* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurophysiology
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Animal echolocation wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
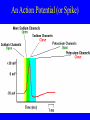
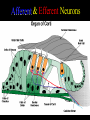
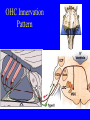
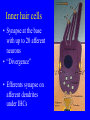
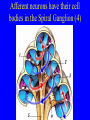
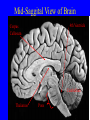
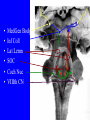
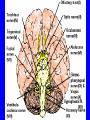
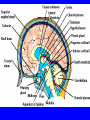
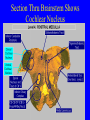
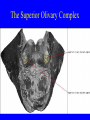
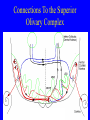
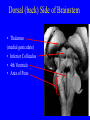
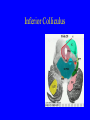
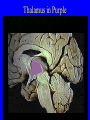
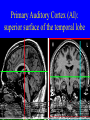
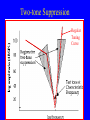
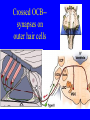
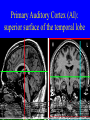
Neurophysiology • • • • • • • • Neurons Gross Anatomy The Central Auditory Nervous System Frequency and Intensity encoding Central Auditory Processing Binaural Processing Central Control (Descending Systems) Cortical Processing The Neuron • Dendrites receive synaptic stimulation (neurotrans.) • Action Potential generated in soma near axon • AP conducted along axon from Node to Node (saltatory conduction) • AP produces release of neurotransmitter at terminal boutons An Action Potential (or Spike) Two Descriptors for Neurons • Afferent (sensory)-- carrying signals toward the brain • • Efferent (motor) -- carrying signals from brain to periphery • Afferent & Efferent Neurons 4 Types of Cochlear Neurons • INNER HAIR CELLS > Multiple (10 to 20) Afferent synapses > (Efferents synapse on afferent dendrites) • OUTER HAIR CELLS: > Large Efferent synapses engulf base of cell > Small (& not very active) Afferent synapses IHC Innervation Pattern OHC Innervation Pattern Inner hair cells • Synapse at the base with up to 20 afferent neurons • “Divergence” • Efferents synapse on afferent dendrites under IHCs IHC activation alters firing rate Afferent neurons have their cell bodies in the Spiral Ganglion (4) Central Nervous System Structures • Nucleus = a group of nerve cell bodies • Fiber Tract = a group of axons Major Components of the Central Auditory Nervous System (CANS) • • • • • • • VIIIth cranial nerve Cochlear Nucleus Superior Olivary Complex Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex Brainstem Mid-brain Thalamus Temporal Lobe Mid-Saggital View of Brain 4th Ventricle Corpus Callosum Cerebellum Thalamus Pons • • • • • • MedGen Body Inf Coll Lat Lemn SOC Coch Nuc VIIIth CN Neural Web-Site http://rprcsgi.rprc.washington.edu/ neuronames/hierarchy.html Section Thru Brainstem Shows Cochlear Nucleus The Superior Olivary Complex Connections To the Superior Olivary Complex Superior Olivary Processing Supports Localization • Lateral SO-- Interaural Intensity Differences • Medial SO-- Interaural Time Differences (These are the two primary acoustic cues for localizing sounds) Dorsal (back) Side of Brainstem • Thalamus (medial geniculate) • Inferior Colliculus • 4th Ventricle • Area of Pons Inferior Colliculus Thalamus in Purple Auditory Radiations Connect • Medial Geniculate Body (in purple) to • Primary Auditory Cortex (in blue) Lateral-Superior view of brain Primary Auditory Cortex (AI): superior surface of the temporal lobe Brain Photos Web-Sites http://rpiwww.mdacc.tmc.edu:80/se/anatomy /brain/ http://www.ets.uidaho.edu/med532/start.htm Neurophysiological Measures • Gross Evoked Potentials-- Voltage changes in response to auditory stimulation recorded from the scalp • Single-Unit Measures-- Voltage (or other) changes recorded within a neuron Auditory Evoked Potentials • Recorded in different time intervals (“epochs”) following a sound • Earlier epochs come from lower in the system • Later epochs come from higher in the system Examples of AEP Epochs • Electrocochleography-- within 5 milliseconds • Auditory Brainstem Response-- thru 10 ms • Middle Latency Response-- thru 75 ms • Auditory Late Response-- thru 200 ms Auditory Brainstem Response IV Amplitude (V) III I V II Amp V Wave V Latency Time (ms) 0 10 GENERATORS of ABR WAVES I II III IV V = Distal VIIIth nerve = Medial VIIIth nerve = Cochlear Nucleus = Superior Olivary Complex = Lateral Lemniscus & Inferior Colliculus Single-Unit Measures • Post-Stimulus Time Histogram-- Shows firing rate changes over time • Period or Interval Histograms-- Show phase-locking of neural firing Tuning Curves • Iso-Rate Function -- Shape similar to what we’ve already described (Fig 6.12 b) • Iso-level Function -- Shows spike rate as a function of frequency-- peak at a single frequency (Fig 6.12a) Two-Tone Suppression • The response to one tone can be reduced or eliminated by introducing a second tone near the neuron’s CF. • (Fig 6.16) • Second tone can be either one which normally would excite the neuron or not Two-tone Suppression Regular Tuning Curve Frequency Coding • The Place Code-- each neuron has a characteristic frequency • Periodicity Pitch-- neurons phase-lock to stimuli Intensity Coding • Firing rate increases in single neurons • Spread of activation to a wider range of neurons-- “Density of Discharges” • Latency of Firing (shorter delay at higher levels) Efferent (Descending) Control • Cochlear Efferents come from Superior Olivary Complex --The Olivo-Cochlear Bundle (OCB) • Uncrossed OCB-- synapses on dendrites under inner hair cells • Crossed OCB-- synapses on outer hair cells • Both use inhibitory neurotransmitters Uncrossed OCB-- synapses on dendrites under inner hair cells Crossed OCB-synapses on outer hair cells Efferent Control (cont’d) • The Acoustic Reflex • Auditory Cortex and Thalamus also send descending fibers to auditory brainstem locations The Acoustic Reflex Afferent: Efferent: • VIIIth nerve • VIIth nerve nucleus • Cochlear Nucleus • VIIth nerve • Superior Olivary Complex • Stapedius muscle Primary Auditory Cortex (AI): superior surface of the temporal lobe 6 Cortical Layers • Thalamic inputs >IV • project to pyramidal cells in layer III • Divergence from III – within AI – other cortical areas – contra AI • V and VI >>thalamus &IC Cortical Neurons • Tonotopically and Spatiotopically organized • Highly Adaptable • Sensitive to CHANGES in Frequency and Intensity – Coding virtual pitch – demodulating complex signals (e.g. speech) Cortical Processing • • • • Pattern Recognition Duration Discrimination Localization of Sounds Selective Attention Cerebral Dominance/Laterality • Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) • Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli