* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pharm chapter 8 [3-16
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
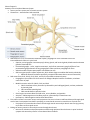
Pharm Chapter 8 Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System Sensory nervous system part of somatic nervous system Piloerection – goose bumps; SNS controlled SNS located in T1-L2; also called thoracolumbar system; preganglionic nerve cell bodies arise from intermediolateral columns in spinal cord o Superior cervical ganglion innervates pupil, salivary glands, and lacrimal glands; blood vessels and sweat glands of head and face o Prevertebral ganglia – celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric ganglia; different from paravertebral ganglia because of long preganglionic fibers and short postganglionic fibers o Adrenal medulla contains postsynaptic neuroendocrine cells o SNS has organ-specific receptor expression, which allows drugs to modulate SNS activity selectively Albuterol dilates bronchioles specifically; metoprolol decreases heart rate and contractility PNS comes from CN III, CN VII, CN IX, CN X, and S2-S4; also called craniosacral system o Preganglionic nerve fibers for CN III come from Edinger-Westphal nucleus of midbrain; stimulates constriction of pupil o Medulla contains nuclei for CN VII, CN IX, and CN X CN VII stimulates salivary secretion by submaxillary and sublingual glands, and tear production by lacrimal gland CN IX stimulates parotid gland CN X extends down to proximal colon o Sacral region innervates distal and mid colon, urinary bladder, and genitalia o Atropine – PNS antagonist used to dilate pupils or systematically increase heart rate o Ipratropium – PNS antagonist used to dilate bronchioles First-order neurons from motor cortex; send projections that cross in lower medulla and descend through spinal cord in lateral corticospinal tract before synapsing on second-order neurons in ventral horns of spinal cord o Projections from second-order neurons exit through ventral roots and join dorsal roots carrying sensory nerve fibers to form spinal nerves Endings of sensory nerves in skin and joints enter through dorsal roots o Neurons for vibration and proprioception ascend through ipsilateral dorsal columns in spinal cord and synapse with secondary neurons in contralateral lower medulla o Sensory neurons for pain and temperature synapse with secondary neurons in posterior horn of spinal cord and cross in spinal cord to ascend in contralateral spinothalamic tract o Both spinothalamic tract and dorsal column tracts connect with third-order neurons in thalamus before reaching somatosensory cortex o Pancuronium – antagonist of neuromuscular junction activity; used to increase paralysis during surgery o Edrophonium and neostigmine increase neuromuscular junction activity; used in diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis (autoimmune disease of decreased skeletal muscle stimulation) Anatomy of the Central Nervous System Midbrain, pons, and medulla collectively called brainstem; connect spinal cord with cerebrum, diencephalon, and cerebellum Cerebral hemispheres contain cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and basal ganglia o Stimulation of part of precentral gyrus induces peripheral motor function; ablation inhibits movement o Barbiturates and benzodiazepines – commonly prescribed hypnotics and sedatives that potentiate action of inhibitory neurotransmitters in cortex o General anesthetics have effects on cerebral cortex o Cerebral white matter (includes corpus callosum) transmits signals between cortex and other areas of CNS; consists primarily of myelinated axons that have associated vascular network of small arteries, veins, and capillaries; inflammatory cells collect around vessels in diseases like MS; small arterioles especially affected by systemic hypertension o Basal ganglia consist of deep nuclei of gray matter: caudate and putamen (together called striatum) and globus pallidus – help initiate and control cortical actions (movement, behavior, rudimentary cognition) Regions of basal ganglia responsible for movement ensure intended actions carried out and irrelevant movements inhibited Parkinson’s disease caused by degeneration of dopaminergic pathway that arises in substantia nigra in midbrain and terminates in striatum (nigrostriatal tract); degeneration prevents basal ganglia from properly initiating motor activity, resulting in decreased intended movement and unintended tremor; causes decreased (flat) affect characteristic of Parkinson’s Levodopa (part of Sinement) acts on striatum to ameliorate clinical manifestations o Limbic system – rim (limbus) around cortex; consists of cingulate gyrus, hippocampal formation (including hippocampus and surrounding