* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons & the Nervous System
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
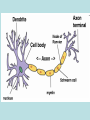
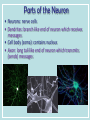
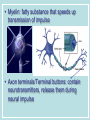
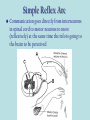
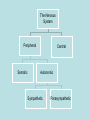
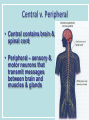
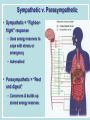
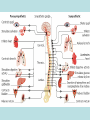
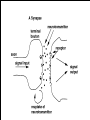
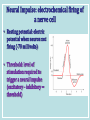
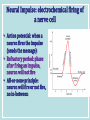
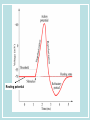
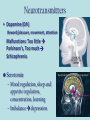
Neurons & the Nervous System Chapter 2: The Brain and Behavior Today’s Goal You will be able to…. • Identify the parts of a neuron and their functions in creating & sending neural messages. Parts of the Neuron • Neurons: nerve cells • Dendrites: branch-like end of neuron which receives messages • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages • Myelin: fatty substance that speeds up transmission of impulse • Axon terminals/Terminal buttons: contain neurotransmitters, release them during neural impulse Types of Neurons • Sensory neurons: send messages from sensory receptors to the spinal cord & brain • Motor neurons: relay messages from brain & spinal cord to muscles & glands • Interneurons: transmits neural stimulus between sensory & motor neurons (found only in Central nervous system) Simple Reflex Arc • Communication goes directly from interneurons in spinal cord to motor neurons to move (reflexively) at the same time the info is going to the brain to be perceived The Nervous System Peripheral Somatic Central Autonomic Sympathetic Parasympathetic Central v. Peripheral • Central contains brain & spinal cord • Peripheral – sensory & motor neurons that transmit messages between brain and muscles & glands Autonomic v. Somatic • Somatic – voluntary - controls purposeful body movements • Autonomic – involuntary – automatic activities – heartbeat, respiration, digestion, dilation of pupils, etc. Sympathetic v. Parasympathetic • Sympathetic = “Fight-orflight” response – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! • Parasympathetic = “Rest and digest” – Conserves & builds up stored energy reserves Today’s Goal You will be able to…. • Describe how neurons communicate to send messages in the brain and body The Synapse • Synapse (synaptic cleft): gap between dendrites of one neuron and axon of another • Receptor sites: parts of dendrite which receive neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters: chemical substances involved in sending neural impulses Neural Impulse: electrochemical firing of a nerve cell • Resting potential: electric potential when neuron not firing (-70 millivolts) • Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (excitatory – inhibitory = threshold) Neural Impulse: electrochemical firing of a nerve cell • Action potential: when a neuron fires the impulse (sends the message) • Refractory period: phase after firing an impulse, neuron will not fire • All-or-none principle: neuron will fire or not fire, no in-between Resting potential Synapses • Excitatory neurotransmission: increases the likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire • Inhibitory neurotransmission: decreases likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire Today’s Goal You will be able to… • Discuss how the major neurotransmitters affect the body and one’s behavior Substances that Affect Neurotransmitters • Agonist: similar to the NT, mimics its effects • Antagonist: inhibits the release of NT by sending neuron, or blocks receptor site for NT on receiving neuron Neurotransmitters • Acetylcholine (ACh) EXCITATORY (sometimes inhibitory) Memory, muscle contractions, learning Malfunctions: Alzheimer’s Disease Neurotransmitters • Dopamine (DA) Reward/pleasure, movement, attention Malfunctions: Too little Parkinson’s, Too much Schizophrenia • Serotonin – Mood regulation, sleep and appetite regulation, concentration, learning – Imbalance depression Neurotransmitters • Norepinephrine – Involved in autonomic nervous system (sympathetic) arousal – Imbalances: Depression, seizures • GABA – Function: Reduce anxiety, relax for sleep Imbalance: Anxiety disorders, tremors, insomnia • Endorphins pain control