* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System Study Guide 1
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
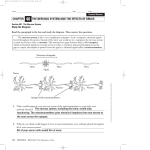
Name _________________________________ Hour ____ Studyguide on the Nervous System – Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron 1. What are the 3 functions of the Nervous System? 2. What other system works coordinate activities in order to maintain homeostasis. 3. What is homeostasis? 4. What does the Central Nervous System consist of? 5. What does the Peripheral Nervous System consist of? For questions 6. – 8. Use the diagram below to fill in your answers. The Nervous System A Brain B Spinal Cord C D Afferent Division of PNS Efferent Division of PNS E G F Somatic Sensory Receptors Visceral Sensory Receptors H Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System J I Skeletal muscle K Sympathetic Nervous System L Parasympathetic Nervous System Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands 6. Using your notes, write out the pathway that the nervous system will use after eating a meal. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 7. You see broken glass on the road ahead. Write out the pathway that the nervous system will take to avoid this glass. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 9. What are the 2 main types of cells in neural tissue? 10. What does an astrocyte do? 11. What does an oligodendrocyte do? 12. What does a microglial cell do? 13. What does an ependymal cell do? 14. What is the blood-brain barrier and why is it important? 15. What is myelin and why is it important? 16. What does a Schwann cell do? 17. What happens during Multiple Sclerosis? 18. – 24. Label the following parts of the neuron below: (a) axon, (b) cell body, (c) dendrites, (d) internodes, (e) myelin, (f) nodes of Ranvier, (g) synaptic terminals 25. In the picture above, which direction will the impulse travel? 26. Why can’t neurons replace themselves if they are damaged? 27. The brain and spinal cord have grey matter. Why do parts of the brain and spinal cord look “greyer” than others? 28. Which neuron is multipolar and which is unipolar? 29. – 30. Where are multipolar neurons found (2 places)? 31. Where are unipolar neurons found? 32. – 34. Explain the difference between a sensory neuron, a motor neuron, and an interneuron? 35. When does a neuron have a -70 mV difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell? 36. Why does this difference exist? 37. What 4 things can stimulate a neuron’s cell membrane? 38. What must take place in order for the neuron to trigger? (Explain this in terms of the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell.) 39. Why is the triggering of a neuron considered an all-or-none principle? 40. What happens during the depolarization period? 41. How does myelination speed up how fast the impulse travels? 42. What happens during the repolarization period? 43. What happens during the refractory period? 44. So the impulse has been traveling down the axon and now reaches the synaptic terminal. What happens next? 45. Label presynaptic neuron, the synaptic cleft, and the postsynaptic neuron in the drawing below: 46. Where are neurotransmitters made? 47. Once calcium ions move into the presynaptic neuron, what happens to the vesicles containing neurotransmitters? 48. If the neurotransmitter is excitatory, what will happen next? 49. If the neurotransmitter is inhibitory, what will happen next? 50. What is hyperpolarization? 51. Which neurotransmitters are excitatory? 52. Which neurotransmitters are inhibitory? 53. Which drawing show s the divergence of neurons and which shows the convergence of neurons 54. When would the divergence of neurons be useful? 55. When would the convergence of neurons be useful?