* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PSY 301 – Summer 2004
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
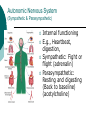
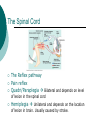
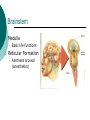
Introduction to Psychology Class 8: Neuroscience 1 Myers: 38-51 June 22, 2006 Biological Psychology A branch of psychology that concerns itself with the links between biology and behavior. Other terms: Behavioral neuroscientist, neuropsychologist, physiological/biopsychologist, behavioral endocrinologist etc. Origins of brain-mind connection Phrenology (1800) Phineas Gage (1848) bumps on skull could reveal mental abilities Iron rod through skull. Changes in personality 1990’s decade of the brain: fMRI, PET The Neuron Parts Dendrites, Body, Axon Hillock, Axon, Myelin sheath, Nodes of Ranvier, Terminal branches, Terminal Buttons, Synaptic cleft Concepts Action Potential, Type of signals, Threshold stimulus, All-or-None response Action Potential Resting Potential (70mv) Depolarization (50mv threshold) Action potential Repolarization (back to neg charge) Hyperpolarizaton The Synapse Cajal Sherrington NT Reuptake Agonists and antagonists Neurotransmitters Overview NERVOUS SYSTEM 3 types of neurons Types of Neurons SENSORY/AFFERENT From the organ to the spinal cord (and brain) MOTOR/EFFERENT From the spinal cord (and brain) to the organ INTERNEURONS In between Autonomic Nervous System (Sympathetic & Parasympathetic) Internal functioning E.g., Heartbeat, digestion, Sympathetic: Fight or flight (adrenalin) Parasympathetic: Resting and digesting (Back to baseline) (acetylcholine) The Spinal Cord The Reflex pathway Pain reflex Quadri/Paraplegia Bilateral and depends on level of lesion in the spinal cord Hemiplegia Unilateral and depends on the location of lesion in brain. Usually caused by stroke. The Brain Evolutionarily evolved Brainstem Limbic System Cortex Brainstem Medulla Basic life functions Reticular Formation Alertness arousal (anesthetics) Cerebellum Cerebellum Fine motor movements Thalamus Atop brainstem Sensory Relay station All 5 senses except for smell Limbic System (all bilateral) Amygdala Hypothalamus Aggression and fear; processing emotional memories Hunger, thirst, body temperature, sexual behavior Controls pituitary gland (master gland) which produced hormones Olds and Milner – pleasure centers Hippocampus Memory consolidation (HM, memento)