* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
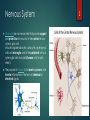
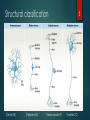
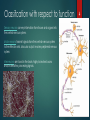
1 Diversity of neurons STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION by András Salma Nervous System Glial cells are non-neural sells that provide support and protection for neurons In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system glial cells include Schwann cells (myelin sheat). The purpose of neurons is to receive, process, and transfer information in the form of chemical or electrical signals. 2 Structural classification (Central NS) (Peripheral NS) Pseudounipolar (P) 3 Pyramidic (C) Classifcation with respect to function Sensory neurons convey information from tissues and organs into the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to the effector cells. Muscular output involves peripheral nervous system. Interneurons are found in the brain, highly branched axons and/or dendrites, processing signals. 4 Neurotransmitters Cholinergic neurons: Nicotinic receptors. Acetylcholine is synthesized from choline and acetyl coenzyme A. GABAergic neurons: Gamma aminobutyric acid--GABA is one of two common neuroinhibitors. GABA is synthesized from glutamate neurotransmitters by the enzyme glutamate decarboxylase. Glutamatergic neurons: Glutamate is one of two primary excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, the other being Aspartate. Glutamate receptors are one of four categories, three of which are ligand-gated ion channels and one of which is a G-protein coupled receptor (often referred to as GPCR).Glutamate is synthesized from the amino acid glutamine Dopaminergic neurons: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is connected to mood and behaviour, and modulates both pre and post synaptic neurotransmission. Serotonergic neurons: Serotonin can act as excitatory or inhibitory. A lack of serotonin at postsynaptic neurons has been linked to depression. Drugs that block the presynaptic serotonin transporter are used for treatment, such as Prozac and Zoloft. 5