structures), and amygdala Responsible for emotion, social behavior, autonomic control, perception of pain, and memory Memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s caused by degeneration of hippocampal formation Many drugs of abuse stimulate brain reward pathway which includes nucleus accumbens and its projections to limbic system Diencephalon divided into thalamus and hypothalamus o Thalamus has several distinct nuclei and is located medially and inferior to cerebral cortex Some nuclei link sensory pathways from periphery in cerebral cortex Some nuclei act as connections between basal ganglia and cortex Thalamus filters and modulates sensory information, dictating which signals reach conscious awareness o Hypothalamus lies ventral to thalamus; controls ANS, pituitary gland, and essential behaviors (hunger, thermoregulation) Clonidine – antihypertensive medication; mediated by action at receptors on brainstem neurons controlled by hypothalamus Neurons originating in medial hypothalamus secrete hormones either directly into systemic circulation (vasopressin from axon terminals in posterior pituitary) or into portal system that controls hormone secretion by anterior pituitary Initiates complex behaviors in response to hunger, extreme temperature, thirst, and time of day Cerebellum divided into cerebellar vermis (central), cerebellar hemispheres (lateral), and flocculonodular lobe o Receives inputs from wide variety of sources and sends output primariliy to motor areas of cerebral cortex via thalamus o Has certain cognitive functions such as timing of repetitive events and language o Alcohol and certain antiepileptic drugs toxic to cerebellum; especially affect vermis (controls balance) Brainstem connects spinal cord to thalamus and cerebral cortex; arranged with midbrain superior, medulla inferior, and pons bridging midbrain and medulla o Gives rise to most of cranial nerves o Regulates PNS output to salivary glands and iris o Medulla contains control centers that direct output of autonomic nuclei, pacemakers that regulate heart rate and breathing, and centers that control reflex actions such as coughing and vomiting o Several relay structures in pons play role (in conjunction with midbrain) in regulating vital functions such as respiration; base of pons contains white matter tracts connecting cerebral cortex and cerebellum o Neurons in periaqueductal gray (especially in midbrain) send descending projections to spinal cord that modulate pain perception Clusters of diffusely projecting neurons lie throughout brainstem, hypothalamus, and surrounding base of brain o Include locus ceruleus, raphe neucleus o Comprise reticular activating system responsible for consciousness and sleep regulation o Nuclei each use a different neurotransmitter o It’s via these nuclei that antihistamines cause sedation and cocaine causes heightened alertness Spinal cord – white matter tracts connect periphery and spinal cord with more rostral divisions of CNS; gray matter forms nuclear columns o Sensory neurons located in dorsal horns of gray matter; motor neurons in ventral horns of gray matter o Sensory neurons relay information from periphery to more rostral divisions of CNS via dorsal columns (spinothalamic tracts) o Motor neurons relay commands arising in central motor areas and descend in corticospinal tract to peripheral muscles o Interneurons connecting sensory and motor neurons responsible for reflexes Cellular Organization of the Nervous System Cellular organization of autonomic and peripheral nervous system involves limited number of neurons that make few connections o Somatic and sensory info carried directly between spinal cord and periphery o Autonomic nerves – signal must undergo synaptic transmission between preganglionic and postganglionic neuron o Few ancillary neuronal connections made, and little or no modification of info occurs In CNS, info not simply relayed from one area to another; receive signals from numerous sources and distribute axons widely (some neurons synapse with hundreds of thousands of other neurons) o Connections can be excitatory or inhibitory o 3 major motifs of CNS: long tract neuronal systems, local circuits, and single-source divergent systems PNS organized exclusively as long tract system Long tract neuronal organization involves neural pathways that connect distant areas of nervous system o In PNS, signals transmitted with little modification (if initial membrane depolarization strong enough, AP transmitted directly to spinal cord) o Motor end plates – where motor neuron connects with muscle to work o Divergent signaling – one preganglionic neuron makes synaptic connections with many postganglionic neurons; results in some processing and modification, but not appreciably o CNS long