* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
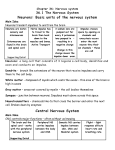
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems TPJ 3M Nicole Klement Human Organ Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Skeletal Muscular Circulatory Immune Respiratory Digestive Excretory 8. Reproductive 9. Nervous 10. Endocrine 11. Integumentary 7. The Human Nervous System Nervous system: the control system that enables animals to detect a stimulus and coordinate a response. Human Nervous System Nervous System has 2 parts: 1.Central Nervous System 2.Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Autonomic Diagram of the Human Brain Cerebrum Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Corpus callosum Cerebellum What does the brain do? Take a moment on your computer to research one part of the brain and the role it plays in controlling your body or thought processes. Parts of the Nervous system Terminology related to Neurons: A nerve cell or neuron: a specialized cell that uses electrical signals to communicate with other cells. Impulse: an electrical signal that travels through neurons Nerve: a bundle of neurons Dendrites: carry impulses to the cell body Axon: carry impulses away towards other cells Myelin sheath: fatty white covering on the axon that speeds up the impulse Axon terminals: the ends of the axons which come close to the dendrites of other neurons. Synapse: the space between the axon terminal and the dendrite of a neighbouring neuron Diagram of a Human Neuron Dendrite Cell body Myelin sheath Axon Node of Ranvier Axon terminals Types of Neurons Animals with a brain have three different types of neurons: 1. sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors in the eye (sight), ear (hearing), tongue (taste) and skin (pressure and heat) to the spinal cord and brain 2. motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain to muscles for movement or a gland for hormone secretion. 3. interneurons: link the sensory and motor neurons directly, producing reflexes Reflex arc Reflex arc: when sensory neurons synapse with interneurons in the brain or spinal cord, sending the impulse directly back to the motor neurons, producing a reflex. reflex arcs produce very fast responses to stimuli reflex actions are predictable, automatic, and unlearned. Ex1) smelling the aroma of pizza: sensory neurons send an impulse to the brain, which synapse directly to interneurons, which sends the impulse directly to salivary glands beneath the tongue. Ex2) palmar reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s hand, the hand will automatically grasp in response Ex3)rooting reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s cheek, the baby will turn its head towards the touch Your reflexes Student Activity Knee jerk reflex Triceps reflex Eye reflex Sensing of the skin with toothpicks Hand closing reflex – how fast are you? Brain Technology TED talk