* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Theta model wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
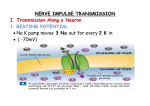
An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet brain A model network To drive from your house to a town hundreds of kilometres away, you will have to travel on many different roads. In order for the road network to function roads have to join up with each other. spinal cord neurons This is a good model of your nervous system. It is a complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses The nervous system There is a small gap where the end of one neuron joins with another. Professor Charles Sherrington, who worked at the University of Oxford in the early 20th century, named this a synapse. Drugs and toxins can interfere with synapses Ecstasy (MDMA) works by increasing the amount of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain. It blocks serotonin re-uptake pumps on the pre-synaptic neuron. High levels of serotonin induces feelings of euphoria. Botulinum toxin (botox) is made by bacteria and causes muscle paralysis by blocking impulses between motor neurons and muscles. It does this by binding to the neurotransmitter receptor on muscles. Your task You are going to use a model to create a stop-capture animation of what happens at a synapse. What to do 1. Work in a pair or small group. 2. Research what happens at a synapse. Use textbooks, the internet and the images supplied on this worksheet. 3. Decide what materials you are going to use to create your model. Plan a simple storyboard for your animation on paper. 4. Use a tablet/phone or camera to create the animation. http://www.oxfordsparks.net/video/youve-got-nerve Motor neuron Close-up of synapse Direction of impulse Muscle cells A diagram to show two neurons and a close-up view of the synapse in between them http://www.oxfordsparks.net/video/youve-got-nerve The connection between a motor neuron and a muscle is known as a neuromuscular junction. Impulses from the neuron are transmitted to the muscle cells by the movement of neurotransmitters across a synapse.