* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE NEURON
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Theta model wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
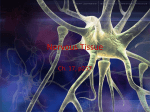
Lesson Overview The Neuron SEC 31.1 THE NEURON Lesson Overview The Neuron THINK ABOUT IT How do we know about the world outside our bodies? When you reach for a ball at a ballgame, how does your body make this happen? How do the sights, sounds, and smells at the ballgame get into your mind? The answers to all these questions are found in the nervous system. Lesson Overview The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System • collects information about the body’s internal and external environment • processes that information • responds to it. Lesson Overview The Neuron Parts of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) • consists of the brain and spinal cord • processes information and creates a response Lesson Overview The Neuron Parts of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system (PNS) • consists of nerves and supporting cells • collects information about the body’s external and internal environment • creates a response in glands or muscles Lesson Overview The Neuron Neurons The messages carried by the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses. Nervous system impulses are transmitted by cells called neurons. Lesson Overview The Neuron Types of Neurons Grouped according to the direction an impulse travels 1. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs, such as the eyes and ears, to the CNS (spinal cord and brain). 2. Motor neurons carry impulses from the CNS (brain and the spinal cord) to muscles and glands. 3. Interneurons process information from sensory neurons and then send commands to other interneurons or motor neurons. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons The largest part of a typical neuron is the cell body, which contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons Spreading out from the cell body are short, branched extensions called dendrites. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons The long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body is the axon. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons An axon ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons Neurons may have dozens of dendrites, but usually they have only one axon. In most animals, axons and dendrites of different neurons are grouped into bundles called nerves. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons In some neurons, the axon is surrounded by an insulating membrane called the myelin sheath. Nodes are gaps in the myelin where the axon membrane is exposed. Lesson Overview The Neuron Structure of Neurons As an impulse moves along the axon, it jumps from one node to the next. This causes an impulse to travel faster than it would without a myelin sheath. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Nerve Impulse An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Resting Neuron Neurons have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron is negative compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting potential. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Resting Neuron The movement of sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+) is responsible for the charge difference. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Moving Impulse A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus large enough to start a nerve impulse. The impulse travels quickly down the axon toward the axon terminals. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Moving Impulse The impulse will cause the nerve cell to become positively charged. This is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Moving Impulse When the impulse passes, the neuron becomes negatively charged and the resting potential is restored. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Synapse The point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. A space, called the synaptic cleft, separates the axon terminal from the next cell. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Synapse The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny structures filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals travel across a synapse to cause an impulse in another cell. Lesson Overview The Neuron The Synapse Then neurotransmitters are broken down or recycled by the axon terminal.