* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Physiology of Neurons
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
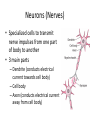
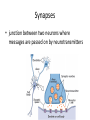
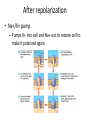
Structure and Physiology of Neurons Nervous System Lecture 2 Neurons (Nerves) • Specialized cells to transmit nerve impulses from one part of body to another • 3 main parts – Dendrite (conducts electrical current towards cell body) – Cell body – Axon (conducts electrical current away from cell body) Synapses • junction between two neurons where messages are passed on by neurotransmitters Resting neuron structure • Contain potassium (K+) ions inside neuron • Sodium (Na+) ions are outside plasma membrane and don’t normally pass inward Polarized neuron • Inactive (not sending an impulse) • Inside of neuron negatively charged to compared to outside Stimulated neuron- Depolarization • Na+ gates in membrane open and Na+ rushes into cell causing inside to be more positive than outside of cell which activates neuron to transmit an action potential Action potential • nerve impulse which causes the axon to release a neurotransmitter into synapse that binds to next neuron stimulating it Cell Repolarization • After action potential • K+ rushes out of cell causing the inside to become negative again • Must occur before neuron can send another nerve impulse After repolarization • Na+/K+ pump – Pumps K+ into cell and Na+ out to restore cell to make it polarized again