tract neurons display divergent signaling but also receive synaptic connections from many upstream neurons (convergent signaling) Center-surround signaling – using both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters to localize signal; activates neurons that map to one area of body and inhibits neurons that surround it Local circuit neurons maintain connectivity primarily within immediate area; responsible for modulating signal transmission; neurons in cerebral cortex organized into 6 layers o While info flows into one layer and out a different layer through long tract connections, links between layers process signals and interpret inputs o Local synaptic connections both excitatory and inhibitory, ensuring only certain patterns of inputs passed along Info originating in lateral geniculate neurons enters primary visual cortex through long tract (optic tract); in area of cortex designed to perceive lines, outgoing neurons excited only if incoming neurons fire in particular pattern (line in particular orientation); outgoing signal might serve as input to another area of brain that recognizes shapes; if area receives appropriate pattern of lines from appropriate sources, it might recognize particular object (tic-tac-toe board) Single-source divergent circuit organization – seen in nuclei in brainstem, hypothalamus, and basal forebrain; neurons originating in one nucleus innervate many target cells; diffuse system of organization o Divergent neurons exert modulatory influence by using neurotransmitters (biogenic amines) that act on G protein-coupled receptors that alter resting potential and ion channel conductance of neuronal PMs, altering ease of depolarization o Neurons constituting single-source divergent circuits don’t generally have myelin sheaths because modulatory influences vary over course of minutes or hours rather than fractions of second Axons highly branched, enabling synaptic connections with large number of target neurons o o Neurons originating in locus ceruleus innervate cerebral cortex and cerebellum for vigilance and responsiveness to unexpected stimuli; drugs such as cocaine inhibit reuptake of catecholamines such as norepinephrine and act on this system to cause hypervigilance Raphe nuclei responsible for modulating pain signals in spinal cord and locus ceruleus; also innervates forebrain modulating responsiveness of neurons in cortex; antidepressants that block reuptake of serotonin act here o Basal nucleus of Meynert projects to cortex and regulates alertness o Pedunculopontine nucleus controls sleep-wake cycles and arousal; cells in basal forebrain that receive inputs from here degenerate in several diseases, including Alzheimer’s o Tuberomamillary nucleus affected by antihistamines to cause drowsiness Neurotransmitters PNS only uses acetylcholine and norepinephrine Amino acid transmitters: glutamate, aspartate, GABA, and glycine Biogenic amine neurotransmitters (derived from decarboxylated amino acids): dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, serotonin, and histamine Acetylcholine is a class unto itself Purines (adenosine and ATP) used in central neurotransmission NO – lipid-soluble gas; diffusible neurotransmitter in CNS Amino acid neurotransmitters – can be acidic (glutamate, aspartate; primarily excitatory) or neutral (GABA, glycine; primarily inhibitory) o Glutamate, aspartate, and glycine alpha-amino acids (used for protein synthesis) o Glutamate is primary excitatory neurotransmitter; acts on both ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels) and metabotropic (G protein-coupled) receptors Excessive excitation of certain glutamate receptors is one way ischemic injury can cause neuronal death Felbamate – used in treatment of refractory epilepsy; inhibits NMDA glutamate receptor reducing excessive neuronal activity associated with seizures; use limited by bone marrow suppression and liver failure o GABA is primary inhibitory neurotransmitter Barbiturates and benzodiazepines bind to GABA receptors and potentiate effect of GABA by allosteric mechanisms Biogenic amines and ACh used by diffuse neuronal systems to modulate complex CNS functions (alertness, consciousness); norepinephrine released to effect SNS response o Synthesized from amino acid precursors o Divided into catecholamines (dopamine, norepi, epi; derivatives of tyrosine), indoleamine (serotonin; synthesized from tryptophan), histamine (formed from histidine) o Catecholamines formed tyrosine L-DOPA dopamine norepi epi Levodopa is L-DOPA; used to compensate for loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra; doesn’t cross BBB so not effective for Parkinson’s Dopamine precursors and receptor agonists used to treat Parkinson’s Dopamine receptor antagonists used to treat schizophrenia