* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download xpx tampa bay
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
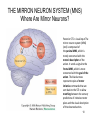
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
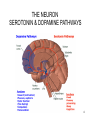
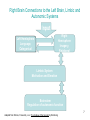
XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 THE NEURON The Highways and Byways of the Brain • 100 billion neurons • Every neuron may be touched by as many as 10,000 other nerve cell axons • 1000 trillion different possible synaptic connections (more connections in one brain than stars in the universe) • 16 billion neurons in the cerebral cortex alone • Neurons form dense connected plexus in different areas of the brain • The activation of neurons and their networks are the building block of all mental processes • The greater the stimulation in terms of frequency of signals (30-1000/sec) the stronger are the electrochemical signals. 2 3 THE NEURON SEROTONIN & DOPAMINE PATHWAYS 4 5 6 Right Brain Connections to the Left Brain, Limbic and Autonomic Systems Input Left Hemisphere Language, Categorical Right Hemisphere Imagery, Relational Limbic System Motivation and Emotion Brainstem Regulation of autonomic function 7 Adapted from Schore, Foreword, p. xiv, The shadow of the tsunami by Bromberg Social Brain Functions Face Processing Which face shows more emotion: The face in the middle, or the two “right” sides (far left) or the two “left” sides (far right)? 8 THE MIRRON NEURON SYSTEM Mirror Neurons are Innate and Epigenetic The capacity for babies to imitate others is online from birth. Meltzoff tested a baby 41 minutes old, who, like the baby seen in this slide from a 1977 Science article, imitated the motor actions of facial expressions. Babies can learn by imitating (contra Piaget who thought must be 2) and they enjoy being imitated (peek-a-boo and remember co-imitation in the video?). Fire together, wire together the way the innate mirror neuron system is built. Imitation in pre-verbal toddlers. Imitation is lifelong. Memes. 9 THE MIRRON NEURON SYSTEM (MNS) Where Are Mirror Neurons? Posterior STS = visual input The mirror neuron system (MNS) (red) is composed of the parietal MNS, which is mostly concerned with the motoric description of the action. It sends a signal to the frontal MNS, which is more concerned with the goal of the action. The black arrows represent copies of motor imitative commands that are sent back to the STS to allow matching between the sensory predictions of imitative motor plans and the visual description of the observed action. 10 11 12