* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System II – Neurons
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
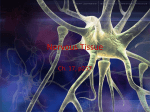
Name: Date: SciTec 3 Nervous System II – Neurons Neurons Information is transmitted through which is made up of Also called We have about neurons in our bodies! What do they do? o and information What makes them special? 1. Can be a. Reacts to a stimulus and changes it into an electrical signal (nerve impulse) 2. They are a. Transmits nerve impulse from one neuron to another 3. Consume lots of and a. Would only survive a few minutes without oxygen 4. Can live more than years a. You get one set of neurons and that’s it! You keep them your entire life. 5. Cannot a. They cannot be replaced if destroyed! 1 Name: Date: SciTec 3 What do they look like? (Whole fibre) 2 Name: Date: SciTec 3 Parts of the Neuron Structure Dendrites Soma Nucleus Axon Schwann Cells Myelin sheath Nodes of Ranvier Axon terminal Description and Function The branched projections of the neuron. ____________ and ____________ electrochemical signals from other neurons . The bulbous end of a neuron. The cell “body” Contains the ____________________. Contains the genetic material of the cell. Controls the cell’s ____________________. The nerve fibre. ________________ electrical impulses way from the soma ___________________ information Glial cells Non-neuronal cells; the glue of the nervous system Form the ________________________. Fatty layer formed around the ______________ of a neuron. Helps ______________ the speed at which impulses propagate along the axon because the impulses can hop between the _______________________________. __________________ in myelin sheath. Allow for ____________________ across the cell membrane which propagates the electrical impulses. The _______________________ projects of the neuron. Releases __________________________________ to next neuron. 3 Name: Date: SciTec 3 Sending a Signal • Signals are sent via • Travels from neuron to neuron until reaches target • Always • receive the message or transform them into electrical nerve impulses • • to and Created by K+ and Na- ion movement Travel from one neuron to another via • These are chemical substances secreted by the axon terminal that travel across the transmission zone between neurons to the next dendrite Transmission zone is called a 4













![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)