* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
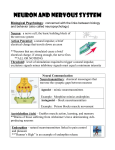
Nervous System Jeopardy Test Review Game Brain Neurons Senses Senses 2 HodgePodge 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 The largest part of the brain (divided into left and right hemispheres) and four lobes in each hemisphere. What is the cerebrum The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions and contains three parts: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata)? What is the brain stem? It directs most incoming sensory signals to the proper regions of the cerebral cortex (ex: vision to occipital lobe and speech to the frontal lobe) What is the thalamus? This part of the brain controls muscle coordination and balance by receiving sensory impulses form muscles, joints, and sensory organs. What is the cerebellum? This structure is part of the brain stem that relays communications between the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum? What is the pons? These are the three major categories of neurons. What are: 1)Sensory (messages from sensory receptors to CNS), 2)Motor (messages from CNS to muscles and glands) 3)Interneurons (connection between neurons)? These are the three parts of a neuron and their general functions. What are: a)dendrites: receive message from neuron b)cell body: control center for neuron/contains nucleus and organelles c)axon: sends electrical impulse/message away from cell body The period in which a neuron cannot send a signal What is the refractory period? This is the main difference between a neuron at “resting potential” and one undergoing an “action potential” What is during resting potential, a neuron is more negative on the inside (Na+ ions more prevalent on outside). When in action potential, polarity switches and cell becomes more positive on inside as ion channels open up and Na+ ions flood in? This is a)where neurotransmitters are released from and b)how neurotransmitters either deliver (or not) the electrical impulse to the postsynaptic neuron. What is a)neurotransmitters are released into synaptic cleft from the axon terminal and b)they open ion channels to allow the ions to flood in and change the polarity of the cell (to take it out of resting potential). These are three of the four structures light must pass through before reaching the retina. What is a)cornea (thin, protective layer over eye), b)pupil (“hole” changes in size with amount of light), c)iris (gives you eye color), and d)lens (adjusts size with muscles to properly focus light on the retina) The coiled, snail-shaped tube consisting of three fluid-filled chambers that deliver the vibration to the hair cells. What is the cochlea? The innermost, lightsensitive layer of the eye. What is the retina? These are the retinal photoreceptors that allow you to see colors What are cones? Muscles attached to the “this structure” adjust its size and allow it to bend the rays of the incoming light (to adjust correctly on the retina). What is the lens? Specialized chemoreceptors called ______are located in the mucous lining of the epithelium of nasal passages. What are Olfactory receptors? This is the first structure of the ear to vibrate What is the tympanic membrane? These sensory receptors are located throughout the interior of the body and at the base of the epidermis. What are pain receptors? Balance is maintained by mechanoreceptors in the three fluid-filled ___________of the inner ear. What are semicircular canals? This is the region of the ear that separates the middle ear from the inner ear. What is the oval window. This is an automatic response of the body that occurs very rapidly and without conscious control. (Ex. Kneejerk) What is a reflex? This is the reason a reflex occurs so quickly and automatically. The message bypasses the brain (only goes to the spinal cord). In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. What are: Photoreceptors, thermoreceptors? A characteristic of a drug addiction in which a larger and larger amount of drug is needed to achieve the desired sensation What is tolerance? The type of neurotransmitter that cocaine “messes” with by blocking the presynaptic reuptake channels. What is dopamine? More Brain More Neurons More Senses Even More Senses Oddballs 200 100 200 100 200 100 200 100 200 100 400 200 400 20 400 200 400 200 400 200 600 300 600 300 600 300 600 300 600 300 800 400 800 400 800 400 800 400 800 400 1000 500 1000 500 1000 500 1000 500 1000 500 The part of the brain that maintains homeostasis and controls hormone production. What is the hypothalamus? The CNS constantly interacts with the _____ via 12 pairs of cranial nerves that connect the brain with the head and neck What is the PNS? The ______ ____ lies throughout the brain stem and is a network of neurons that controls respiration and circulation and helps separate signals that are important from unimportant. What is the Reticular formation? One of the divisions of the the PNS is the _____that contains motor neurons that direct the movement of skeletal muscles; it is a voluntary system What is the somatic nervous system? The division of the autonomic nervous system that helps in “fight or flight.” What is the sympathetic divsion? This is the reason the neuron becomes more positively charged during an action potential. What is neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, opening ion channels, so Sodium can flood through the ion channels and change the polarity of the cell? This type of neuron is found only in the brain and spinal cord (they form interconnections between neurons) What are interneurons? This type of neuron receives messages from receptors like thermoreceptors and pain receptors and sends the message toward the CNS. What are sensory neurons? This insulates the neuron which speeds up the transmission of action potentials along the axon. What is the myelin sheath? State the 5 step path of a nerve impulse. What is: receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, muscle/gland Another name for the tympanic membrane What is the eardrum? This part controls the air pressure beyond the tympanic membrane What is the Eustachian tube? Carries visual information in the form of action potentials from the retina to the thalamus (which then gets transferred to occipital lobe of cerebrum) What is the optic nerve? This structure is pigmented and controls the size of the eye’s opening. What is the iris? There are 10000 of these chemoreceptors embedded between bumps called papillae on the tongue, on the roof of the mouth and in your throat. What are taste buds? The ______that line the cochlea are delicate and cannot be regenerated. They are usually damaged by loud noises. They take the vibration and send electrical impulse to brain through auditory nerve What are hair cells? _____, which is the inability to distinguish certain colors, is caused by faulty or missing cones. What is colorblindness? Seeing:Photoreceptors:: Hearing :: ______ What are mechanoreceptors? (sense movement/vibrations) Hearing is a physical or chemical sense. (Choose correct answer) What is a physical sense? This is the tube-like structure that carries sound waves from the external ear to the tympanic membrane. What is the auditory canal? Cocaine is a highly addictive ______, a drug that generally increases the activity of the CNS. What is a stimulant? Alcohol is a _______, a drug that decreases the activity of the CNS What is a depressant? ______is a major drug found in tobacco that mimics the action of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. What is nicotine? At a normal synapse, dopamine is reabsorbed by ________found on the presynaptic cell. What are Reuptake channels 4 of the 6 categories of psychoactive drugs What are: stimulants, depressants, inhalants, narcotics, hallucinogens, and THC?