* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurochemistry of executive functions
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive flexibility wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Executive dysfunction wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
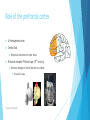
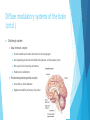
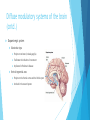
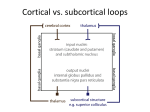
Neurochemistry of executive functions Saeed Basirian Jahromi Aalto university February 2016 What are executive functions? A range of higher-order cognitive functions that enable organized and goaldirected behavior. Includes: Planning Execution of plans (motor system) Flexibility (sensitivity to feedback) Selective attention Working memory Emotions Decision making Problem solving and reasoning Role of the prefrontal cortex A heterogeneous area Central hub Reciprocal connections to other areas Historical example: Phineas Gage (19th century) Extensive damage to frontal lobe due to accident Personality change *Images from Wikipedia Constituents of executive functions Setting and keeping goals across different timescales Ability to sequence sub goals Inhibition of competing/interfering impulses Measured by reaction time in neuropsychological tests Deficiency in ADHD patients Flexibility to feedback Motor system Hierarchy of increasingly complex motor sequences Responsible for motor imagery and planning Complex network of prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and thalamus responsible for choosing between alternative actions and inhibiting competing plans Constituents of executive functions (cntd.) Selective attention and working memory Selecting and manipulating task-relevant information Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex Hierarchy of memory schemas in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex Emotions and mood *Image from thebrain.mcgill.ca Relevant neuropsychological tests Stroop color-word task Word fluency test Wisconsin card sorting test Diffuse modulatory systems of the brain Regulate vast assemblies of post-synaptic neurons Properties: A small number of neurons at the core of each system Arise from the central core of the brain (mostly brain stem) Each neuron can influence many others They release neurotransmitters in the extra-cellular fluid 4 major systems: norepinephrine, serotonin, acetylcholine, dopamine Diffuse modulatory systems of the brain (cntd.) Noradrenergic system Locus Coeruleus in Pons Innervates almost everywhere! Involved in regulation of attention, arousal, sleep-wake cycles, learning and memory, anxiety and pain, mood, and brain metabolism Best activated by new, unexpected, nonpainful stimuli Participates in general arousal of the brain in interesting events Increases brain responsiveness *Images hereafter from Mark F. Bear et al., Neuroscience: exploring the brain Diffuse modulatory systems of the brain (cntd.) Serotonergic system Mostly clustered in the 9 Raphe nuclei (in brain stem) Those more rostral innervate in the same way as locus ceoruleus Also most active when animal is aroused This and noradrenergic systems part of the ascending reticular activating system Also involved in regulating: sleep-wake cycles, mood, and certain types of emotions Diffuse modulatory systems of the brain (cntd.) Cholinergic system: Basal forebrain complex Several related nuclei medial and ventral to the basal ganglia Also regulates general brain excitability during arousal, and sleep-wake cycles Has a special role in learning and memory Possible role in Alzheimer’s Pontomesensephalotegmental complex: Acts mainly on dorsal thalamus Regulates excitability of sensory relay nuclei Diffuse modulatory systems of the brain (cntd.) Dopaminergic system Substantia nigra Projects to striatum (in basal ganglia) Facilitates the initiation of movement Implicated in Parkinson’s disease Ventral tegmental area Projects to the frontal cortex and the limbic system Involved in the reward system Effect of dopamine in basal ganglia Low dopamine level Reduced ability to initiate actions and shift cognitive sets disease Parkinson’s High dopamine level Inability to prevent inadvertent shifts in sets Schizophrenia Other neurotransmitters Blocking NMDA glutamate receptors decreased WCST performance Benzodiazepines enhancing GABA receptors Alcohol (ethanol) enhancing GABA receptors Increased inhibition (sedation) Key points Executive functions are a range of higher-order cognitive functions that enable organized and goal-directed behavior. The prefrontal cortex acts as the central hub for executive functions. The 4 diffuse modulatory neurotransmitter systems have an impact on executive functions. Dopamine especially greatly affects the ability to initiate actions and shift cognitive sets. References Introduction to cognitive neuroscience, Iiro P. Jääskeläinen Neuroscience: exploring the brain, Mark F. Bear et al., 2015 Neural bases of set-shifting deficits in Parkinson’s disease, O. Monchi et al., The journal of neuroscience, 2004 www.wikipedia.org Questions?