates. Interpret the graph at stage 4 with respect to the events that are occurring. Hyperpolarization – More K+ outflows than is necessary, thus undershooting threshold, more than repolarizing the membrane. Refractory period – Although repolarized, the neuron has a period when it is unable to fire. What has to occur to re-establish the original conditions so that a neuron can fire again? After the membrane Once the impulse reaches the end of the axon a different set of events has to occur to allow the impulse to continue to another neuron. This requires the crossing of the synapse. Most transmissions across a synapse are of a chemical nature. Synapse Summary The gated channels for Ca2+ respond to the action potential by opening up. In turn, the Ca2+ enters the cell and triggers the release of neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds with protein receptors on the next neuron membrane. Neurotransmitters degrade or are recycled shortly after so as not to cause continuous stimulation. Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine – stimulates muscles to contract at neuromuscular junctions. At other junctions, acts as an inhibitor. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin (I) – all are amino acid derivatives. Work between neurons. First three may be excitatory or inhibitory. GABA – inhibitory, within the brain. Saltatory Conduction Neurons with a myelin sheath (Schwann cells) allow a much faster conduction of impulses because the impulse “jumps” between the gaps (nodes of Ranvier) of the cells rather than traveling along the whole length of the axon. The Bigger Picture Billions upon billions of neurons and other cells make up your nervous system. Appearance can be somewhat modified based on location and function. CNS – brain, spinal cord Peripheral – all other nerves – Somatic – sensory, motor – Autonomic – sympathetic, parasympathetic You are always on your mind! This diagram illustrates the relative amount of brain mass devoted to some important parts of the body. Why do you think some areas require much more than others?