* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Teenagers
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
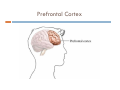
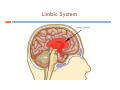
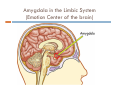
5.$%234!.$).' 4%%.!'%23 ICS School Counseling Department 2017 April 20, 2017 Prefrontal Cortex Prefrontal Cortex CEO of the brain Does not get fully developed until mid twenties Prone to risky behaviors due to immature impulse control Controls the Amygdala (the emotion center of the brain in the Limbic System) What feels good is very important especially to teenagers, whose brains have not fully developed Prefrontal Cortex Limbic System Amygdala in the Limbic System (Emotion Center of the brain) Dopamine Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a pleasure seeking chemical that is responsible for transmitting signals in between the nerve cells (neurons) of the brain. One of the best described roles for dopamine neurons is in learning about rewards. Dopamine neurons become activated when something good happens unexpectedly, such as the sudden availability of food or seeing new things in a mall or during travel. Surprise brings us pleasure! When new stimuli are involved, our brain releases more dopamine. We experience a temporary feeling of happiness. Dopamine “The balance of excitatory to inhibitory neurotransmitters and increased dopamine (pleasure seeking chemical) activity in adolescence may have implications for adolescent risk-taking and vulnerability to boredom.” Serotonin Serotonin – a chemical in the brain that’s involved in regulation of mood & behavior (I feel this way, so I will do this or not do this. It can be very dangerous if teens just rely on their feelings to determine their actions. Their impulse control is immature. -> Risky behaviors…increased incidence of unintentional injuries, violence, substance abuse, unintended pregnancy, and sexually transmitted diseases. ) Changes in the levels of the neurotransmitters Dopamine & Serotonin in the Amygdala in the Limbic System, the emotional place of the brain, make adolescents more emotional and more responsive to rewards & stress. Teens respond especially to social rewards. (Peer Pressure) The need to be liked by their peers is paramount!!! Increase in emotional variability (high & low emotions) also can increase adolescents’ vulnerability. Cognitive Changes Adolescents make HUGE gains in cognitive development. They begin to think abstractly!!! By Age 15 – Basic thinking abilities are comparable to those of adults. (The Prefrontal Cortex is not fully formed until mid 20’s.) Thoughts & ideas lead to character & personality formation (Who am I? I want to be this way and think this. Why? I want to try this.) Biological changes in the brain interact with increased experience, knowledge, & changing social demands to produce rapid cognitive growth. Descriptions of Self at Different Ages 9 yr old: I have brown hair. I have blue eyes. I love sports and school. There are 6 people in my family. My teacher is Mrs. Amy. (Fact based thinking) 11yr old: I’m a girl. “I’m a truthful person. I’m not pretty. I try to be helpful…Mostly I’m good, but I lose my temper. I’m not well liked by some girls and boys. I don’t know if boys like me….” (Thinking becomes abstract.) 17 yr old: “I am a human being… a girl… I am a moody person…an indecisive person… an ambitious person. I am a big curious person… I am lonely.” I don’t know why I’m diligent and lazy at the same time. “I am a liberal person. I am a radical.” “I am not a classifiable person (i.e., I don’t want to be.)” (Thinking is even more abstract.) More Cognitive Changes Helps with Social Cognition Increased Introspection & Self-consciousness Imaginary Audience – egocentric thinking that many people are enthusiastically listening to or watching him or her Ex. A girl spills soda on her dress at a party. Personal Fable- a tendency to think that a teen’s thoughts & feelings are unique Examples: Getting pregnant is something that won’t happen to me. An adolescent breaking up with his or her 1st girlfriend/ boyfriend is a TRAGEDY! This terrible thing has only happened to me!!! Around 18 years of age By the end of high school, teenagers conform less with their friends’ misconduct and develop independence and autonomy. (They don’t just do what their friends do to be liked.)