* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download מצגת של PowerPoint
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Adult neurogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
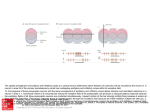
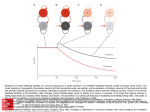
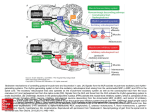
Yoav Livneh [email protected] 02-6585163 Neuronal development (generally) neurogenesis and migration outgrowth of axons and dendrites, and synaptogenesis Refinement of synaptic connections Adult neurogenesis (hippocampus) * also occurs in the adult olfactory bulb Neuronal development (in the adult hippocampus) Ge et al., J Physiol, 2008 GABA in neuronal development Ben-Ari, Nature Reviews: Neuroscience, 2002 1. Genesis of neurons (and migration). 2. Outgrowth of axons and dendrites, and synaptogenesis. 3. Refinement of synaptic connections. Development of GABA (and glutamate) currents in adult-born hippocampal neurons 7 dpi 14 dpi 28 dpi evoked Glu. currents evoked GABA currents tonic GABA currents 3 dpi DCX (doublecortin) - a marker for immature neurons Bicuculine – GABAa-R antagonist CNQX – AMPA-R antagonist The big question – What is the role of these tonic excitatory GABA currents? Exploration and manipulation of GABA currents in adult-born hippocampal neurons exc. inh. - GABA is excitatory from 3 to ~14 dpi. - Afterwards GABA currents mature to become inhibitory. - shRNA-mediated knockdown of NKCC1 (chloride transporter) eliminated the excitatory nature of GABA (high [Cl]in is not maintained). ~inh. Perforated patch – initially keeps the original intracellular content. Whole-cell patch – content is very rapidly replaced with the electrode’s content. How will this manipulation affect adult-born neuron development? Effects of eliminating excitatory GABA currents – part I (dendritic development) - Shorter total dendritic length. - Less branches. - Occupy a smaller volume of space. Excitatory GABA currents are essential (necessary) for proper dendritic development Effects of enhancing excitatory GABA currents (should be positively correlated) Pentobarbital – GABA agonist The opposite, complementary, trends were observed with administration of a GABA agonist (suggesting it might also be sufficient). Effects of eliminating excitatory GABA currents – part II (inhibitory synaptic integration) evoked spontaneous - Less neurons with evoked inhibitory responses. - Lower evoked response amplitudes. - Lower spontaneous response frequencies (but similar amplitudes). Excitatory GABA currents are essential for proper inhibitory synaptic integration Effects of eliminating excitatory GABA currents – part II (excitatory synaptic integration) evoked spontaneous - Dramatically less neurons with evoked excitatory responses. - Lower evoked response amplitudes. - Lower spontaneous response frequencies (but similar amplitudes). Excitatory GABA currents are essential for proper excitatory synaptic integration Effects of eliminating excitatory GABA currents from birth (KO mice) The same trends were observed with NKCC1 KO mice. Conclusions and interpretations Conclusions: -At the initial stages of the development of adult-born neurons, GABA is excitatory due to high intracellular Cl concentration (mediated by the transporter NKCC1). - This excitatory action of GABA is essential (necessary and perhaps sufficient) for proper development of dendrites and synaptic connections. Interpretations: - New neurons initially “listen” to network activity, before they “talk” (what they “hear” might affect their integration). - Tonic excitatory GABA might act through low-threshold (-57 mV) Ttype calcium channels (expressed in these neurons). Calcium then initiates changes in gene expression, cytoskeletal rearrangement, etc. Questions?




























![Anti-GABA antibody [5A9] ab86186 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008296205_1-9b8206993c446f240db0ef9ab99a7030-150x150.png)


