* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
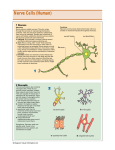
TOPIC: The Nervous System AIM: How does the Nervous System help maintain Homeostasis? HW: TEXT BOOK READ PAGES 558-562. Do Vocabulary Definitions for words on page 558 Background Information Neuron = a nerve cell Impulse = messages sent by nerve cells Voluntary = have conscious control over Involuntary = do not have conscious control over What is the function of the Nervous System? • A system that conducts impulses to CONTROL and COORDINATE body activities. Life Function associated with the Nervous system is REGULATION. Organization of Nervous System Nerves, which make up nervous systems, are organized in the following way… Nervous System: Peripheral Nervous system Somatic Nervous System Central Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Division Parasympathetic Division Central Nervous System (CNS) What are the components of the CNS and How do they work together to maintain homeostasis? Components: Brain and Spinal Cord Send, receive, and process messages from the Peripheral NS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – What are the components of the PNS and How do they work together to maintain homeostasis? Nerves that connect the CNS with the rest of an organism’s body. Information Processing: Typical Nerve Pathway Sensory input Integration (brain analyzes) Motor output Somatic Nervous System – What are the components of the Somatic NS and How do they work together to maintain homeostasis? Nerves that regulate voluntary functions. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) What are the components of the Automatic NS and How do they work together to maintain homeostasis? Nerves that control all involuntary functions Sympathetic Division How does the Sympathetic Division regulate body activities? • Slows down body functions • Rest and Digest!! Parasympathetic Division • How does the Parasympathetic Division regulate body activities? By speeding up body activities Fight or flight Information Processing: Typical Nerve Pathway Sensory input Integration (brain analyzes) Motor output Answer on separate sheet of loose leaf and leave on desk upon Exit. How does the Nervous system function to maintain Homeostasis? TOPIC: NERVOUS SYSTEM Aim: How does a neuron conduct an impulse? • Do Now: Handout: Vocabulary Map: NUERON HW: Page 552 in Text Book Vocabulary Definitions General Neuron Axon Dendrites Myelin sheath Cyton Synaptic terminal Synapse Axon Terminals • YouTube - The Human Body: Nervous System (2nd Ed., Rev.) (clip) Vocabulary: Parts of a Neuron • Dendrites: Receive impulses and direct them toward the cyton. • Cyton: Cell Body – conducts impulses from dendrites to axon • Axon: Transmits impulses from cyton to terminal branches at Synapse. Parts continued • Myelin Sheath: Fatty covering on Axon that helps speed up impulse conduction. • Axon Terminals: Where the axon ends and the neurotransmitters are secreted. THE SYNAPSE • YouTube - Neural Synapse The Synapse: Gap Between neurons The following occurs at the synapse: Neurotransmitters are secreted from axon terminals to transmit impulses across the synapse to the dendrites of the next neuron. Neurotransmitters • Chemicals secreted to transmit impulses across a synapse. • They have specific shapes and only receptors of the same shape will accept them. Handout: Activity - Synapse TOPIC: NERVOUS SYSTEM AIM: How do different types of neurons function to conduct impulses? Three types of neurons 1. Sensory 2. Inter or Associative • 3. Motor Handout for Notes Sensory Neurons: • Transmit impulses from your senses into the CNS. Where are Sensory Neurons located? In the CNS or PNS? Inter Neurons: Associative between Neurons • Process impulses from the sensory neurons and send impulses to the motor neurons. Where are Inter neurons located? Motor Neurons • Transmit impulses from the Inter neurons to the muscles, glands, or organs that will be producing the response. Where are the Motor Neurons located? NEW VOCAB WORD: EFFECTOR The muscles, glands, or organs producing the response. • YouTube - Central Nervous System, Reflex Arc On Loose Leaf • Describe the path of an impulse through the three types of neurons. • What is the difference between a regular reaction and a reflex? HW: Worksheet Review • MovieSource: The Nervous System TOPIC: Nervous System AIM: How do the parts of the Brain help maintain homeostasis? DO Now: Worksheet HW: STUDY FOR QUEST on Nervous System and Midterm Finish Flip Books The Cerebrum Characteristics: * Largest part of the Brain * Divided into hemispheres (Right & Left) • The Cerebrum Controls all voluntary activities. • These include: movement, speaking and language, memory, and senses. The Cerebellum Second largest part of the Brain. The Cerebellum regulates Balance and Coordination of movements. The Medulla Also known as the BRAINSTEM It becomes continuous with the spinal cord Regulates all Involuntary Activities such as heart rate, breathing rate, etc. Video Clip : The story of Phineus Gage Phineus Gage Nervous System Diseases and Disorders – Schizophrenia – Depression – Alzheimer’s Disease – Parkinson’s Disease