Cocaine and amphetamines activate brain reward pathways dependent on dopaminergic neurotransmission Dopamine made in cytoplasm and transported into synaptic vesicles where it can be converted to norepi; in adrenal medulla, norepi transported back into cytoplasm to make epi Clonidine – partial agonist on presynaptic α2-receptors Antidepressants increase synaptic concentration of norepi by blocking reuptake (tricyclics) and others increase intracellular pool of norepi available by inhibiting its degradation (MAOIs) o Serotonin (5-HT) – tricyclics block serotonin uptake (as well as norepi); SSRIs more selective in blocking reuptake of serotonin o Histamine plays role in maintenance of arousal via tuberomamillary nucleus of hypothalamus and sensation of nausea via area postrema in floor of 4th ventricle Most antihistamines act on peripheral histamine H1 receptors (mediates inflammatory response to allergic stimuli) or H2 receptors (treating PUD) Peripherally acting antihistamines can act as sedatives or antiemetics acting via central neuroanatomic substrates Acetylcholine used to depolarize striated muscle; used in ANS by all preganglionic neurons and PNS postganglionic neurons o Muscle paralytics interfere with neurotransmission at motor end plate o Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors increase local ACh concentration by interfering with metabolic breakdown o In CNS, ACh is diffuse system neurotransmitter Donepezil – reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibit helps patients with dementia Scopolamine – antimuscarinic drug that may cause drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, and dreamless sleep because of central cholinergic blockade (drug normally acts in periphery) Pilocarpine – cholinergic agonist; induces cortical arousal and alertness Purinergic neurotransmitters (adenosine and ATP) affected by caffeine (competitive antagonist at adenosine receptors and causes mild stimulant effect) o Adenosine receptors located on presynaptic noradrenergic neurons act to inhibit release of norepi o Antagonism of adenosine receptors by caffeine causes release of norepi to be disinhibited NO diffuses through neuronal membrane and binds to receptors in target cell o Receptors for NO in presynaptic neurons allow for retrograde message o All NO drug agents affect periphery, not central Neuropeptides also have endocrine actions; includes opioids, tachykinins, secretins, insulins, and gastrins o Includes pituitary hormone release and inhibiting factors o Opioids include enkephalins, dynorphins, and endorphins Blood-Brain Barrier L-DOPA usually administered (not dopamine) because it’s able to cross BBB and dopamine isn’t BBB protects brain from toxic substances in blood and from neurotransmitters such as epi, norepi, glutamate, and dopamine that have systemic effects in body tissues but would also bind to receptors in CNS and cause undesirable effects In CNS, endothelial cells of capillaries form tight junctions (no fenestrae) that prevent diffusion of small molecules across vessel wall o Endothelial cells don’t have pinocytotic vesicles that transport fluid from blood vessel lumen to extracellular space o Blood vessels covered by cellular processes derived from astroglia that selectively transport certain nutrients from blood to central neurons Water-soluble substances typically can’t cross BBB, but lipophilic substances (O2 and CO2, etc.) can (low oil-water partition coefficients can’t cross barrier, but high oil-water partition coefficients can) Glucose transported across BB by hexose transporter that allows it to move down its concentration gradient (facilitated diffusion) Amino acids transported by 3 transporters: one for large neutral amino acids (valine, phenylalanine), one for smaller neutral amino acids and polar amino acids (glycine, glutamate), and one for alanine, serine, and cysteine o L-DOPA transported by large neutral amino acid transporter; used for Parkinson’s patients o After meals with high protein content, too many substrates, and transport of L-DOPA ineffective BBB contains ion channels to ensure ion concentrations of brain maintained at homeostatic levels Potentially toxic lipophilic compounds can be excluded from brain by multiple drug resistance (MDR) transporters that pump hydrophobic compounds out of brain back into blood vessel o MDR transporters present in many cell types and can be cause of tumor resistance to chemotherapy Metabolic BBB maintained by enzymes that metabolize compounds transported into CNS endothelial cells o Aromatic L-amino decarboxylase (DOPA decarboxylase) metabolizes peripheral L-DOPA to dopamine o Carbidopa – inhibitor of DOPA decarboxylase; unable to cross BBB itself, so doesn’t interfere with LDOPA conversion in brain itself