* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
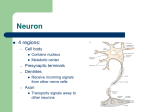
Neuron Structure Synapse The Synapse 1. Synthesis of neurotransmitter (NT) 2. Storage and transport of NT within vesicles 3. NT Release 4. Activation of postsynaptic receptors 5. Termination of transmitter effect (e.g. reuptake) Resting Potential Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. Action Potential • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value – Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit the axon Myelin • Myelin is a fatty, waxy substance coating the axon of some neurons. • Functions: – Speeds neurotransmission – Insulates neurons from each other – Makes neurotransmission more efficient Neurotransmitters • • • • • • • Serotonin Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine Epinephrine GABA Endorphins Midline Brain View Brainstem • Brainstem is a primitive portion of brain – Pons: involved in respiration, sleep regulation, dreaming – Medulla: involved in life support functions such as respiration and heart rate – Reticular activating system is an arousal system within the brainstem Subcortical Brain Areas • Corpus callosum: band of axons that interconnects the hemispheres • Thalamus: sensory relay area • Limbic system: involved in emotionality • Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, fighting, homeostasis • Cerebellum: involved in motor control Limbic System: Seat of Motivation, Emotions Cerebral Cortex • Cortex refers to the outer covering of the brain – Consists of left and right hemispheres – Cortex is divided into lobes • Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory • Parietal: Body sensations • Occipital: Vision • Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension – Localization of function: do discrete circuits carry out different functions? Cortical Lobes Cerebral Cortex Motor and Somatosensory Cortex Language areas: Broca & Wernicke Primary Visual Pathways Dorsal and Ventral Visual Pathways Split brain: Hemispherical Specialization Brain imaging technologies • Positron Emission Tomography (PET) • Makes use of radioactive tracer to measure cerebral blood flow. Brain imaging technologies • Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) • Uses electromagnets to measure oxygen levels in brain. Brain imaging technologies Electroencephalogram (EEG): event-related potentials (momentary shifts in electrical activity of brain associated with external signals) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS): Produces ‘virtual’ lesions