* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensing the Environment
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
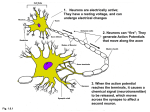
This week: Sensing and Responding to the Environment Sensing and reacting to the environment is critical Failure to properly sense and react to the environment can be fatal Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 Neurons: cells specialized for transmitting signals CB 48.4 In the brain neurons are shorter and highly interconnected Fig 48.5 Signals move through neurons in one direction Fig 48.4 Axon Signals Signals move along a neuron via movement of ions across the membrane Fig 48.4 Axon Signals Ion movement across the membrane causes the signal to travel from one end to the other Fig 48.11 At rest a neuron is polarized. The electrical signal is a depolarization that moves along the neuron. Fig 48.11 At the synapse the electrical signal is converted to a chemical signal: neurotransmitters electrical at synapse chemical electrical Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. CB 48.14 http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/actionp.html electrical at synapse chemical electrical Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 CB 49.4 The brain and the central nervous system integrate the various incoming signals Different regions of the cerebral cortex integrate different inputs/outputs CB 49.15 Visualizing the specialization of brain regions CB 49.17 Some body parts have more sensory input/ motor control CB 49.16 Some responses are to subtle stimuli CB 48.3 Circadian Rhythms: daily patterns set by light (northern flying squirrel) We are not conscious of much of what happens in the brain CB 48.3 Today’s video about different human reactions to cool: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XHmM7gJhscU Nervous System Signaling Stimulus Integration Transduction Transmission Response Smells are detected by receptor neurons in our nose. Each receptor is sensitive to a different chemical Fig 50.15 Activating more neurons leads to stronger perception Fig 50.15 This stretch sensitive neuron transduces different signals depending on the amplitude of the stimulus Fig 50.2 Light is detected in the eye by receptors on the retina Fig 50.18 Some vision problems arise from misshapen too long eyeballs too short Fig 50.19 AAL 42.10 Light receptor neurons of the eye: Rods detect black and white Cones detect colors…one type of cone for each color - red, blue, and green No light No Signal Inhibitory neurotransmitter Fig 50.22 Membrane depolarized light Signal sent No inhibitory neurotransmitter Fig 50.22 Polar Membrane Vertebrate retina structure Fig 50.23 Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 Response Responses can be release of hormones, change in cell activity, or muscle contraction