* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Bird vocalization wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Substantia nigra wikipedia , lookup
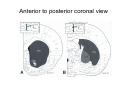
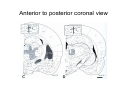
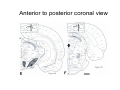
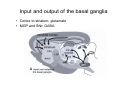
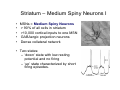
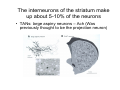
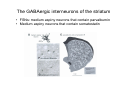
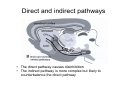
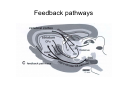
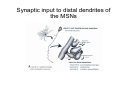
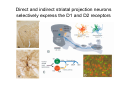
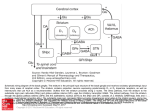
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 [email protected] A small number of neurons… • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating behavior • Essential for several types of learning The cortico-basal ganglia circuits consist of: • Neocortex • The striatum (caudate - putamen and the core of nucleus accumbens) • The globus pallidus (GP) (lateral and medial) • The subthalamic nucleus (STN) • Substantia nigra (SN) (pars compacta and pars reticulata) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) Anterior to posterior coronal view Anterior to posterior coronal view Anterior to posterior coronal view Input and output of the basal ganglia • Cortex to striatum: glutamate • MGP and SNr: GABA The striatum • The major input nucleus of the BG. • Made up of the putamen, the caudate nucleus and nucleus accumbens which have similar histological and anatomical characteristics. • Receive input from most of the cortex (and the thalamus) • Complex bidirectional interaction with the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) • Output to both segments of the globus pallidus (GP) & the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) Striatum – Medium Spiny Neurons I • MSNs = Medium Spiny Neurons • > 90% of all cells in striatum • >10,000 cortical inputs to one MSN • GABAergic projection neurons • Dense collateral network • Two states: – ‘down’ state with low resting potential and no firing – ‘up’ state characterized by short firing episodes. Striatum – Medium Spiny Neurons II • MSNs are typically quiet with no baseline firing. • Sensory and movement related response comprises of a short high frequency burst. • Highly specific to portion of the task and parts of the movement but can respond to several events. • Affected by sequence context or reward contingency. The interneurons of the striatum make up about 5-10% of the neurons • TANs: large aspiny neurons – Ach (Was previously thought to be the projection neuron) The GABAergic interneurons of the striatum • FSNs: medium aspiny neurons that contain parvalbumin • Medium aspiny neurons that contain somatostatin The medial globus pallidus and the SNr • Primarily made up of GABAergic projection neurons. • Firing rate at rest is 60-100 spikes/s and is highly irregular (The ultimate Poissonian neuron). • Sensory and motor response is broad and includes increases and decreases of firing rate. The lateral globus pallidus (GPe) • Same morphology as the MGP • High frequency pausers (HFP) & lowfrequency bursters (LFB) • Internal to the basal ganglia with no external connections for input or output The subthalamic nucleus • Made up mainly of projection neurons. Firing rate at rest is 2030 spikes/s with short burst following movement. • The projection neurons are glutamatergic and send their output to the GPi & SNr. • In addition to its role in the indirect pathway, has direct cortical inputs forming the hyperdirect pathway. Direct and indirect pathways • The direct pathway causes disinhibition • The indirect pathway is more complex but likely to counterbalance the direct pathway Feedback pathways Cortical input to the striatum originates from most cortical areas • Primary and higher order sensory areas, motor, premotor, and prefrontal regions, and limbic cortical areas. • The input is organized topographically – – – – Frontal areas project to rostral striatum Sensorimotor cortex projects to dorsolateral striatum Parietal cortex projects to caudal striatum Highly interconnected cortices may overlap in the striatum • Numbers: – There are 17 million cortico-striatal cells – There are almost 2.8 million striatal projection neurons – No 2 striatal neurons share their cortical input Synaptic input to distal dendrites of the MSNs Inputs to the proximal and distal dendrites of the MSNs Direct and indirect striatal projection neurons selectively express the D1 and D2 receptors Components of the indirect pathway Synaptic inputs to the SNr • The SNc and SNr cannot be distinguished based on the morphological properties of the neurons – Dopaminergic neurons – GABAergic neurons