* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
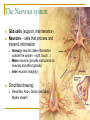
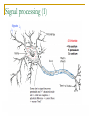
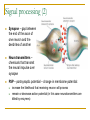
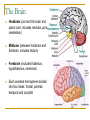
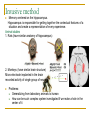
Memory, Brain (Chapter 8.1) Vengertsev Dmitry Agenda Goals: 1) provide general overview of what we do know about underlying biological processes and brain structures that support memory 2) introduce difficulties in conducting this kind of research The Neuron The Brain Methods of Investigation the way memory stored in the brain The Neuron Memory involves a persistent change in the relationship between neurons: Structural modification Biochemical events within neurons that change the way in which neighboring neurons communicate Squire, 1987 The Nervous system Glia cells (support, maintenance) Neurons – cells that process and transmit information Sensory neurons (take information outside the system – light, touch…) Motor neurons (provide instructions to muscles and affect glands) Inter-neurons (majority) Simplified drawing: Dendrites, Axon, Soma (cell body) Myelin sheath Signal processing (1) Signal processing (2) Synapse – gap between the end of the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: increase the likelihood that receiving neuron will process remain or decrease action potential (in this case neurotransmitters are killed by enzymes) The Brain Hindbrain (connect the brain and spinal cord, includes medulla, pons, cerebellum) Midbrain (between hindbrain and forebrain, includes tectum) Forebrain (includes thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebrum) Each cerebral hemisphere divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital Methods of Investigation Invasive (involve damage to brain) accidents animal studies recording from single neurons Noninvasive (little risk) measuring blood flow, electrical activities at the brain,… Invasive method Memory centered on the hippocampus. Hippocampus is responsible for getting together the contextual features of a situation and create a representation of every experience. Animal studies 1. Rats (have similar anatomy of hippocampus) 2. Monkeys (have similar brain structure) Micro-electrode implanted in the brain recorded activity of single group of neurons. Problems: Generalizing from laboratory animals to human How can be such complex system investigated if we make a hole in the center of it Noninvasive methods (1) CT (computer tomography) shows brain structure measure difference in absorption of X-rays by tissues with different density PET (position emission tomography) shows activity neurons use glucose as a source of energy. Patient’s injected with radioactive glucose and do task MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) shows brain structure magnetic resonance Noninvasive methods (2) functional MRI Electroencephalograms (EEGs) MRI + tracking blood flow in the brain the more active brain area is the more blood flows to it produce picture of brain activity measure pattern of electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp Event-related potentials (ERPs) instantaneous changes in EEG associated with a presentation of particular stimulus Noninvasive methods (3) Behavioral studies Kinsbourne and Cook: compare performance on a balancing task when subject (right-handed person) either vocalize or remain silent Results: right hand: better not to speak (reason: left hemisphere controls the right hand and also is the seat of language) left hand: speak! speak! (reason: verbalizing helped by distracting the subjects enough that they didn’t focus too much attention on balancing) Thank you!